Stereo Headphone Wiring refers to the specific arrangement of electrical connections within a stereo headphone cable that allows each earpiece to receive a separate audio signal, creating a stereo sound effect.
This wiring is crucial for delivering a realistic and immersive audio experience, as it enables users to hear sounds coming from different directions, enhancing spatial awareness and auditory perception. A common example is in music listening, where stereo headphone wiring allows for the reproduction of the full stereo mix, with instruments and vocals appearing to be positioned accordingly in the soundstage.
Stereo headphone wiring has significant relevance in various fields, including audio production, gaming, and virtual reality, where accurate and precise sound reproduction is paramount. A key historical development was the introduction of the 3.5mm TRS (Tip, Ring, Sleeve) connector in the 1950s, which became the industry standard for stereo headphone connections and is still widely used today. This transition paved the way for the widespread adoption of stereo headphones and the enhanced audio experiences they offer.
Understanding the key aspects of Stereo Headphone Wiring is essential for comprehending its functionality and significance in various applications. These aspects encompass diverse dimensions related to its design, usage, and impact.
- Signal Transmission: Stereo Headphone Wiring facilitates the transmission of separate audio signals to each earpiece, enabling the perception of stereo sound.
- Connector Types: Different types of connectors, such as TRS, TRRS, and XLR, are used for stereo headphone wiring, each with its own set of features and applications.
- Cable Length and Material: The length and material of the cable can affect signal quality and durability.
- Impedance and Sensitivity: These factors determine the compatibility between headphones and audio sources.
- Noise Isolation: Stereo headphone wiring can incorporate shielding and other techniques to minimize external noise interference.
- Comfort and Ergonomics: The design of the wiring should consider comfort and ease of use, especially for extended listening sessions.
- Durability and Construction: The durability of the wiring is crucial for longevity and reliability.
- Compatibility: Stereo headphone wiring should be compatible with a wide range of audio devices.
These aspects are interconnected and play a crucial role in delivering an optimal audio experience. For instance, the choice of connector type depends on the compatibility with the audio source, while the cable length and material impact signal transmission quality. Understanding these aspects enables informed decision-making when selecting and using stereo headphones for various applications.
Signal Transmission
Signal transmission is a fundamental aspect of stereo headphone wiring, as it allows for the delivery of distinct audio signals to each ear, creating a stereo soundscape. This is achieved through the use of a specialized cable with multiple conductors, each carrying a separate audio channel. The wiring configuration ensures that the left and right audio signals are routed to the corresponding earpieces, enabling the listener to experience the spatial separation and directionality of sound.
Without proper signal transmission, stereo headphones would only be capable of producing monaural sound, where both earpieces receive the same audio signal. This would result in a flat and unimmersive listening experience, lacking the depth and realism that stereo sound provides.
Real-life examples of signal transmission in stereo headphone wiring can be found in various applications, including:
- Music listening: Stereo headphones allow listeners to enjoy music with a wide stereo soundstage, where instruments and vocals appear to be positioned in different locations.
- Gaming: Stereo headphones enhance the gaming experience by providing directional audio cues, allowing players to locate opponents and navigate virtual environments more effectively.
- Virtual reality: Stereo headphones play a crucial role in creating immersive virtual reality experiences, transporting users to different worlds with realistic spatialized audio.
Understanding the principles of signal transmission in stereo headphone wiring is essential for appreciating the benefits and applications of this technology. It enables us to design and utilize stereo headphones effectively, unlocking immersive and engaging audio experiences in various domains.
Connector Types
Connector types play a crucial role in stereo headphone wiring, as they determine the physical interface between the headphones and the audio source. The choice of connector depends on factors such as compatibility, signal quality, and intended use.
