Wiring an electrical switch involves connecting electrical wires to a switch to control the flow of electricity to a device or light fixture. For instance, a single-pole switch in a home’s electrical wiring system allows a user to turn on or off a light bulb.
Wiring electrical switches is crucial for controlling electrical devices and ensuring safety in electrical systems. Proper wiring prevents electrical hazards, such as electrical fires, shocks, and equipment damage. A significant historical development was the invention of the tumbler switch, which improved switch reliability and safety compared to earlier designs.
In this article, we will delve deeper into the various types of electrical switches, their wiring techniques, and practical applications in residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
A thorough understanding of the essential aspects of wiring an electrical switch is paramount for safe and effective electrical installations. These aspects encompass various dimensions, including electrical safety, component selection, wiring techniques, testing procedures, and applicable codes and standards.
- Safety
- Circuit Protection
- Switch Types
- Wiring Diagrams
- Tools and Materials
- Step-by-Step Instructions
- Testing and Troubleshooting
- Codes and Standards
- Applications
- Maintenance and Inspection
These aspects are interconnected and influence the overall quality and reliability of the electrical installation. For instance, selecting the appropriate switch type for the intended application ensures optimal performance and longevity. Proper wiring techniques, guided by established codes and standards, minimize electrical hazards and ensure safe operation. Regular maintenance and periodic inspections help identify any issues or potential problems, enabling timely corrective actions to maintain electrical safety and system integrity.
Safety
Safety is of paramount importance when wiring an electrical switch. Electrical installations involve working with potentially hazardous electrical currents, and any oversights or errors can lead to serious consequences such as electrical shocks, fires, or equipment damage. Therefore, adhering to established safety guidelines and practices is essential to ensure the well-being of individuals and the integrity of electrical systems.
-
Electrical Hazards
Electrical hazards arise from improper wiring, faulty components, or damaged insulation, which can lead to electrical shocks, short circuits, or fires. Understanding these hazards and taking appropriate precautions, such as wearing proper protective gear and using insulated tools, is crucial for safe electrical work.
-
Circuit Protection
Circuit protection devices, such as fuses and circuit breakers, play a vital role in preventing electrical overloads and short circuits that could cause damage or fires. Selecting and installing the correct circuit protection devices is essential to ensure the safety of electrical systems and equipment.
-
Proper Wiring Techniques
Following established wiring techniques, including proper wire sizing, secure connections, and correct polarity, is essential for safe electrical installations. Poor wiring practices can lead to loose connections, overheating, and increased risk of electrical hazards.
-
Testing and Inspection
Thoroughly testing and inspecting electrical installations before energizing them is crucial to identify any potential issues or defects. This includes checking for proper connections, insulation integrity, and correct polarity. Regular maintenance and periodic inspections also help ensure the ongoing safety and reliability of electrical systems.
By prioritizing safety throughout the process of wiring an electrical switch, individuals can minimize the risks associated with electrical work and help ensure the safety of themselves, others, and the electrical system as a whole. Neglecting safety protocols can have severe consequences, emphasizing the importance of adhering to established guidelines and practices.
Circuit Protection
Circuit protection plays a critical role in wiring an electrical switch, as it safeguards electrical circuits and equipment from potential damage or hazards. An electrical switch, which controls the flow of electricity to a device or light fixture, must be integrated with appropriate circuit protection mechanisms to ensure the safety and reliability of the electrical system.
Circuit protection devices, such as fuses and circuit breakers, are essential components of any electrical installation. They act as safety measures to prevent electrical overloads or short circuits, which can lead to overheating, fires, or damage to electrical equipment. Fuses and circuit breakers work by interrupting the flow of electricity when it exceeds a predetermined safe level. This prevents excessive current from flowing through the circuit, potentially causing damage or posing a fire hazard.
In the context of wiring an electrical switch, circuit protection is critical to safeguard the switch itself and the connected electrical devices or fixtures. For instance, if a light switch is connected to a circuit without proper circuit protection, an overload or short circuit could cause the switch to overheat, melt, or even catch fire. Circuit protection devices effectively prevent such scenarios by breaking the circuit before dangerous levels of current can flow through the switch.
Understanding the connection between circuit protection and wiring an electrical switch underscores the importance of incorporating appropriate circuit protection measures into any electrical installation. This understanding enables individuals to make informed decisions about the selection and installation of circuit protection devices, ensuring the safety and longevity of their electrical systems.
Switch Types
In the context of wiring an electrical switch, understanding the various types of switches available is crucial for selecting the most appropriate switch for the intended application and ensuring proper installation. Different switch types offer unique features, capabilities, and wiring requirements, making it essential to be familiar with their distinctions.
