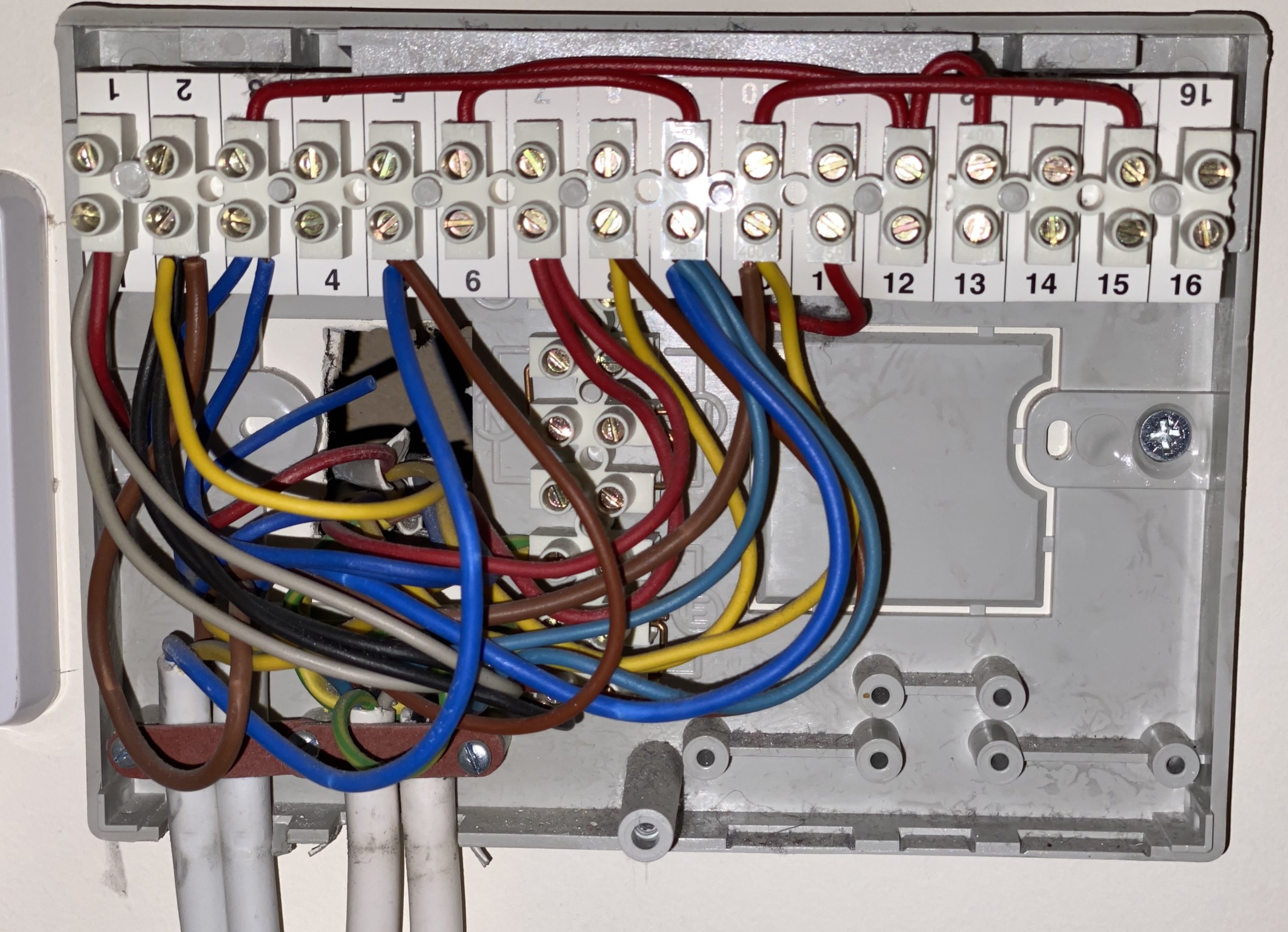
Junction Box Wiring refers to the electrical connections made within a junction box, a crucial component for distributing and safeguarding electrical circuits in various settings. For instance, in a residential setup, a junction box in the attic would facilitate the connection of multiple electrical wires, allowing for the distribution of power to different rooms.
Junction Box Wiring holds immense importance in electrical systems. It ensures secure and organized connections, safeguarding against potential electrical hazards. Its benefits include enhanced safety, improved circuit organization, and easier maintenance. Historically, the development of insulated junction boxes revolutionized electrical wiring by providing safer and more reliable connections.