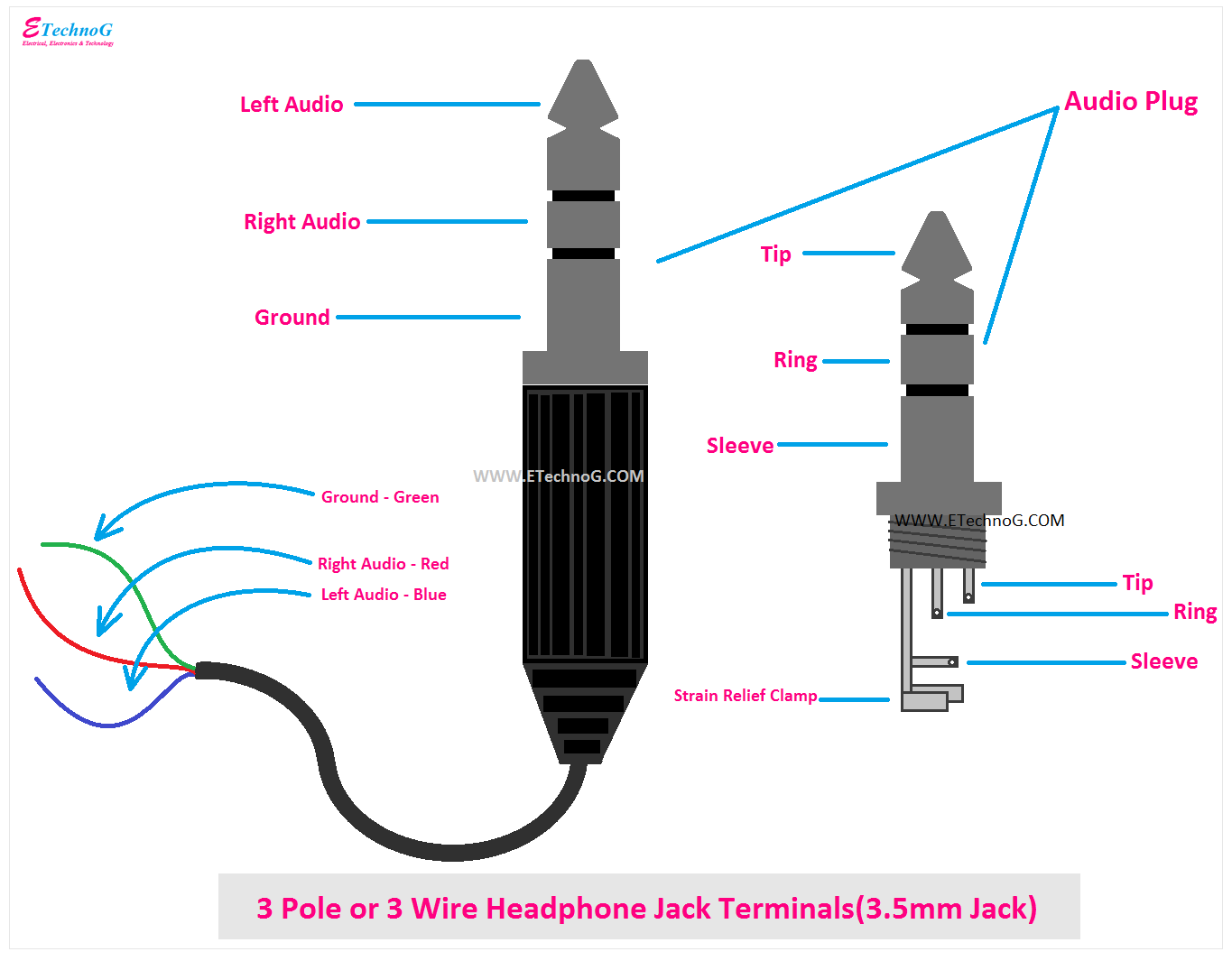
TRS (Tip, Ring, Sleeve) connectors are commonly used for stereo headphones, featuring three conductors for left audio, right audio, and ground. This type of connector is widely compatible with various audio devices, including smartphones, laptops, and audio interfaces.
TRRS (Tip, Ring, Ring, Sleeve) connectors are an extension of TRS, adding an additional conductor for microphone support. This allows for the use of stereo headphones with built-in microphones, enabling hands-free communication and voice commands.
XLR connectors are primarily used in professional audio applications, offering a balanced audio connection with three pins for positive, negative, and ground signals. XLR connectors provide excellent signal quality and are commonly found in studio environments and live sound setups.
Understanding the different connector types is essential for selecting the appropriate headphones for specific applications. For instance, if microphone support is required, a headset with a TRRS connector would be necessary. Similarly, for professional audio recording or live performances, XLR connectors ensure the best possible signal integrity.