-
Single-Pole Switch
A single-pole switch is the most basic type of electrical switch, designed to control a single light or device. It has two terminals and is typically used in residential and commercial lighting applications.
-
Double-Pole Switch
A double-pole switch is similar to a single-pole switch but controls two separate circuits or devices. It has four terminals and is often used in commercial and industrial applications.
-
Three-Way Switch
A three-way switch is used to control a single light or device from two different locations. It has three terminals and requires a special wiring configuration known as a three-way circuit.
-
Four-Way Switch
A four-way switch is used to control a single light or device from three or more locations. It has four terminals and is typically used in larger homes or commercial buildings.
Selecting the appropriate switch type is essential for proper wiring and functionality. Single-pole switches are suitable for most residential lighting applications, while double-pole switches are used for controlling larger loads or separate circuits. Three-way and four-way switches are commonly employed in multi-location lighting control scenarios, such as hallways or stairwells. Understanding the different switch types and their applications enables individuals to make informed decisions during the wiring process, ensuring the safe and efficient operation of electrical systems.
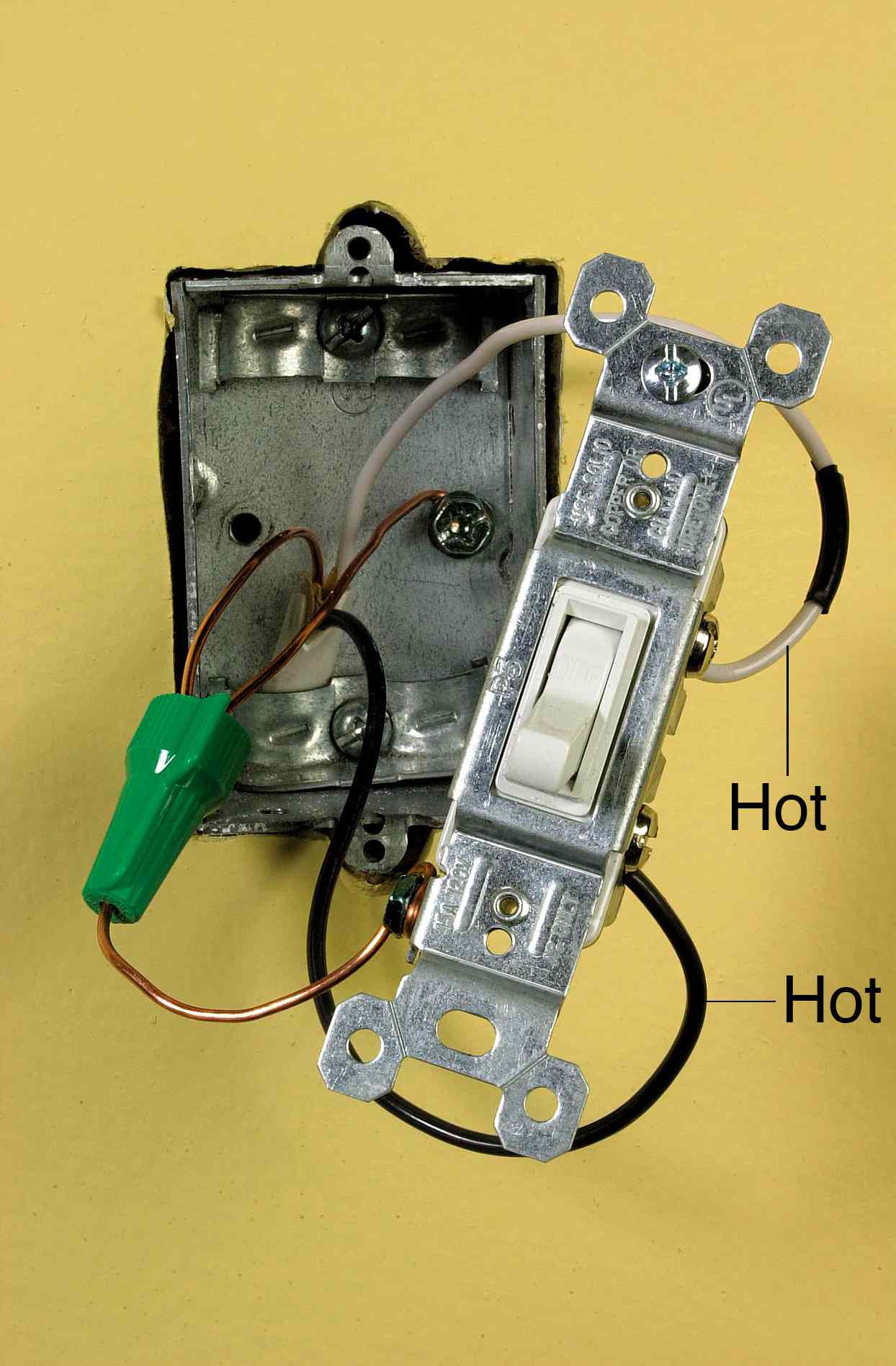
Wiring Diagrams
Wiring diagrams play a critical role in the process of wiring an electrical switch. They provide a visual representation of the electrical connections and components involved, serving as a guide for electricians and other professionals during the installation process. Wiring diagrams are essential for ensuring the proper functionality and safety of electrical systems.
