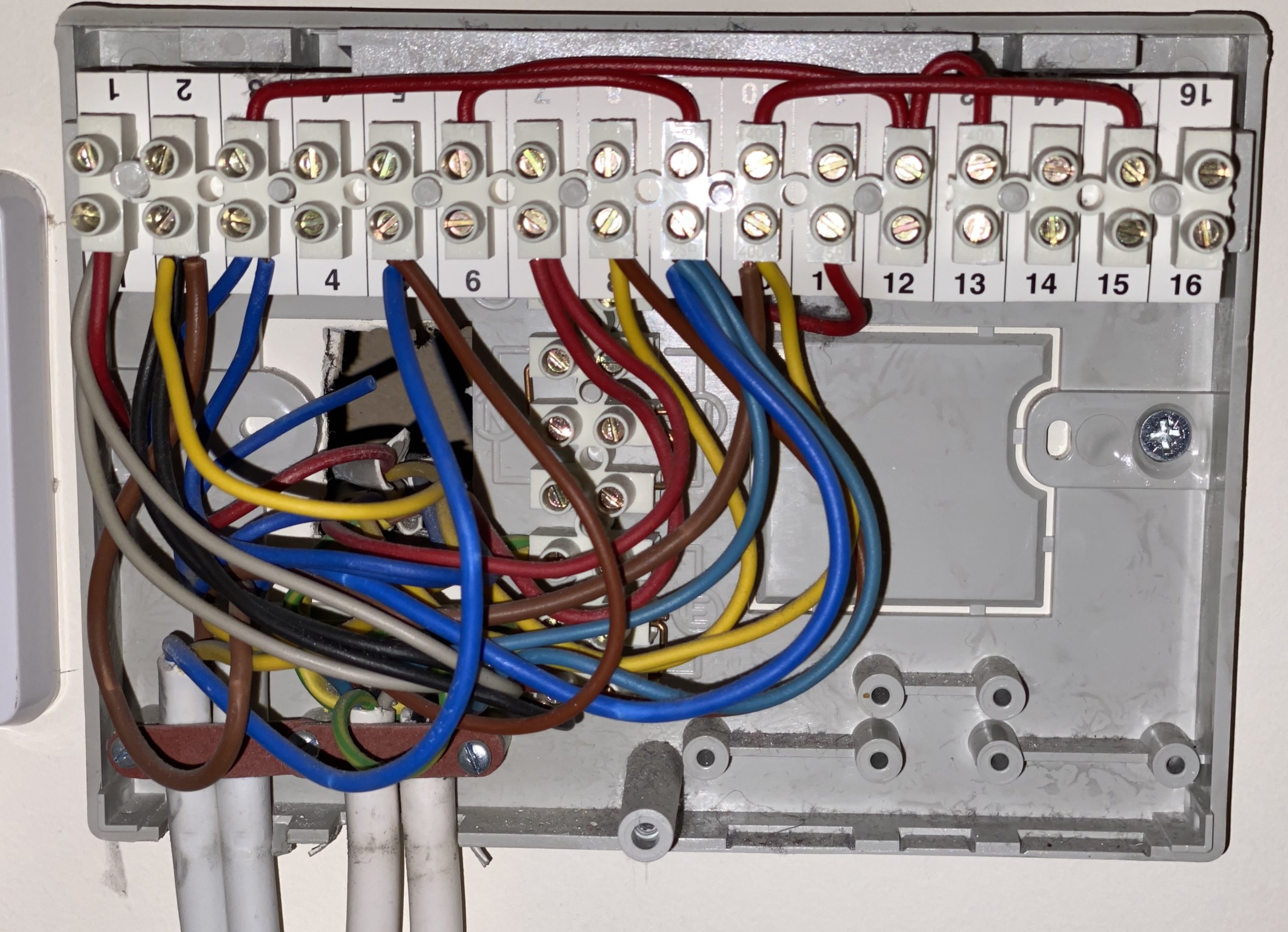
Wiring In Junction Box refers to connecting electrical wires within an enclosed casing to create a distribution point for power and signals. In homes, a junction box is commonly installed at the center of a ceiling to distribute power to ceiling fixtures, fans, and smoke detectors.
Junction boxes are crucial for safe and organized electrical systems. They protect wire connections from exposure and damage, facilitating easy access for maintenance and troubleshooting. Historically, the development of insulated junction boxes in the early 1900s revolutionized electrical safety by minimizing the risk of electrical fires.