In summary, the connection between connector types and stereo headphone wiring is critical for establishing a reliable and effective audio connection. Choosing the right connector type ensures compatibility, signal quality, and the desired functionality, enhancing the overall audio experience across various applications.
Cable Length and Material
In the context of stereo headphone wiring, cable length and material play a significant role in determining the overall performance and user experience. The length of the cable affects signal transmission, while the material influences signal quality and durability.
A longer cable introduces more resistance into the circuit, which can lead to signal loss and reduced audio quality. This is particularly noticeable in high-impedance headphones, where longer cables can result in a noticeable drop in volume and clarity. Therefore, for extended listening sessions or professional applications, shorter cables are generally preferred to maintain optimal signal quality.
The material of the cable also impacts signal transmission and durability. Copper is a commonly used material for headphone cables due to its excellent conductivity and durability. However, oxygen-free copper (OFC) is a higher-quality option that provides better signal transmission and reduced signal degradation over time. OFC cables are often used in high-end headphones and professional audio applications.
Understanding the relationship between cable length and material and stereo headphone wiring is crucial for selecting the appropriate headphones for specific needs. For instance, if portability is a priority, shorter cables may be preferred. Conversely, for stationary listening setups or professional use, longer cables may be necessary to accommodate the distance between the headphones and the audio source.
In summary, cable length and material are integral components of stereo headphone wiring, influencing signal quality, durability, and overall performance. By considering these factors, users can make informed decisions when choosing headphones that meet their specific requirements and provide an optimal listening experience.
Impedance and Sensitivity
In the context of stereo headphone wiring, impedance and sensitivity play critical roles in ensuring compatibility and optimal performance between headphones and audio sources. Impedance, measured in ohms (), represents the electrical resistance of the headphones, while sensitivity, measured in decibels per milliwatt (dB/mW), indicates the headphones’ efficiency in converting electrical signals into audible sound.
- Impedance Matching: The impedance of headphones should be compatible with the output impedance of the audio source. When impedance is mismatched, it can lead to reduced volume, distorted sound, or damage to the headphones or audio source.
- Sensitivity and Volume: Headphones with higher sensitivity require less power to produce the same volume level compared to headphones with lower sensitivity. This is important for portable devices or low-powered audio sources, as it allows for adequate volume without overloading the source.
- Frequency Response: Impedance and sensitivity can affect the frequency response of headphones. Headphones with higher impedance may exhibit reduced bass response, while headphones with lower sensitivity may have a narrower frequency range.
- Headphone Amplifiers: For high-impedance headphones or low-powered audio sources, a headphone amplifier may be necessary to provide sufficient power and drive the headphones effectively.
Understanding impedance and sensitivity is crucial for selecting compatible headphones and audio sources. By considering these factors, users can ensure optimal sound quality, volume levels, and overall listening experience. Matching impedance and sensitivity also helps prolong the lifespan of both the headphones and the audio source by preventing damage due to improper operation.
Noise Isolation
Noise isolation is a crucial aspect of stereo headphone wiring, as it plays a significant role in delivering an immersive and distraction-free listening experience. Stereo headphone wiring employs various techniques to reduce external noise interference and enhance sound quality.
One common technique is the use of shielding materials, such as copper braids or metal foils, which are incorporated into the cable to block electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI). These materials create a protective barrier, preventing unwanted signals from entering the headphones and disrupting the audio signal.
Another technique is the utilization of ear tips or ear pads made from noise-isolating materials, such as memory foam or silicone. These materials conform to the shape of the ear canal, creating a seal that physically blocks out external noise. This is particularly effective in noisy environments, such as during commutes or in public spaces.
The benefits of noise isolation in stereo headphone wiring are numerous. It allows listeners to enjoy their music or other audio content without distractions, creating a more immersive and enjoyable experience. Furthermore, noise isolation can improve sound quality by reducing background noise, making it easier to hear the details and nuances of the audio.
Real-life examples of noise isolation in stereo headphone wiring can be found in various products, such as noise-canceling headphones and in-ear monitors used by musicians and audio engineers. Noise-canceling headphones use active noise cancellation technology to further reduce external noise, while in-ear monitors often feature specialized ear tips designed to provide excellent noise isolation.
Understanding the connection between noise isolation and stereo headphone wiring enables users to make informed choices when selecting headphones for their specific needs and listening environments. By considering noise isolation capabilities, users can optimize their listening experience and enjoy their audio content to the fullest.
