A wiring headset jack is an audio connector that allows headsets or headphones to connect to electronic devices like smartphones, laptops, and audio players. A well-known example is the 3.5mm jack, a standard in consumer electronics for decades.
Wiring headset jacks enable convenient audio input and output, facilitating hands-free communication, music listening, and media consumption. Over the years, they have undergone advancements, including the introduction of multi-pole jacks to support additional features like microphones and volume control.
In the following article, we will delve deeper into the technical aspects, advantages, and ongoing evolution of wiring headset jacks, providing a comprehensive understanding of this indispensable audio interface.
Wiring headset jacks are vital components in audio systems, enabling connectivity and functionality. Understanding their essential aspects is crucial to grasp their significance.
- Types: 3.5mm, 2.5mm, USB-C
- Configuration: Mono, stereo, multi-channel
- Functionality: Audio input, output, microphone support
- Compatibility: Device compatibility, standards compliance
- Materials: Copper, gold-plating, insulation
- Durability: Resistance to wear, tear, and corrosion
- Design: Shape, size, aesthetic considerations
- Accessories: Adapters, extensions, converters
- Trends: Wireless connectivity, noise cancellation
These aspects encompass the technical specifications, functionality, compatibility, durability, and evolving trends associated with wiring headset jacks. Understanding these aspects allows for informed decision-making when selecting and using these connectors, ensuring optimal audio performance and user experience.
Types: 3.5mm, 2.5mm, USB-C
The physical configuration of a wiring headset jack, encompassing its size, shape, and number of conductors, plays a crucial role in determining its functionality and compatibility. Among the most prevalent types are the 3.5mm, 2.5mm, and USB-C jacks.
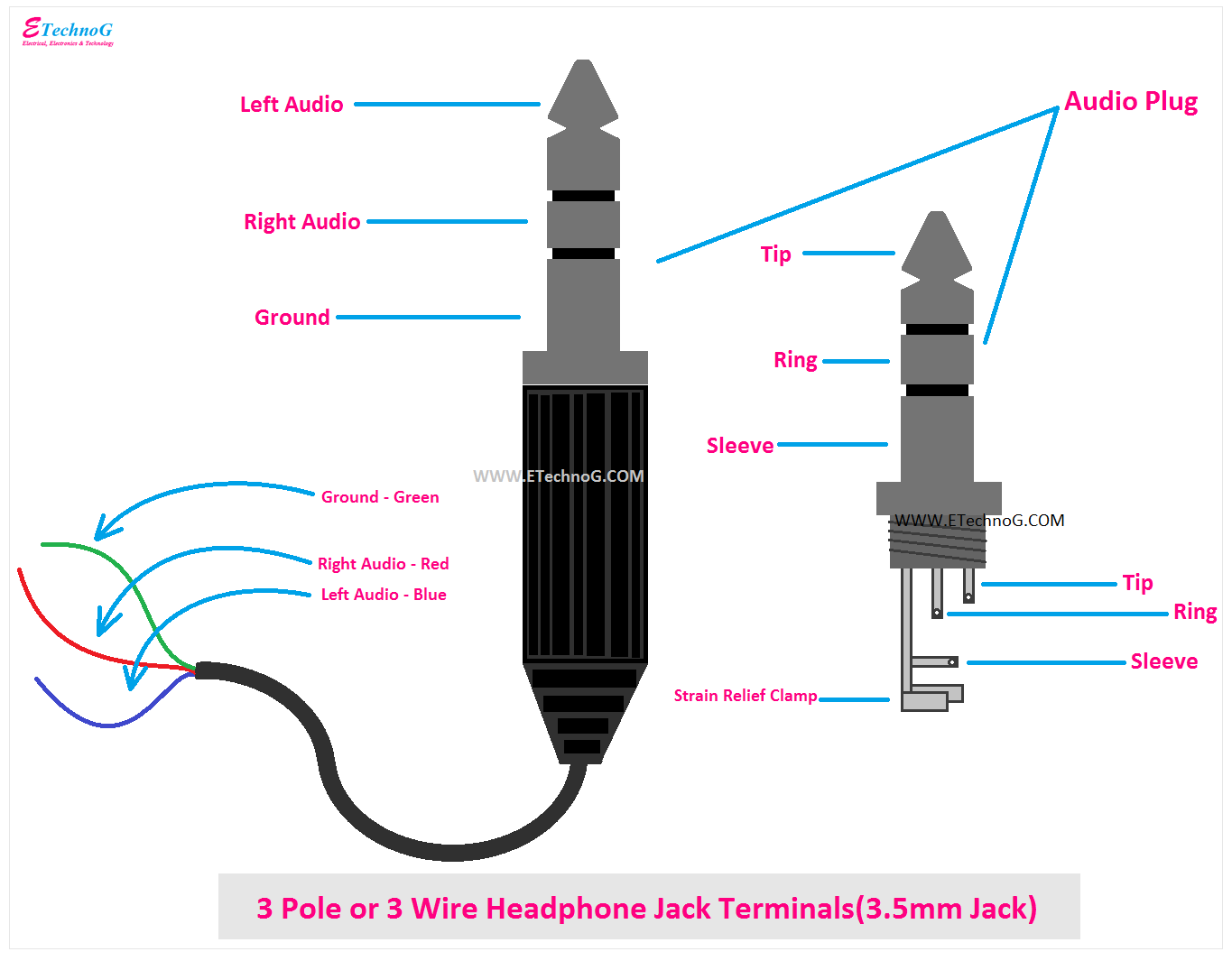
The 3.5mm jack, also known as the TRS (tip-ring-sleeve) connector, has been the industry standard for decades. Its widespread adoption stems from its compact size and versatility, supporting both audio input and output. The 2.5mm jack, commonly found in older mobile phones and some laptops, is a smaller version of the 3.5mm jack, catering to space constraints in portable devices. In contrast, the USB-C jack, a relatively recent development, offers a more compact and versatile solution, supporting not only audio but also power delivery and data transfer.
Understanding the different types of wiring headset jacks is essential for ensuring compatibility between audio devices. For instance, a headset with a 3.5mm jack will not be compatible with a device that only has a USB-C port. Adapters or converters may be necessary to bridge the gap between different jack types. Furthermore, the choice of jack type can impact audio quality, with higher-quality jacks featuring better materials and construction, leading to improved signal transmission and reduced noise.
In summary, the type of wiring headset jack is a critical factor determining compatibility, functionality, and audio quality. Understanding the characteristics and capabilities of different jack types allows users to make informed decisions when selecting and using audio devices.