This article will delve into the essential components of a junction box, different types available, and best practices for wiring connections, providing a comprehensive guide to junction box installation and maintenance.
Wiring in junction boxes is a crucial aspect of electrical systems, ensuring safe and efficient distribution of power and signals. The key aspects involved in wiring junction boxes include:
- Box selection: Choosing the right size and type of junction box for the application.
- Wire preparation: Stripping and preparing the ends of wires for proper connections.
- Terminal selection: Using appropriate terminals for the wire gauge and connection type.
- Wire connections: Making secure and reliable connections between wires and terminals.
- Insulation: Covering exposed connections with electrical tape or other insulating materials.
- Grounding: Ensuring proper grounding of the junction box and all connected devices.
- Box fill: Maintaining adequate space within the junction box to prevent overcrowding and overheating.
- Cover installation: Securing the junction box cover to protect the connections.
- Labeling: Clearly identifying the contents and purpose of the junction box for future reference.
These aspects are interconnected and essential for the proper functioning and safety of electrical systems. For instance, proper wire preparation and terminal selection ensure good electrical contact, while insulation and box fill prevent short circuits and overheating. Grounding protects against electrical shock, and labeling facilitates troubleshooting and maintenance.
Box selection
In the context of “Wiring In Junction Box,” selecting the right size and type of junction box is crucial for ensuring safety, organization, and functionality. Various factors come into play when making this choice, encompassing practical considerations, code requirements, and long-term implications.
- Box Size: The size of the junction box should accommodate the number and size of wires to be connected, as well as any additional components like wire nuts or splicing connectors. Overcrowding the box can lead to overheating and potential fire hazards.
- Box Type: Junction boxes come in different types, including single-gang, double-gang, and multi-gang boxes, which determine the number of devices or wires that can be accommodated. Selecting the appropriate type ensures adequate space for connections and prevents overcrowding.
- Material: Junction boxes can be made of metal or plastic, each with its own advantages and applications. Metal boxes provide better durability and grounding, while plastic boxes are more economical and easier to work with.
- Environmental Considerations: For outdoor or wet locations, weatherproof junction boxes are necessary to protect the connections from moisture and other environmental factors that could compromise safety and functionality.
Careful consideration of these factors ensures the selection of junction boxes that meet specific application requirements, ensuring the safety, reliability, and longevity of the electrical system. Failure to choose the right junction box can lead to poor connections, overheating, and potential electrical hazards.
Wire preparation
In the context of “Wiring In Junction Box,” wire preparation is a crucial step that ensures secure and reliable electrical connections. It involves stripping the insulation from the ends of wires to expose the conductive metal, which is then shaped and connected to terminals or other wires. Proper wire preparation is essential for minimizing electrical resistance, preventing short circuits, and ensuring the overall safety and functionality of the electrical system.
- Stripping the Insulation: Using a wire stripper or utility knife, the outer insulation of the wire is carefully removed to expose the conductive metal below. The length of insulation stripped should be appropriate for the type of connection being made.
- Cutting the Wire: Once the insulation is stripped, the wire is cut to the desired length using wire cutters. Clean, precise cuts ensure proper contact and minimize the risk of frayed or damaged wires.
- Shaping the Wire: In certain cases, the exposed wire may need to be shaped or bent to fit into terminals or other components. Using pliers or other tools, the wire is carefully bent or formed without damaging the conductive strands.
- Tinning the Wire: For improved connections and corrosion resistance, the exposed wire strands can be coated with solder. This process, known as tinning, creates a protective layer that enhances electrical conductivity and prevents oxidation.
meticulous wire preparation not only ensures the proper functioning of electrical systems but also contributes to their longevity and safety. Neglecting this step can lead to loose connections, overheating, and potential electrical hazards. By adhering to proper wire preparation techniques, electricians and DIY enthusiasts can create secure and reliable electrical connections that meet code requirements and ensure the efficient and safe operation of electrical systems.
Terminal selection
When wiring in junction boxes, selecting the appropriate terminals is crucial for ensuring secure and reliable electrical connections. Terminals serve as the interface between wires and other components within the junction box, providing a means of connecting, distributing, and terminating electrical circuits. Using terminals that match the wire gauge and connection type is essential for maintaining proper electrical flow and preventing potential hazards.
The wire gauge, which refers to the thickness of the wire, determines the current-carrying capacity and the size of the terminal required. Using terminals that are too small for the wire gauge can lead to overheating and potential fire hazards. Conversely, using terminals that are too large can result in loose connections and electrical arcing, which can also pose safety risks.