As we delve into this article, we will explore the intricacies of Junction Box Wiring, including its types, installation techniques, and the various codes and regulations that govern its implementation. A thorough understanding of these aspects is essential for safe and efficient electrical installations.
Junction Box Wiring encompasses a wide range of essential aspects, each playing a critical role in ensuring the safety, reliability, and efficiency of electrical systems. These aspects are multifaceted and interdependent, and a thorough understanding of their significance is paramount for effective electrical installations.
- Safety: Paramount importance, safeguarding against electrical hazards.
- Organization: Structured wiring, memudahkan troubleshooting dan pemeliharaan.
- Codes and regulations: Compliance ensures adherence to safety standards.
- Types: Varied designs for specific applications, e.g., weatherproof, explosion-proof.
- Installation techniques: Proper methods for secure and reliable connections.
- Materials: Durable and non-conductive materials for longevity and safety.
- Circuit protection: Integrated devices safeguard against overloads and short circuits.
- Grounding: Essential for safety, providing a low-resistance path to the earth.
- Inspection and maintenance: Regular checks ensure ongoing safety and functionality.
- Troubleshooting: Systematic approach to identify and resolve electrical issues.
These aspects are interconnected and form a comprehensive framework for Junction Box Wiring. Understanding their individual significance and their collective interplay is fundamental to the design, installation, and maintenance of robust and safe electrical systems. By adhering to codes and regulations, employing proper techniques, and utilizing appropriate materials, electricians can ensure the integrity of Junction Box Wiring, safeguarding both property and individuals from electrical hazards.
Safety
Junction Box Wiring plays a pivotal role in ensuring the safety of electrical systems by safeguarding against potential electrical hazards. A primary cause of electrical fires is faulty wiring and connections, which can result from improper installation or damaged components within junction boxes. Junction Box Wiring addresses this concern by providing a structured and organized approach to electrical connections, ensuring secure and reliable junctions.
As a critical component of Junction Box Wiring, safety measures are meticulously implemented to prevent electrical hazards. These measures include the use of insulated materials, proper grounding techniques, and the incorporation of circuit protection devices. Insulated materials prevent accidental contact with live wires, while proper grounding provides a safe path for any excess current to flow, minimizing the risk of electrical shocks. Circuit protection devices, such as fuses or circuit breakers, trip when excessive current flows, preventing overheating and potential fires.
In real-life applications, the safety benefits of Junction Box Wiring are evident. For instance, in commercial buildings, junction boxes are strategically placed to facilitate easy access for maintenance and troubleshooting, reducing the risk of electrical accidents. In residential settings, junction boxes are often located in attics or basements, providing a centralized point for managing electrical connections, enhancing safety and preventing potential hazards.
Understanding the connection between safety and Junction Box Wiring is crucial for various stakeholders involved in electrical systems. Electricians must possess a thorough knowledge of safety protocols and regulations to ensure proper installation and maintenance of junction boxes. Building inspectors play a vital role in verifying the adherence to safety codes and standards, ensuring the integrity of electrical systems. Homeowners and building occupants should be aware of the importance of junction boxes in maintaining electrical safety and promptly report any potential hazards or concerns.
Organization
In the realm of electrical systems, organization plays a pivotal role in facilitating troubleshooting and maintenance. Junction Box Wiring embodies this principle by providing a structured approach to electrical connections, ensuring clarity and accessibility. A well-organized Junction Box Wiring system allows electricians to quickly identify and resolve issues, minimize downtime, and enhance overall system reliability.
As a critical component of Junction Box Wiring, organization stems from the strategic placement and labeling of junction boxes. This structured approach enables technicians to trace circuits efficiently, identify connection points, and pinpoint potential problems with ease. Moreover, organized Junction Box Wiring simplifies additions or modifications to electrical systems, reducing the likelihood of errors and costly rework.
In real-life applications, the benefits of organized Junction Box Wiring are evident across various industries. In commercial buildings, for instance, structured wiring facilitates efficient troubleshooting during maintenance or renovations, minimizing disruptions to business operations. In residential settings, organized junction boxes in attics or basements allow homeowners to safely access and manage electrical connections, fostering a sense of control and enabling prompt responses to electrical issues.