Configuration: Mono, stereo, multi-channel
The configuration of a wiring headset jack, denoting the number of conductors and the arrangement of channels, directly influences the audio capabilities of the connected headset or headphones. Three primary configurations exist: mono, stereo, and multi-channel.
Mono jacks feature a single conductor, carrying a single audio signal, resulting in monaural audio output. This configuration is commonly used in telephone headsets and low-cost consumer electronics. Stereo jacks, on the other hand, employ two conductors, enabling the transmission of two separate audio channels, creating a more immersive stereo soundscape. This configuration is ubiquitous in consumer audio devices, such as smartphones, laptops, and home audio systems.
Multi-channel jacks, often found in professional audio applications, utilize three or more conductors to accommodate additional audio channels. This allows for more complex audio setups, including surround sound systems and multi-channel recording. The number and arrangement of conductors in multi-channel jacks vary depending on the specific application and desired functionality.
Understanding the configuration of a wiring headset jack is essential for selecting the appropriate headset or headphones for a particular application. Mono jacks are suitable for basic audio needs, while stereo jacks provide a more immersive listening experience. Multi-channel jacks cater to advanced audio setups, offering greater flexibility and control over channel routing and mixing.
Functionality: Audio input, output, microphone support
The functionality of a wiring headset jack encompasses its ability to transmit and receive audio signals, enabling a range of communication and entertainment applications. Three key aspects of this functionality include audio input, output, and microphone support, each playing a vital role in the overall user experience.
- Audio input: This refers to the jack’s capability of receiving audio signals from an external source, such as a microphone or musical instrument. It allows users to record their own voices or sounds for various purposes, such as voice calls, audio recording, and musical performances.
- Audio output: This aspect pertains to the jack’s ability to transmit audio signals to headphones or speakers, enabling users to listen to music, podcasts, or other audio content. The quality of the audio output depends on factors such as the jack’s design, materials, and compatibility with the connected device.
- Microphone support: Many wiring headset jacks incorporate microphone support, allowing users to engage in hands-free communication. This is crucial for applications such as phone calls, video conferencing, and online gaming, where clear and efficient voice transmission is essential.
- Multi-functionality: Modern wiring headset jacks often combine multiple functions, such as audio input, output, and microphone support, into a single connector. This allows for a more versatile and user-friendly experience, enabling seamless switching between different audio sources and modes of communication.