The connection type also plays a role in terminal selection. Different types of terminals are designed for specific connection methods, such as screw terminals, spring terminals, and crimp terminals. Choosing the right terminal type ensures a secure connection and prevents accidental disconnections. For instance, in high-vibration environments, spring terminals provide a more secure connection than screw terminals due to their ability to maintain contact under movement.
Real-life examples of appropriate terminal selection in junction boxes include using insulated wire connectors, commonly known as wire nuts, to join multiple wires together. These connectors are sized according to the wire gauge and provide a secure and insulated connection. Another example is using ring terminals to connect wires to screw terminals on electrical devices. Ring terminals are crimped onto the wire, providing a secure and reliable connection with minimal risk of loosening.
Understanding the importance of terminal selection in junction boxes enables electricians and DIY enthusiasts to create safe and efficient electrical systems. By using appropriate terminals that match the wire gauge and connection type, they can ensure proper electrical flow, prevent overheating and electrical hazards, and contribute to the overall reliability and longevity of the electrical system.
Wire connections
When wiring in junction boxes, making secure and reliable connections between wires and terminals is crucial for the proper functioning and safety of the electrical system. These connections ensure that current flows efficiently, preventing overheating, voltage drops, and potential electrical hazards.
-
Terminal types and selection
Different types of terminals are available, each designed for specific wire gauges and connection methods. Selecting the right terminal ensures a secure connection and prevents accidental disconnections. -
Wire preparation
Properly preparing the wire before making the connection is essential. This includes stripping the insulation to the correct length, shaping the wire if necessary, and tinning the wire strands to improve conductivity and prevent corrosion. -
Connection techniques
Various connection techniques can be used, such as twisting and soldering, crimping, or using wire connectors. Choosing the appropriate technique for the specific application ensures a reliable and long-lasting connection. -
Insulation and protection
Once the connections are made, they should be properly insulated and protected to prevent accidental contact and short circuits. This can be achieved using electrical tape, heat shrink tubing, or other insulating materials.
By meticulously following these practices, electricians and DIY enthusiasts can create secure and reliable wire connections in junction boxes, ensuring the safe and efficient operation of electrical systems. Proper wire connections are essential for preventing electrical fires, ensuring optimal current flow, and maintaining the integrity of the electrical system over time.
Insulation
In the context of “Wiring In Junction Box,” insulation plays a critical role in ensuring the safety and reliability of electrical connections. Exposed connections can lead to short circuits, electrical fires, and other hazards. Insulation serves as a protective barrier, preventing these risks and ensuring the proper of the electrical system.
When wires are connected within a junction box, the exposed ends of the wires must be insulated to prevent accidental contact and short circuits. This is typically achieved using electrical tape or heat shrink tubing. Electrical tape is a self-adhesive tape made of a flexible insulating material, while heat shrink tubing is a tube-shaped material that shrinks when heated, providing a tight and durable insulation layer.
By covering exposed connections with insulating materials, electricians and DIY enthusiasts can create safe and reliable electrical systems. Proper insulation prevents electrical hazards, ensures optimal current flow, and maintains the integrity of the electrical system over time. Real-life examples of insulation in junction boxes include using electrical tape to insulate wire connections in ceiling fixtures, switches, and outlets. Heat shrink tubing is often used to insulate and protect connections in high-vibration environments, such as automotive wiring.
Understanding the importance of insulation in junction boxes enables individuals to make informed decisions when working with electrical systems. By meticulously following best practices for insulation, they can contribute to the safety, reliability, and longevity of electrical installations.
Grounding
In the context of “Wiring In Junction Box,” grounding plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and proper functioning of electrical systems. Grounding provides a low-resistance path for electrical current to flow back to the electrical source, protecting against electrical shocks, equipment damage, and electrical fires.
When a junction box is properly grounded, it creates a conductive path between the electrical system and the earth ground. This path allows any fault currents or surges to safely dissipate into the ground, preventing them from flowing through unintended paths, such as through people or equipment. Grounding also helps to stabilize the voltage within the electrical system, reducing the risk of voltage fluctuations and electrical noise.
Real-life examples of grounding in junction boxes include the use of grounding wires, which are connected to the ground terminal of the junction box and routed back to the electrical panel’s grounding system. Additionally, metal junction boxes themselves can provide a grounding path if they are properly bonded to the electrical grounding system.