Comfort and Ergonomics
In the realm of stereo headphone wiring, comfort and ergonomics play a pivotal role in enhancing the user experience, particularly during extended listening sessions. The design of the wiring should meticulously consider factors that contribute to the overall comfort and ease of use of headphones.
- Weight and Balance: The weight and balance of headphones can significantly impact comfort, especially during prolonged use. Lightweight headphones reduce strain on the head and neck, while proper weight distribution ensures a comfortable fit.
- Adjustable Headband: An adjustable headband allows users to customize the fit of their headphones, ensuring a snug and secure fit without causing discomfort. This is particularly important for users with different head sizes or shapes.
- Cushioning and Padding: Adequate cushioning and padding on the ear cups and headband contribute to long-term comfort. Soft and breathable materials prevent pressure points and reduce fatigue during extended listening sessions.
- Cable Length and Strain Relief: The length and strain relief of the headphone cable play a role in comfort and ease of use. An optimal cable length provides freedom of movement without tangles, while strain relief at the cable terminations prevents damage and ensures durability.
By considering these ergonomic factors in stereo headphone wiring, manufacturers can create headphones that provide a comfortable and enjoyable listening experience, even during extended use. Comfortable headphones enhance the overall user experience, allowing listeners to immerse themselves in their audio content without distractions or discomfort.
Durability and Construction
In the realm of stereo headphone wiring, durability and construction play a paramount role in ensuring the longevity and reliability of these essential components. Durable headphones can withstand the rigors of everyday use and transportation, while reliable wiring ensures a consistent and uninterrupted audio experience. Here are some key aspects of durability and construction to consider:
- Robust Materials: The choice of materials used in headphone wiring and construction significantly impacts their durability. Sturdy plastics, reinforced cables, and corrosion-resistant metals enhance the headphones’ ability to withstand physical stress and environmental factors.
- Strain Relief: Reinforcements at the points where the cable meets the headphones and connectors prevent damage caused by repeated bending and pulling. Strain relief extends the lifespan of the wiring and ensures a secure connection.
- Connector Quality: Durable connectors, such as gold-plated or reinforced plugs, resist wear and tear, ensuring a reliable connection between the headphones and audio source. High-quality connectors also minimize signal loss and maintain sound fidelity.
- Build Craftsmanship: The overall build quality of headphones reflects their ability to withstand everyday use. Well-constructed headphones feature tight tolerances, secure joints, and a robust design that minimizes the risk of breakage or failure.
By prioritizing durability and construction in stereo headphone wiring, manufacturers can create headphones that provide a long-lasting and reliable audio experience. Durable headphones are a worthwhile investment, offering peace of mind and minimizing the need for frequent replacements. Whether for personal use, professional applications, or demanding environments, durability is a critical factor in selecting headphones that will perform consistently and withstand the test of time.
Compatibility
Within the realm of stereo headphone wiring, compatibility plays a crucial role in ensuring a seamless and versatile listening experience. Compatibility refers to the ability of stereo headphones to connect and function effectively with various audio devices, including smartphones, laptops, audio interfaces, and home stereo systems.
- Connector Compatibility: Stereo headphone wiring incorporates different types of connectors, such as 3.5mm TRS, TRRS, and XLR, to cater to the diverse connectivity options found on audio devices. Compatibility ensures that headphones can be physically connected to the audio source without the need for adapters or converters.
- Impedance Matching: The impedance of headphones should be compatible with the output impedance of the audio device to achieve optimal sound quality. Mismatched impedance can lead to volume issues, distortion, or damage to the headphones or audio source.
- Power Requirements: Stereo headphone wiring should consider the power requirements of the headphones. High-impedance headphones may require an external headphone amplifier to provide adequate volume and drive the headphones effectively.
- Functionality Compatibility: Compatibility also encompasses the functionality of stereo headphones. Features such as inline controls for volume, playback, and microphone support should be compatible with the audio device to ensure seamless operation.
By ensuring compatibility in stereo headphone wiring, users can enjoy a wide range of audio content from multiple devices with ease. Compatibility enables headphones to adapt to different listening environments and usage scenarios, enhancing the overall user experience and ensuring a consistent and enjoyable audio experience.









Related Posts