One of the main reasons why wiring diagrams are so important is that they allow electricians to visualize and plan the electrical connections before they start working. This helps to avoid errors and ensures that the switch is wired correctly. Wiring diagrams also provide a reference point for troubleshooting if any problems arise in the future.
There are many different types of wiring diagrams, but they all share some common elements. These elements include symbols that represent electrical components, such as switches, outlets, and light fixtures. The diagrams also show the wires that connect these components and the direction of the current flow. In the context of wiring an electrical switch, the wiring diagram will typically show the switch, the electrical box it is mounted in, and the wires that connect the switch to the power source and the load (e.g., a light fixture).
Understanding how to read and interpret wiring diagrams is an essential skill for anyone who works with electrical systems. By following the wiring diagram, electricians can ensure that the electrical switch is wired correctly and safely.
Tools and Materials
When wiring an electrical switch, having the appropriate tools and materials is essential for ensuring a safe and effective installation. These components play a crucial role in the overall process, from selecting the correct switch type to making secure electrical connections.
-
Electrical Switch
The electrical switch is the central component of the wiring process. Choosing the right switch for the intended application is essential, considering factors such as the number of circuits to be controlled, the type of load (e.g., lighting, motor), and the desired switch style.
-
Electrical Box
The electrical box houses the switch and provides a secure enclosure for the electrical connections. Selecting the appropriate box size and type (e.g., single-gang, double-gang) is important to accommodate the switch and the number of wires.
-
Wires
Electrical wires are used to connect the switch to the power source and the load. Proper wire selection involves determining the correct wire gauge (thickness) and insulation type based on the electrical load and circuit requirements.
-
Tools
Essential tools for wiring an electrical switch include a voltage tester, wire strippers, screwdrivers, and a non-contact voltage detector. These tools help ensure accurate measurements, safe wire handling, and proper connections.
The selection and proper use of tools and materials in wiring an electrical switch go beyond basic functionality, contributing to the overall safety and reliability of the electrical system. Using high-quality materials and employing proper wiring techniques minimize the risk of electrical hazards, such as short circuits or electrical fires. By understanding the significance of each component and its application, individuals can make informed decisions when wiring an electrical switch, ensuring the safe and efficient operation of their electrical systems.
Step-by-Step Instructions
Step-by-step instructions play a critical role in the context of wiring an electrical switch. They provide a structured and detailed guide that outlines the necessary steps involved, ensuring safe and effective installation. Understanding the components and implications of step-by-step instructions is essential for successful electrical work.
-
Components and Preparation
Step-by-step instructions typically begin by listing the required components and tools, along with any necessary safety precautions. This helps ensure that individuals have everything they need before starting the wiring process.
-
Safety Considerations
Electrical work involves handling electricity, which can be hazardous if not handled properly. Step-by-step instructions emphasize safety measures, such as turning off the power at the circuit breaker and using insulated tools, to minimize the risk of electrical shocks or accidents.
-
Wiring Techniques
Detailed instructions guide individuals through the process of connecting the electrical switch to the power source and the load. This includes stripping wires, making secure connections, and ensuring proper polarity to prevent electrical issues.
-
Testing and Troubleshooting
Step-by-step instructions often include instructions for testing the switch and troubleshooting any potential problems. This helps ensure that the switch is functioning correctly and safely before being put into use.
By following step-by-step instructions carefully, individuals can approach the task of wiring an electrical switch with confidence, knowing that they have a clear and reliable guide to ensure a safe and successful installation.
Testing and Troubleshooting
In the context of electrical installations, testing and troubleshooting play a critical role in ensuring the safety, functionality, and longevity of electrical systems. This is particularly true when wiring an electrical switch, a task that requires precision and attention to detail to avoid electrical hazards and ensure proper operation.
Testing involves verifying that the electrical switch is wired correctly and functioning as intended. This can be done using a voltage tester or multimeter to check for proper voltage and continuity. Troubleshooting, on the other hand, involves identifying and resolving any issues that may arise during the wiring process or after the switch has been installed. This may include addressing loose connections, faulty components, or incorrect wiring.
Real-life examples of testing and troubleshooting in the context of wiring an electrical switch include:
- Using a voltage tester to ensure that the power is off at the circuit breaker before starting to wire the switch.
