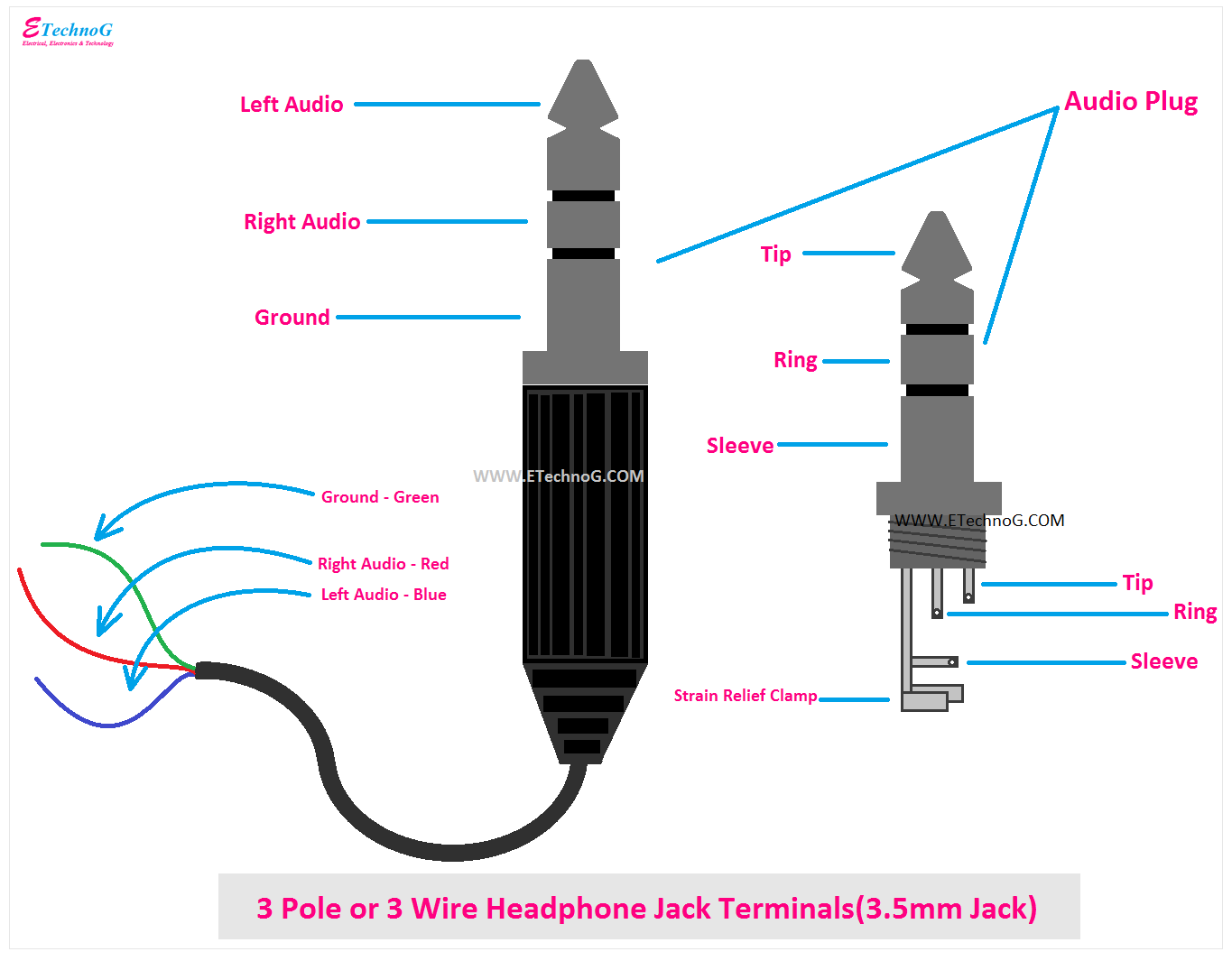
Headphone jack wiring refers to the standardized arrangement of wires and connections within an audio jack specifically designed for headphones or earphones. A common example is the 3.5mm TRS (tip, ring, sleeve) connector, where the tip carries the left audio channel, the ring carries the right audio channel, and the sleeve is the common ground.
This wiring scheme ensures compatibility between headphones and audio devices, allowing for seamless audio transmission and playback. It provides a reliable and convenient means of connecting headphones, offering benefits such as portability, ease of use, and wide industry adoption. One key historical development in this area was the standardization of the 3.5mm TRS connector in the 1960s, which became the widely accepted standard for portable audio devices.
In this article, we will delve deeper into the specifications, variations, and technical aspects of headphone jack wiring, exploring its historical evolution, ongoing developments, and the factors influencing its design. Our focus will also encompass the implications and considerations for audio quality, user experience, and the future of headphone connectivity in the consumer electronics industry.