Understanding the connection between organization and Junction Box Wiring is crucial for various stakeholders. For electricians, adhering to structured wiring practices ensures efficient installations, simplified maintenance, and reduced troubleshooting time. Building inspectors rely on organized Junction Box Wiring to verify code compliance and ensure the safety and reliability of electrical systems. Homeowners and building occupants benefit from the ease of troubleshooting and maintenance, empowering them to address minor electrical issues and maintain a safe living environment.
Codes and regulations
In the intricate world of electrical systems, codes and regulations serve as the guiding principles, establishing minimum safety requirements to protect individuals and property from electrical hazards. Junction Box Wiring, as a crucial component of these systems, plays a pivotal role in upholding these standards, ensuring the integrity and reliability of electrical installations.
Codes and regulations provide a comprehensive framework for Junction Box Wiring, dictating specific guidelines for materials, installation techniques, and safety measures. These regulations are meticulously crafted by experts to minimize electrical risks, prevent fires, and safeguard human life. By adhering to these codes, electricians can ensure that junction boxes are installed and maintained to the highest standards of safety.
Real-life examples abound, demonstrating the critical connection between codes and regulations and Junction Box Wiring. In commercial buildings, regular inspections are conducted to verify compliance with electrical codes, including Junction Box Wiring. This ensures that junction boxes are properly installed, accessible for maintenance, and protected from environmental hazards. In residential settings, adherence to codes and regulations during Junction Box Wiring guarantees the safety of homeowners and their families, reducing the risk of electrical shocks, fires, and other potential hazards.
Understanding the relationship between codes and regulations and Junction Box Wiring is paramount for various stakeholders. Electricians must possess a thorough knowledge of these codes to perform installations and repairs safely and effectively. Building inspectors rely on codes and regulations to assess the compliance of electrical systems, ensuring the protection of occupants and property. Homeowners and building occupants can take comfort in knowing that Junction Box Wiring adheres to established safety standards, providing peace of mind and a safer living environment.
Types
In the realm of electrical systems, Junction Box Wiring encompasses a diverse range of junction box types, each meticulously designed to cater to specific applications and environmental conditions. This specialization ensures that Junction Box Wiring can effectively address the unique challenges posed by different settings, prioritizing safety, reliability, and code compliance.
The significance of varied junction box types lies in their ability to withstand specific environmental factors or hazardous conditions. For instance, weatherproof junction boxes are constructed with durable materials and tight seals to protect against moisture, dust, and extreme temperatures, making them ideal for outdoor applications or areas prone to harsh weather conditions. Explosion-proof junction boxes, on the other hand, are designed to contain potential explosions or fires within their enclosures, making them essential in hazardous environments such as chemical plants or mines.
Real-life examples abound, highlighting the practical applications of specialized junction box types within Junction Box Wiring. In industrial settings, explosion-proof junction boxes are indispensable for ensuring safety in areas where flammable gases or volatile materials are present. In coastal regions, weatherproof junction boxes are extensively used to protect electrical connections from the corrosive effects of saltwater and moisture.
Understanding the connection between “Types: Varied designs for specific applications, e.g., weatherproof, explosion-proof.” and “Junction Box Wiring” is critical for various stakeholders. Electricians must possess a comprehensive knowledge of the different junction box types and their appropriate applications to ensure the safety and reliability of electrical installations. Building inspectors rely on this understanding to verify code compliance and adherence to safety standards. Homeowners and building occupants can take comfort in knowing that Junction Box Wiring incorporates specialized junction box types to address the specific needs of their environment, enhancing safety and peace of mind.
Installation techniques
Within the realm of electrical systems, Junction Box Wiring relies heavily on the implementation of proper installation techniques to ensure the security and reliability of electrical connections. These techniques encompass a range of practices and considerations that directly impact the overall safety and functionality of Junction Box Wiring systems.
The significance of proper installation techniques in Junction Box Wiring stems from their ability to prevent electrical hazards and ensure the longevity of electrical systems. By adhering to established guidelines and industry best practices, electricians can minimize the risk of loose connections, insulation damage, and other issues that could lead to electrical fires, shocks, or system failures. Moreover, proper installation techniques contribute to the overall efficiency and reliability of electrical systems, reducing energy loss and minimizing the need for costly repairs or replacements.
