Thermostat Wiring for Boiler refers to the electrical connections between a thermostat and a boiler system, designed to regulate the boiler’s operation based on the desired temperature settings.
This wiring is essential for maintaining a comfortable indoor temperature. When the thermostat detects a temperature drop, it sends a signal to the boiler, triggering it to produce heat. Conversely, when the desired temperature is reached, the thermostat signals the boiler to shut off, preventing overheating.
Thermostat Wiring for Boiler systems has seen significant advancements over time, including the adoption of advanced control algorithms and wireless communication technologies. This evolution has led to improved comfort, energy efficiency, and user convenience.
In the following sections, we will explore the specific components involved in Thermostat Wiring for Boiler systems, the principles of their operation, and considerations for efficient and safe installation.
The essential aspects of Thermostat Wiring for Boiler systems encompass the fundamental components, principles, and considerations involved in their design, installation, and maintenance. Understanding these aspects is crucial for ensuring efficient and reliable operation of the system.
- Components: Understanding the functions of the thermostat, boiler, and wiring components, including terminals, relays, and switches.
- Wiring Diagrams: Interpreting electrical schematics to correctly connect the thermostat to the boiler.
- Voltage Compatibility: Ensuring that the thermostat and boiler operate at the same voltage to prevent damage.
- Zone Control: Utilizing multiple thermostats to control different heating zones for improved comfort and energy efficiency.
- Smart Thermostats: Exploring the advantages of programmable and Wi-Fi-enabled thermostats for enhanced control and convenience.
- Safety Considerations: Emphasizing the importance of proper grounding, polarity, and circuit protection to prevent electrical hazards.
- Troubleshooting: Identifying common problems and providing guidance on how to diagnose and resolve them.
- Maintenance: Outlining regular checks and maintenance procedures to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the system.
These aspects are interconnected and play vital roles in ensuring the effective and safe operation of Thermostat Wiring for Boiler systems. Proper installation and maintenance are crucial for maintaining a comfortable indoor environment while optimizing energy consumption.
Components
In the context of Thermostat Wiring for Boiler systems, understanding the functions of individual components is paramount to comprehending the overall operation and ensuring efficient system performance. The thermostat serves as the control center, continuously monitoring the indoor temperature and comparing it to the desired setpoint. When a temperature adjustment is required, the thermostat sends a signal to the boiler through electrical connections.
The boiler, upon receiving the signal from the thermostat, initiates the combustion process to generate heat. This heat is then distributed throughout the building via pipes or radiators. The wiring components, including terminals, relays, and switches, facilitate the electrical communication between the thermostat and the boiler, ensuring that the system operates smoothly and efficiently.
For instance, terminals provide secure electrical connections between different components, while relays act as electronic switches, allowing the thermostat to control the boiler’s operation without directly handling high electrical currents. Switches, on the other hand, enable manual override of the system, allowing users to adjust temperatures or switch between heating modes as needed.
Therefore, understanding the functions of these components is critical for effective Thermostat Wiring for Boiler systems. Proper installation and maintenance of these components ensure reliable and efficient operation, contributing to a comfortable indoor environment while optimizing energy consumption.
Wiring Diagrams
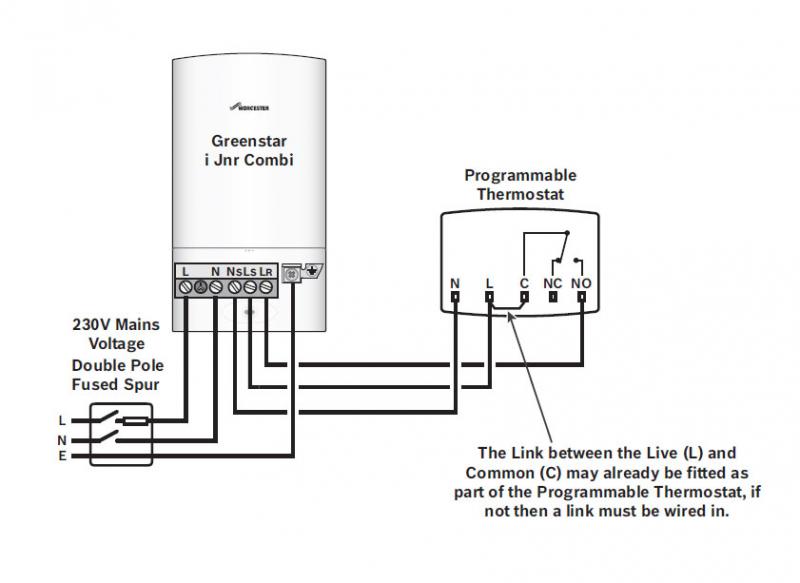
Wiring diagrams serve as visual representations of electrical circuits, providing detailed instructions on how to correctly connect the thermostat to the boiler. Interpreting these diagrams is crucial for ensuring a safe and functional Thermostat Wiring for Boiler system.
- Circuit Components: Wiring diagrams depict various electrical components used in the system, including terminals, wires, relays, and switches. Understanding the symbols and functions of these components is essential for accurate wiring.