Understanding the essential aspects of “Headphone Jack Wiring” is crucial for comprehending its design, functionality, and impact on audio connectivity. As a noun phrase, it encompasses various dimensions that shape the overall concept.
- Standardization: Ensuring compatibility between headphones and audio devices.
- Connector types: TRS, TRRS, and other variations.
- Wiring scheme: Arrangement of wires for audio channels and ground.
- Materials: Conductors and insulators used in wire construction.
- Quality: Impact on audio signal transmission and durability.
- Durability: Resistance to wear and tear, ensuring longevity.
- History: Evolution of headphone jack wiring over time.
- Future trends: Advancements and innovations in headphone connectivity.
These aspects are interconnected, with each influencing the overall performance and user experience of headphone jack wiring. For instance, standardization enables widespread compatibility, while connector types determine the physical interface and compatibility with different devices. Wiring scheme and materials impact audio quality, while durability ensures reliable performance over time. Understanding these aspects provides a comprehensive view of headphone jack wiring, its significance in the audio industry, and its evolving nature in the face of technological advancements.
Standardization
Standardization is a critical aspect of headphone jack wiring, ensuring that headphones and audio devices can communicate effectively and deliver a seamless user experience. Without standardized wiring, each manufacturer could create unique headphone jack designs, leading to incompatibility and frustration for consumers. The 3.5mm TRS connector, for instance, has become the industry standard for portable audio devices, allowing headphones from different brands to be used with a wide range of audio sources, from smartphones to laptops to portable music players.
The cause-and-effect relationship between standardization and headphone jack wiring is evident in the widespread adoption of standardized connectors. By adhering to established wiring schemes, manufacturers can guarantee that their headphones will be compatible with the vast majority of audio devices on the market. This compatibility extends not only to physical connectivity but also to audio signal transmission, ensuring that both left and right audio channels are correctly routed and that the audio quality is maintained throughout the connection.
Real-life examples of standardization in headphone jack wiring include the aforementioned 3.5mm TRS connector, as well as the newer TRRS connector that supports additional functionality such as microphone input. These standardized connectors have enabled the proliferation of headphones and earphones across various consumer electronics devices, creating a seamless and consistent audio experience for users.
Understanding the connection between standardization and headphone jack wiring is essential for audio engineers, product designers, and consumers alike. By adhering to established standards, manufacturers can ensure that their products are compatible with a wide range of devices, while consumers can have confidence that their headphones will work seamlessly with their audio sources. Furthermore, standardization fosters innovation by creating a common platform for manufacturers to build upon, leading to advancements in headphone technology and improved user experiences.
Connector types
In the realm of headphone jack wiring, connector types play a crucial role in determining the functionality and compatibility of headphones with various audio devices. TRS (tip, ring, sleeve) and TRRS (tip, ring, ring, sleeve) connectors are the most common types found in headphone jack wiring, each serving specific purposes and offering unique advantages.
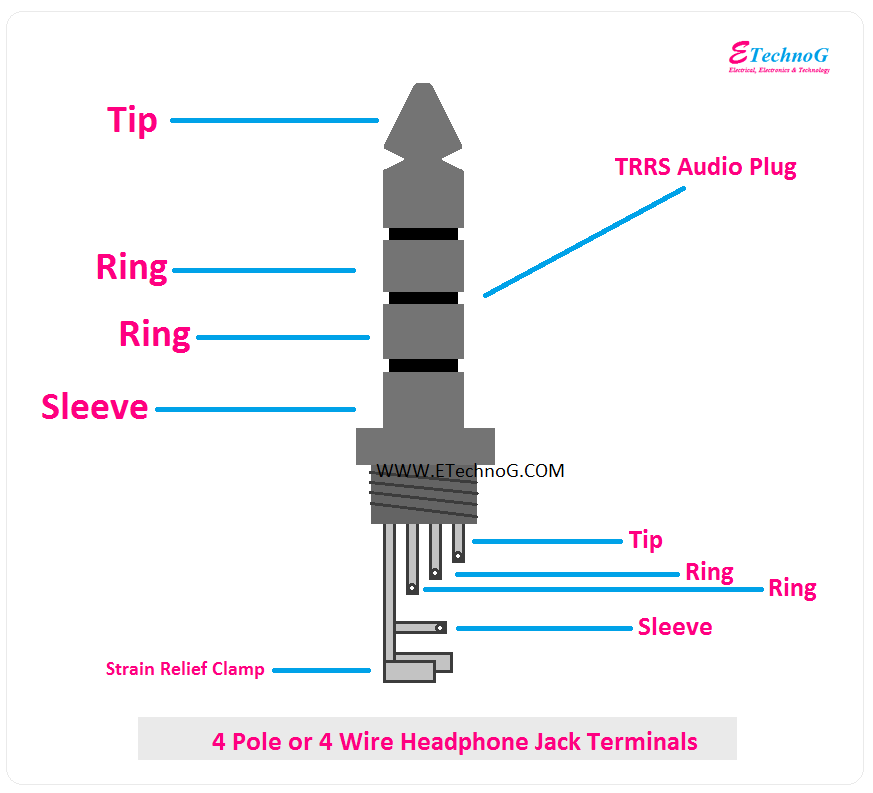
TRS connectors consist of three conductors: the tip carries the left audio channel, the ring carries the right audio channel, and the sleeve is the common ground. This type of connector is primarily used for stereo audio transmission and is commonly found in headphones, earphones, and portable music players. TRRS connectors, on the other hand, have an additional ring conductor that allows for microphone input, making them suitable for use with headsets and other devices that require both audio output and microphone input capabilities.