- Checking for continuity between the switch terminals and the power source and load to verify that the switch is wired correctly.
- Troubleshooting a switch that is not working by checking for loose connections, damaged wires, or a faulty switch.
Understanding the practical applications of testing and troubleshooting is essential for ensuring the safety and reliability of electrical installations. By thoroughly testing and troubleshooting electrical switches, electricians and homeowners can minimize the risk of electrical accidents, ensure that switches function properly, and extend the lifespan of electrical systems.
Codes and Standards
When wiring an electrical switch, adhering to established codes and standards is paramount to ensure safety, reliability, and compliance with regulatory requirements. These codes and standards provide guidelines for the proper selection, installation, and maintenance of electrical components, including switches.
-
Electrical Safety
Electrical codes mandate specific safety measures to prevent electrical hazards such as shocks, fires, and equipment damage. These include requirements for proper grounding, circuit protection, and the use of approved materials and components.
-
Product Standards
Industry standards establish performance and quality requirements for electrical switches. They ensure that switches meet minimum safety and performance criteria, providing a benchmark for manufacturers and a basis for product evaluation.
-
Building Codes
Building codes incorporate electrical codes and standards to ensure that electrical installations in buildings comply with safety regulations. These codes cover aspects such as switch placement, wiring methods, and the protection of electrical systems from environmental factors.
-
Compliance Inspections
Compliance inspections are conducted to verify that electrical installations, including switches, meet the requirements of applicable codes and standards. These inspections help ensure the safety and integrity of electrical systems and can identify potential hazards.
Understanding and adhering to codes and standards when wiring an electrical switch is not only a legal obligation but also a fundamental aspect of responsible electrical practices. By following these guidelines, electricians and homeowners can ensure the safe and reliable operation of electrical systems, minimize the risk of accidents, and maintain compliance with regulatory requirements.
Applications
Within the context of “Wiring An Electrical Switch,” the aspect of “Applications” holds significant importance, encompassing the diverse uses and implications of electrical switches in various settings. From residential to commercial and industrial environments, electrical switches play a crucial role in controlling and managing electrical systems.
-
Residential Lighting
In residential settings, electrical switches are primarily used to control lighting systems. They allow occupants to conveniently turn lights on or off, adjust brightness levels, and create ambiance in different rooms.
-
Appliance Control
Electrical switches are also employed to control appliances such as fans, air conditioners, and kitchen equipment. By incorporating switches into the wiring, users can easily operate these appliances without having to unplug or manually adjust them.
-
Industrial Machinery
In industrial environments, electrical switches serve as critical components in controlling machinery and equipment. They enable operators to start, stop, and adjust the operation of motors, conveyors, and other industrial systems.
-
Safety Systems
Electrical switches play a vital role in safety systems, particularly in emergency situations. Switches connected to fire alarms, security systems, and backup generators allow for quick activation and control in the event of an emergency.
These applications underscore the versatility and importance of electrical switches in modern electrical systems. Understanding their applications is essential for selecting the appropriate switches, ensuring proper wiring, and maximizing the functionality and safety of electrical installations.
Maintenance and Inspection
Maintenance and inspection are crucial aspects of “Wiring An Electrical Switch” that contribute to the longevity, safety, and optimal performance of electrical systems. Regular maintenance and periodic inspections help identify potential issues, prevent failures, and ensure the continued reliability of electrical switches.
-
Periodic Inspections
Regular visual inspections of electrical switches and their surrounding areas are essential to detect any signs of damage, wear, or loose connections. Checking for discoloration, cracks, or unusual odors can help identify potential problems early on.
-
Switch Function Testing
Testing the functionality of electrical switches involves operating them manually to ensure proper on/off switching and smooth operation. Switches should be tested under various load conditions to evaluate their performance and identify any potential issues.
-
Contact Examination
Inspecting the electrical contacts of switches is important to ensure they are clean, free of corrosion, and making proper contact. Worn or damaged contacts can lead to poor electrical connections, overheating, and switch failure.
-
Wiring Inspection
Checking the wiring connected to electrical switches is essential to ensure secure connections, proper insulation, and compliance with electrical codes. Loose or damaged wires can pose safety hazards and affect the performance of the switch.
Maintenance and inspection of electrical switches are not only important for ensuring their proper functioning but also contribute to the overall safety and reliability of electrical systems. By addressing potential issues early on, homeowners and electricians can prevent electrical hazards, extend the lifespan of switches, and maintain the integrity of electrical installations.








![[DIAGRAM] Diagram For Wiring A Three Way Switch](https://i0.wp.com/i.stack.imgur.com/DRDu3.jpg?w=665&ssl=1)
Related Posts