- Wire Gauge and Color Coding: Diagrams specify the appropriate wire gauge and color coding for different connections. This ensures proper current carrying capacity and simplifies troubleshooting.
- Terminal Identification: Each terminal on the thermostat and boiler has a specific purpose. Wiring diagrams clearly label these terminals, guiding the installer in making the correct connections.
- Power and Signal Paths: Diagrams trace the flow of power and control signals throughout the system. This helps identify potential voltage drop issues and ensures that the boiler receives the correct signals from the thermostat.
Accurate interpretation of wiring diagrams is essential for safe and efficient Thermostat Wiring for Boiler systems. Proper connections prevent electrical hazards, ensure optimal boiler operation, and contribute to a comfortable indoor environment.
Voltage Compatibility
Within the context of Thermostat Wiring for Boiler, voltage compatibility plays a critical role in ensuring the safe and efficient operation of the system. Operating the thermostat and boiler at different voltages can lead to equipment damage, electrical hazards, and system malfunctions. This section delves into the various facets and implications of voltage compatibility in Thermostat Wiring for Boiler systems, providing a comprehensive understanding of its importance.
- Electrical Safety: Mismatched voltages can cause electrical overloads, short circuits, and component failures. Ensuring voltage compatibility prevents such hazards, safeguarding the system and the building’s occupants.
- Equipment Protection: Operating the thermostat and boiler at the correct voltage ensures that they operate within their designed parameters, preventing damage to sensitive electronic components and extending the lifespan of the equipment.
- System Performance: Proper voltage compatibility ensures that both the thermostat and boiler work in harmony, providing optimal temperature control and efficient energy usage. Incompatible voltages can disrupt communication between the components, leading to erratic system behavior and reduced comfort levels.
- Installation and Troubleshooting: Understanding voltage compatibility is crucial during installation and troubleshooting. Mismatched voltages can make it difficult to diagnose system issues, leading to incorrect repairs and potential safety concerns.
In summary, voltage compatibility is a fundamental aspect of Thermostat Wiring for Boiler systems, ensuring electrical safety, equipment protection, optimal system performance, and ease of installation and troubleshooting. Adhering to the manufacturer’s voltage specifications and seeking professional assistance for electrical work is essential for reliable and long-lasting operation of the system.
Zone Control
Within the realm of Thermostat Wiring for Boiler systems, zone control emerges as a sophisticated approach to enhance comfort and energy efficiency. It involves employing multiple thermostats to regulate temperatures in distinct heating zones, offering tailored control over various areas of a building. This section delves into the facets and implications of zone control, exploring its components, real-life examples, and advantages within the context of Thermostat Wiring for Boiler systems.
- Individualized Comfort: Zone control allows occupants to set different temperatures for each zone, accommodating varying preferences and activities. This personalized approach enhances comfort levels, ensuring that each area meets the specific needs of its occupants.
- Energy Savings: By dividing the building into zones, zone control enables efficient energy management. Areas that are unoccupied or require lower temperatures can be adjusted accordingly, reducing overall energy consumption without compromising comfort in occupied zones.
- System Optimization: Zone control optimizes the boiler’s operation by reducing the frequency of heating cycles. Instead of heating the entire building to a single temperature, the boiler can focus on heating specific zones as needed, leading to increased efficiency and reduced wear and tear on the system.
- Future Expansion: Zone control provides flexibility for future expansion or renovations. Additional thermostats and heating zones can be easily integrated into the system, allowing for tailored temperature control as the building evolves.
In summary, zone control in Thermostat Wiring for Boiler systems offers a comprehensive approach to enhance comfort, optimize energy efficiency, and provide flexibility for future expansion. By utilizing multiple thermostats to control different heating zones, building owners and occupants can create a comfortable and energy-efficient indoor environment that meets their specific needs.
Smart Thermostats
Within the realm of Thermostat Wiring for Boiler systems, smart thermostats have emerged as a transformative technology, offering enhanced control, convenience, and energy efficiency. These devices seamlessly integrate with the existing Thermostat Wiring for Boiler infrastructure, unlocking a host of benefits that optimize the heating system’s performance.
The connection between Smart Thermostats and Thermostat Wiring for Boiler lies in their complementary roles. Smart thermostats provide an advanced interface for controlling the boiler system, while Thermostat Wiring for Boiler establishes the electrical connections that enable this control. Together, they form a sophisticated system that delivers unparalleled comfort, convenience, and energy efficiency.
Real-life examples of Smart Thermostats integrated with Thermostat Wiring for Boiler systems abound. In residential settings, smart thermostats allow homeowners to remotely control their heating systems, adjust temperatures based on their schedules, and monitor energy consumption. In commercial buildings, smart thermostats enable facility managers to optimize energy usage across multiple zones, reducing operating costs while maintaining occupant comfort.
The practical applications of this understanding extend beyond individual buildings. By integrating smart thermostats with Thermostat Wiring for Boiler systems on a larger scale, cities and municipalities can contribute to sustainability goals. Smart thermostats empower consumers to reduce their carbon footprint by optimizing energy consumption, leading to a systemic reduction in greenhouse gas emissions.