The diverse functionality of wiring headset jacks makes them indispensable in various applications, ranging from personal entertainment to professional communication. Their ability to transmit and receive audio signals effectively contributes to the overall quality and usability of audio devices.
Compatibility: Device compatibility, standards compliance
Within the realm of “Wiring Headset Jack,” compatibility plays a pivotal role, ensuring seamless connectivity and optimal performance across a wide range of devices. It encompasses two key aspects: device compatibility and standards compliance.
- Device Compatibility: This facet pertains to the ability of a headset or headphone to function effectively with various devices, such as smartphones, laptops, and audio players. Factors like jack size, pin configuration, and supported audio formats come into play, determining whether a particular headset is compatible with a specific device.
- Standards Compliance: Adherence to industry standards, such as the Consumer Electronics Association (CEA) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), ensures interoperability between different devices and headsets. Compliance with these standards guarantees that devices and jacks conform to established specifications, promoting universal compatibility and ease of use.
- Connector Variations: The physical design and dimensions of headset jacks vary depending on the intended application and device type. Common connector variations include 3.5mm TRS, 2.5mm TRRS, and USB-C, each with its own unique set of compatibility considerations.
- Feature Support: Compatibility also extends to the supported features, such as microphone functionality, volume control, and noise cancellation. Some devices may require specialized headsets to fully utilize these features, highlighting the importance of matching headset capabilities with device requirements.
In summary, device compatibility and standards compliance are essential aspects of “Wiring Headset Jack,” ensuring the seamless integration of headsets and devices. Understanding these facets helps users make informed choices, ensuring optimal audio experiences and avoiding compatibility issues.
Materials: Copper, gold-plating, insulation
Materials play a crucial role in the performance and durability of wiring headset jacks. The choice of materials for the conductors, contacts, and insulation affects factors such as signal quality, resistance to corrosion, and overall longevity.
-
Conductors: Copper
Copper is the primary conductor material used in headset jacks due to its excellent electrical conductivity and flexibility. High-purity copper ensures minimal signal loss and distortion, contributing to optimal audio quality. -
Contacts: Gold-plating
Gold-plating on the contacts of headset jacks enhances signal transmission and prevents corrosion. Gold’s high electrical conductivity and resistance to oxidation ensure reliable connectivity and long-term durability, even with repeated plugging and unplugging. -
Insulation: PVC, TPE
Insulation materials such as PVC (polyvinyl chloride) and TPE (thermoplastic elastomer) protect the conductors from short circuits and external interference. They provide electrical isolation and contribute to the overall flexibility and durability of the wiring. -
Soldering: Lead-free
Lead-free soldering is increasingly used in headset jack manufacturing to comply with environmental regulations and safety standards. Lead-free solder ensures a strong connection between components while minimizing the environmental impact.
The careful selection and combination of these materials result in wiring headset jacks that deliver exceptional audio performance, durability, and long-term reliability. As technology continues to evolve, new materials and innovative designs may further enhance the capabilities and lifespan of these essential components.
Durability: Resistance to wear, tear, and corrosion
In the realm of “Wiring Headset Jack,” durability plays a critical role in ensuring the longevity and reliability of these essential components. Durability encompasses resistance to wear, tear, and corrosion, affecting both the functionality and lifespan of headset jacks.
Wear and tear are inevitable consequences of repeated use and handling. Durable headset jacks are designed to withstand the stresses of frequent plugging and unplugging, as well as the rigors of everyday use. Robust materials and construction techniques contribute to their ability to endure these mechanical stresses without compromising performance.
Corrosion is another major factor affecting durability. Exposure to moisture and environmental elements can lead to corrosion, which can damage the electrical contacts and degrade the signal transmission capabilities of headset jacks. Corrosion-resistant materials and protective coatings are employed to safeguard against these environmental threats, ensuring reliable connectivity and long-term performance.
Real-life examples of durability in wiring headset jacks include the use of high-quality materials such as gold-plated contacts and reinforced strain relief, which enhance resistance to wear and tear. Additionally, waterproof and dustproof designs provide protection against environmental elements, ensuring reliable performance in challenging conditions.
Understanding the importance of durability in wiring headset jacks allows users to make informed choices when selecting and using these components. Durable headset jacks contribute to a seamless and uninterrupted audio experience, whether for personal entertainment, professional communication, or any other application where reliable audio connectivity is paramount.