Real-life examples abound, demonstrating the practical applications of proper installation techniques within Junction Box Wiring. In commercial buildings, meticulous attention to installation techniques during the wiring of junction boxes is crucial for ensuring the uninterrupted operation of critical systems, such as lighting, HVAC, and security. In residential settings, proper installation techniques in junction boxes contribute to the safety and comfort of occupants by preventing electrical issues that could pose a fire hazard or disruption to daily life.
Understanding the connection between “Installation techniques: Proper methods for secure and reliable connections.” and “Junction Box Wiring” is essential for various stakeholders. Electricians must possess a thorough knowledge of proper installation techniques to ensure the integrity and safety of electrical systems. Building inspectors rely on this understanding to assess the compliance of electrical installations with codes and standards. Homeowners and building occupants can take comfort in knowing that Junction Box Wiring adheres to established installation techniques, enhancing the safety and reliability of their electrical systems.
Materials
Within the realm of “Junction Box Wiring”, the judicious selection and utilization of durable and non-conductive materials play a pivotal role in ensuring the longevity, safety, and reliability of electrical systems. These materials form the very foundation of Junction Box Wiring, safeguarding against potential hazards, optimizing performance, and ensuring code compliance.
- Corrosion Resistance: Junction boxes, often exposed to moisture and harsh conditions, necessitate the use of corrosion-resistant materials such as galvanized steel or PVC to prevent rust and deterioration, ensuring long-lasting performance and structural integrity.
- Electrical Insulation: Non-conductive materials like rubber, plastic, or ceramic are crucial for insulating electrical connections within junction boxes, preventing accidental contact, short circuits, and potential electrical fires.
- Temperature Tolerance: Junction boxes may encounter varying temperatures, particularly in industrial settings. Employing materials with high melting points, such as porcelain or fiberglass, ensures they can withstand heat without compromising safety or degrading over time.
- Impact Resistance: In areas prone to physical impact or vibration, junction boxes made from robust materials like polycarbonate or metal alloys provide exceptional protection, safeguarding internal connections from damage and maintaining electrical integrity.
In real-life applications, the significance of durable and non-conductive materials in Junction Box Wiring is evident. For instance, in outdoor installations, weatherproof junction boxes made from corrosion-resistant materials ensure uninterrupted operation despite exposure to rain, snow, and extreme temperatures. In commercial settings, junction boxes with high electrical insulation prevent electrical hazards in high-voltage environments, minimizing the risk of accidents and downtime. By utilizing durable and non-conductive materials, Junction Box Wiring not only enhances the longevity and safety of electrical systems but also contributes to the overall reliability and efficiency of electrical installations.
Circuit protection
Within the realm of “Junction Box Wiring”, circuit protection stands as a critical aspect, ensuring the safety and reliability of electrical systems. Integrated devices such as fuses, circuit breakers, and ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) play a pivotal role in safeguarding against overloads and short circuits, preventing electrical hazards, minimizing damage to equipment, and upholding code compliance.
- Fuses: Fuses interrupt the flow of excessive current by melting a thin wire, effectively breaking the circuit and preventing damage to electrical components. They are commonly used in residential and commercial settings, offering a cost-effective solution for circuit protection.
- Circuit breakers: Circuit breakers provide reusable protection against overloads and short circuits. When an abnormal current is detected, the breaker trips, cutting off the power supply. Resetting the breaker restores power, eliminating the need for fuse replacement.
- Ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs): GFCIs monitor the balance of current flowing through the circuit. In the event of an imbalance, such as a ground fault, the GFCI promptly breaks the circuit to prevent electrical shocks. They are essential in areas with high moisture or potential for electrical contact with water, such as bathrooms and kitchens.
- Surge protectors: Surge protectors defend against voltage spikes and transients that can damage sensitive electronic equipment. They absorb or divert excess voltage, safeguarding devices from potential harm.
The integration of these protective devices within Junction Box Wiring is crucial for ensuring the safety and functionality of electrical systems. By effectively interrupting current flow during abnormal conditions, these devices minimize the risk of electrical fires, equipment damage, and personal injury. Moreover, they facilitate troubleshooting and maintenance, allowing for quick identification of faults and restoration of electrical service. As a result, circuit protection plays an indispensable role in maintaining a safe and reliable electrical infrastructure.
Grounding
Grounding plays a critical role in electrical systems, including Junction Box Wiring, by providing a low-resistance path for electrical current to flow safely to the earth. This path is essential for protecting against electrical shocks, equipment damage, and electrical fires. Without proper grounding, electrical current can take unintended paths, such as through people or equipment, increasing the risk of hazards.