In summary, Smart Thermostats and Thermostat Wiring for Boiler systems form a synergistic relationship, empowering users with enhanced control, convenience, and energy efficiency. As technology continues to advance, the integration of these systems will play a pivotal role in creating intelligent and sustainable built environments.
Safety Considerations
Within the context of Thermostat Wiring for Boiler systems, safety considerations take paramount importance. Proper grounding, polarity, and circuit protection measures are critical components of any electrical installation, ensuring the safe and reliable operation of the system. Neglecting these safety considerations can lead to electrical hazards, equipment damage, and potential harm to individuals.
Grounding provides a low-resistance path for electrical current to flow back to the source, preventing voltage buildup and reducing the risk of electrical shock. Polarity ensures that electrical current flows in the intended direction, preventing damage to components and ensuring proper system operation. Circuit protection devices, such as fuses and circuit breakers, safeguard the system from overcurrent conditions that could lead to fires or electrical damage.
Real-life examples of improper safety considerations in Thermostat Wiring for Boiler systems can be found in both residential and commercial settings. Loose or missing ground connections can result in stray currents that can cause shocks or equipment malfunctions. Reversed polarity can damage thermostats, boilers, or other connected devices. Inadequate circuit protection can lead to overheating, electrical fires, or even explosions.
The practical applications of understanding safety considerations in Thermostat Wiring for Boiler systems extend beyond individual installations. By adhering to proper grounding, polarity, and circuit protection guidelines, electrical professionals contribute to a safer built environment. This, in turn, reduces the risk of accidents, property damage, and potential legal liabilities.
In conclusion, safety considerations are an integral part of Thermostat Wiring for Boiler systems, ensuring the safety of individuals and the integrity of the system. By prioritizing proper grounding, polarity, and circuit protection, electrical professionals play a vital role in maintaining a safe and efficient electrical infrastructure.
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting forms an integral part of Thermostat Wiring for Boiler systems, enabling the identification and resolution of common problems. By understanding the potential issues, their causes, and effective troubleshooting techniques, individuals can ensure the reliable operation of their boiler systems and maintain a comfortable indoor environment.
-
Identifying Electrical Faults
Thermostat Wiring for Boiler systems rely on electrical connections, making it essential to troubleshoot electrical faults. Open circuits, loose connections, and faulty wires can disrupt communication between the thermostat and the boiler, leading to system malfunctions. Identifying these faults requires careful inspection of wiring, terminals, and connections.
-
Diagnosing Thermostat Issues
Thermostats are the control center of Thermostat Wiring for Boiler systems. Malfunctioning thermostats can result in inaccurate temperature readings, improper boiler operation, or system failures. Troubleshooting thermostat issues involves testing its functionality, checking for proper calibration, and replacing defective components if necessary.
-
Resolving Boiler Problems
Boilers are complex mechanical devices that can encounter various issues. Troubleshooting boiler problems requires an understanding of their operation and potential failure points. Common issues include ignition problems, burner malfunctions, and water circulation issues. Identifying and resolving these problems may involve cleaning components, replacing faulty parts, or adjusting system settings.
-
Addressing Zone Control Malfunctions
Zone control systems allow for independent temperature control in different areas of a building. Troubleshooting zone control malfunctions involves identifying faulty thermostats, verifying zone valve operation, and ensuring proper communication between the components. Resolving these issues often requires a combination of electrical and mechanical troubleshooting techniques.
Effective troubleshooting of Thermostat Wiring for Boiler systems demands a systematic approach, attention to detail, and an understanding of the underlying principles. By following established troubleshooting procedures and utilizing appropriate tools, individuals can diagnose and resolve common problems, ensuring the efficient and reliable operation of their boiler systems.
Maintenance
Within the realm of Thermostat Wiring for Boiler systems, maintenance plays a pivotal role in ensuring the system’s optimal performance and longevity. Regular checks and maintenance procedures are essential to identify potential issues, prevent breakdowns, and extend the lifespan of the components.
-
Routine Inspections
Regular inspections involve visual checks of the thermostat, boiler, wiring, and other components for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections. These inspections help identify potential problems early on, allowing for timely repairs or replacements.
-
Thermostat Calibration
Thermostats require periodic calibration to ensure accurate temperature readings. This involves comparing the thermostat’s readings to a known reference temperature and making adjustments as necessary.
-
Boiler Servicing
Regular servicing of the boiler is crucial for maintaining its efficiency and safety. This includes cleaning the burner, inspecting the heat exchanger, and checking the water pressure and circulation.
-
Zone Control Maintenance
For systems with zone control, regular maintenance involves checking the operation of zone valves, ensuring proper communication between thermostats and the boiler, and balancing the flow of hot water to each zone.
By adhering to a comprehensive maintenance schedule, individuals can minimize the risk of breakdowns, extend the lifespan of their Thermostat Wiring for Boiler system, and ensure a comfortable and efficient indoor environment for years to come.








Related Posts