Design: Shape, size, aesthetic considerations
In the realm of “Wiring Headset Jack,” design encompasses a range of factors that influence both functionality and user experience. Shape, size, and aesthetic considerations play a crucial role in determining the overall appeal, ergonomics, and compatibility of headset jacks.
The shape and size of a headset jack are primarily dictated by the intended application and device compatibility. For instance, the compact 3.5mm jack is a ubiquitous choice for portable devices due to its small size and versatility. In contrast, larger jacks may be employed in professional audio equipment to accommodate additional features or higher power handling capabilities.
Aesthetic considerations are increasingly important, particularly in consumer electronics where headset jacks are often visible components. Manufacturers incorporate design elements such as color, texture, and branding to complement the overall aesthetic of devices. Moreover, the shape and size of headset jacks can influence their ergonomic properties, ensuring a comfortable and secure fit when used with different types of headphones or headsets.
Understanding the connection between design and wiring headset jacks is essential for manufacturers, designers, and users alike. By carefully considering shape, size, and aesthetic aspects, headset jacks can be optimized for specific applications, enhance user experience, and seamlessly integrate with various devices. This understanding also enables informed decision-making when selecting and using headset jacks, ensuring compatibility, functionality, and a satisfying user experience.
Accessories: Adapters, extensions, converters
In the realm of “Wiring Headset Jack,” accessories such as adapters, extensions, and converters play a vital role in expanding the functionality and adaptability of these essential components. These accessories address various compatibility and connectivity challenges, enabling users to seamlessly integrate headset jacks with a wider range of devices and scenarios.
Adapters serve as intermediaries between headset jacks and devices with different jack types or configurations. For example, a 3.5mm to USB-C adapter allows users to connect a headset with a 3.5mm jack to a device with only a USB-C port. Extensions, on the other hand, provide additional cable length, extending the reach of headset jacks, making them more convenient for use in larger spaces or for connecting to devices that are farther apart. Converters perform more complex signal transformations, such as converting analog audio signals to digital signals or vice versa. This enables seamless interfacing between devices with different audio formats.
The practical applications of these accessories are vast. For instance, adapters empower users to connect legacy headsets with 3.5mm jacks to modern smartphones or laptops that may only have USB-C ports. Extensions facilitate comfortable use of headsets in home entertainment systems or professional audio setups where devices are often spaced apart. Converters enable the integration of headsets with specialized equipment, such as mixing consoles or audio interfaces, that require specific signal formats.
Understanding the connection between “Accessories: Adapters, extensions, converters” and “Wiring Headset Jack” enhances the versatility and functionality of headset jacks, allowing users to adapt to diverse connectivity needs. These accessories empower users to maximize the compatibility and usability of their headsets across different devices and scenarios, ensuring an optimal audio experience in a wide range of applications.
Trends: Wireless connectivity, noise cancellation
The evolution of “Wiring Headset Jack” is closely intertwined with emerging trends such as wireless connectivity and noise cancellation. These advancements have reshaped the landscape of audio experiences, offering users greater freedom, convenience, and immersive listening environments.
-
Wireless Connectivity: Bluetooth, Wi-Fi
Wireless connectivity technologies such as Bluetooth and Wi-Fi have liberated users from the constraints of physical wires, allowing for seamless audio streaming and hands-free communication. Bluetooth headphones and headsets have become ubiquitous, offering mobility and convenience in various scenarios, from daily commutes to workouts.
-
Active Noise Cancellation (ANC)
Active noise cancellation technology utilizes built-in microphones and advanced algorithms to detect and cancel out unwanted background noise. ANC headphones create a more immersive and distraction-free listening experience, making them ideal for noisy environments such as airplanes, crowded offices, or public transportation.
-
Hybrid Technologies: Wireless ANC
Combining wireless connectivity with active noise cancellation, hybrid technologies offer the ultimate blend of freedom and immersive audio. Wireless ANC headphones provide the convenience of wireless listening while effectively reducing background noise, allowing users to enjoy their favorite music or podcasts without distractions.
-
Voice Assistant Integration
Many modern headsets and headphones incorporate voice assistant integration, allowing users to control playback, adjust settings, or access information hands-free. This integration enhances convenience and productivity, especially when multitasking or in situations where physical interaction is limited.
In conclusion, the trends towards wireless connectivity, noise cancellation, and integrated technologies are revolutionizing the “Wiring Headset Jack” landscape. These advancements empower users with greater freedom, convenience, and immersive audio experiences, shaping the future of personal and professional audio.









Related Posts