Understanding the importance of grounding in junction boxes enables electricians and DIY enthusiasts to create safe and reliable electrical systems. Proper grounding helps to prevent electrical hazards, ensures optimal current flow, and maintains the integrity of the electrical system over time. By meticulously following best practices for grounding, individuals can contribute to the safety, reliability, and longevity of electrical installations.
Box Fill
In the context of “Wiring In Junction Box,” box fill refers to the amount of space occupied by wires, terminals, and other components within the junction box. Maintaining adequate box fill is crucial for ensuring the safety and proper functioning of electrical systems, as overcrowding and overheating can lead to serious hazards.
- Wire Quantity and Size: The number and size of wires in a junction box can significantly impact box fill. Overcrowding the junction box with too many wires can make it difficult to make proper connections and increase the risk of overheating.
- Terminal Type and Size: The type and size of terminals used in the junction box also affect box fill. Larger terminals, such as wire nuts, take up more space than smaller terminals, such as crimp terminals.
- Component Placement: The way components are placed within the junction box can influence box fill. Leaving sufficient space between wires and terminals allows for proper heat dissipation and memudahkan access for maintenance.
- Environmental Factors: Environmental factors, such as high ambient temperatures or exposure to moisture, can affect box fill considerations. Junction boxes in these environments may require additional space to allow for proper heat dissipation and prevent overheating.
Maintaining adequate box fill is essential for preventing electrical hazards, ensuring optimal current flow, and maintaining the integrity of the electrical system over time. By carefully considering the number and size of wires, terminals, and components, as well as environmental factors, electricians and DIY enthusiasts can create safe and reliable electrical installations.
Cover installation
In the context of “Wiring In Junction Box,” cover installation plays a critical role in ensuring the safety and reliability of electrical systems. The junction box cover serves as a protective barrier, safeguarding the electrical connections within the box from environmental factors, accidental contact, and potential hazards.
Securing the junction box cover is essential for several reasons. Firstly, it prevents dust, moisture, and other contaminants from entering the junction box. These contaminants can cause corrosion, insulation breakdown, and electrical malfunctions. Secondly, a secure cover prevents accidental contact with live electrical connections, reducing the risk of electrical shock and injury. Additionally, a properly installed cover helps to maintain the integrity of the electrical system by preventing the ingress of insects, rodents, and other pests that could damage the wires or terminals.
Real-life examples of cover installation in junction boxes include securing the cover using screws or latches to ensure a tight fit. In outdoor applications, weatherproof junction boxes with gaskets or seals are used to protect the connections from moisture and other environmental elements. Proper cover installation is particularly important in high-traffic areas, such as commercial buildings or industrial settings, where the junction box is more likely to be exposed to physical impact or accidental contact.
Understanding the importance of cover installation in junction boxes enables electricians and DIY enthusiasts to create safe and reliable electrical systems. By meticulously securing the junction box cover, individuals can minimize the risk of electrical hazards, ensure optimal current flow, and maintain the integrity of the electrical system over time. This understanding also highlights the need for regular inspection and maintenance of junction boxes to ensure that the covers remain secure and the connections are protected.
Labeling
Proper labeling of junction boxes is a crucial aspect of “Wiring In Junction Box” as it ensures the safety, organization, and efficiency of electrical systems. Identifying the contents and purpose of junction boxes through clear labeling enables electricians, maintenance personnel, and homeowners to quickly and easily understand the function and layout of electrical circuits within a building.
For instance, labeling junction boxes in residential settings can indicate the specific rooms or areas they serve, such as “Kitchen Lighting” or “Master Bedroom Outlets.” In commercial or industrial environments, junction boxes may be labeled according to their function within a larger system, such as “HVAC Control Panel” or “Emergency Lighting Circuit.” This labeling becomes critical during troubleshooting or maintenance, as it allows technicians to trace circuits and identify potential issues more quickly and accurately.
The practical applications of understanding the importance of labeling junction boxes extend beyond troubleshooting and maintenance. Clear labeling facilitates future modifications or expansions to electrical systems by providing a visual reference for electricians. It also enhances safety by allowing personnel to quickly identify and isolate circuits during emergencies, reducing the risk of electrical shock or fire hazards.
In summary, labeling junction boxes is an essential component of “Wiring In Junction Box” as it provides clear and concise information about the contents and purpose of electrical circuits. This labeling streamlines troubleshooting, maintenance, and future modifications, contributing to the safety, reliability, and efficiency of electrical systems.









Related Posts