In Junction Box Wiring, grounding is achieved through the use of a grounding conductor, which is connected to the grounding busbar in the electrical panel and to all electrical devices and equipment. The grounding conductor provides a low-resistance path for electrical current to flow to the earth in the event of a fault or surge. This prevents the buildup of dangerous voltage levels on electrical components and reduces the risk of electrical shock.
Real-life examples of grounding in Junction Box Wiring include the use of grounding rods driven into the earth, which provide a direct connection to the earth’s grounding system. Grounding clamps are also used to connect electrical equipment to the grounding conductor. In residential and commercial buildings, grounding is an essential part of the electrical system and is required by electrical codes to ensure the safety of occupants and equipment.
Understanding the connection between grounding and Junction Box Wiring is important for electricians, building inspectors, and homeowners. Electricians must ensure that proper grounding techniques are followed during installation and maintenance to protect against electrical hazards. Building inspectors verify that electrical systems are properly grounded according to code requirements. Homeowners can take comfort in knowing that proper grounding in Junction Box Wiring contributes to a safe and reliable electrical system in their homes.
Inspection and maintenance
Regular inspection and maintenance are crucial aspects of Junction Box Wiring, ensuring the ongoing safety and functionality of electrical systems. Junction boxes, being central connection points for electrical circuits, require periodic checks to identify potential issues, prevent failures, and maintain optimal performance. Without proper inspection and maintenance, Junction Box Wiring can deteriorate over time, increasing the risk of electrical hazards and compromising the reliability of the electrical system.
During inspections, electricians thoroughly examine junction boxes for signs of damage, corrosion, loose connections, or overheating. They also check the condition of the wiring, insulation, and grounding connections to ensure they meet safety standards and regulations. Regular maintenance involves cleaning the junction boxes, tightening connections, and replacing any damaged components. These measures help prevent electrical faults, fires, and shocks, ensuring the safe and efficient operation of the electrical system.
Real-life examples abound, highlighting the importance of inspection and maintenance in Junction Box Wiring. In commercial buildings, regular inspections and maintenance of junction boxes help prevent disruptions to critical systems, such as lighting, HVAC, and security. In residential settings, proper maintenance of junction boxes contributes to the safety and comfort of occupants by preventing electrical issues that could pose a fire hazard or disruption to daily life. By adhering to regular inspection and maintenance schedules, potential problems can be identified and addressed promptly, minimizing the risk of accidents and ensuring the longevity of the electrical system.
Troubleshooting
Within the realm of “Junction Box Wiring”, troubleshooting emerges as a systematic and indispensable approach to identifying and resolving electrical issues, ensuring the safety, reliability, and optimal functioning of electrical systems. This process involves a meticulous examination of junction boxes, electrical connections, and components, coupled with a deep understanding of electrical principles and safety protocols.
- Identifying Potential Faults: Troubleshooting begins with recognizing the symptoms of electrical issues, such as flickering lights, tripped circuit breakers, or unusual odors. By carefully observing these signs, electricians can narrow down the potential causes and focus their efforts on specific areas of the Junction Box Wiring.
- Isolating the Problem: Once potential faults are identified, the next step is to isolate the problem by systematically testing individual circuits, connections, and components. This involves using specialized tools and techniques to determine the precise location of the issue, ensuring targeted repairs and minimizing disruption to the electrical system.
- Resolving the Issue: Upon isolating the problem, electricians can proceed with resolving the issue by repairing or replacing faulty components, tightening loose connections, or addressing any underlying electrical imbalances. This stage requires a combination of technical expertise, safety consciousness, and adherence to electrical codes.
- Testing and Verification: After resolving the issue, thorough testing and verification are crucial to ensure the effectiveness of the repairs and the overall integrity of the Junction Box Wiring. This involves testing the affected circuit or component under load to confirm its proper functioning and adherence to safety standards.
Troubleshooting plays a pivotal role in maintaining the safety and reliability of Junction Box Wiring. By promptly identifying and resolving electrical issues, electricians can prevent potential hazards, minimize downtime, and ensure the smooth operation of electrical systems. This systematic approach not only enhances the functionality of electrical installations but also contributes to the overall safety and well-being of individuals and properties.









Related Posts