The relationship between connector types and headphone jack wiring is symbiotic. The design of the headphone jack must accommodate the specific connector type being used, ensuring a secure physical connection and proper signal transmission. Compatibility between headphones and audio devices is largely determined by the matching of connector types. For instance, a headphone with a TRS connector will only be able to connect to an audio device with a TRS jack, and a headset with a TRRS connector requires a TRRS jack for full functionality.
Understanding the connection between connector types and headphone jack wiring is essential for manufacturers, product designers, and consumers alike. By selecting the appropriate connector type for their intended application, manufacturers can ensure compatibility and optimal performance of their products. Consumers, on the other hand, can make informed decisions when choosing headphones or headsets that meet their specific needs and are compatible with their audio devices.
In summary, connector types are a critical component of headphone jack wiring, determining the functionality, compatibility, and user experience of headphones and headsets. TRS and TRRS connectors are the most common types, each serving specific purposes and offering unique advantages. Understanding the connection between connector types and headphone jack wiring is essential for ensuring seamless audio connectivity and optimal performance.
Wiring scheme
Wiring scheme, which refers to the specific arrangement of wires for audio channels and ground, is a fundamental aspect of headphone jack wiring. It determines how audio signals are transmitted from the audio device to the headphones, ensuring proper channel separation and grounding for optimal audio performance.
- Conductors: The wires used in headphone jack wiring are typically made of copper or aluminum, which are excellent conductors of electricity. The number of conductors depends on the type of connector being used, with TRS connectors having three conductors and TRRS connectors having four.
- Insulation: Each conductor is coated with an insulating material, such as plastic or rubber, to prevent electrical interference and ensure signal integrity.
- Grounding: The ground wire, typically represented by the sleeve of the connector, provides a reference point for the audio signal and helps to reduce noise and interference.
- Color coding: To ensure proper wiring and easy identification, the conductors are often color-coded. For example, in TRS connectors, the tip is typically red (left channel), the ring is white (right channel), and the sleeve is black (ground).
Understanding the wiring scheme of headphone jacks is essential for manufacturers, audio engineers, and anyone involved in the design, production, or repair of headphones and audio devices. Proper wiring ensures that audio signals are transmitted accurately and efficiently, resulting in optimal sound quality and a seamless listening experience.
Materials
In the realm of headphone jack wiring, the materials used in wire construction play a crucial role in ensuring signal integrity, durability, and overall audio quality. Conductors, typically made of copper or aluminum, are responsible for carrying the audio signal from the audio device to the headphones. Insulators, made of materials such as plastic or rubber, surround each conductor to prevent electrical interference and maintain signal purity.
The choice of materials for conductors and insulators has a direct impact on the performance of headphone jack wiring. High-quality conductors, such as oxygen-free copper, minimize electrical resistance and ensure efficient signal transmission, resulting in better sound quality. Similarly, high-quality insulators provide excellent dielectric properties, preventing signal loss and distortion. The thickness and geometry of the conductors and insulators also affect the overall capacitance and inductance of the cable, which can influence the frequency response and sound characteristics of the headphones.
Real-life examples of the importance of materials in headphone jack wiring can be found in the use of silver-plated copper conductors in high-end headphones. Silver plating reduces oxidation and further improves conductivity, resulting in enhanced audio clarity and detail. Another example is the use of braided conductors, which reduces cable resistance and improves durability, making them ideal for professional studio applications.
Understanding the connection between materials and headphone jack wiring is essential for manufacturers, audio engineers, and anyone involved in the design or repair of headphones and audio equipment. By selecting the appropriate materials for conductors and insulators, manufacturers can optimize the performance and longevity of their products, ensuring a superior listening experience for users.
Quality
In the realm of headphone jack wiring, quality plays a critical role in ensuring the faithful transmission of audio signals and the long-lasting performance of headphones. The quality of the materials used, the precision of the manufacturing process, and the overall design of the wiring all contribute to the overall quality of the headphone jack wiring.
High-quality headphone jack wiring minimizes signal loss and distortion, resulting in a more accurate and enjoyable listening experience. The use of high-purity conductors, such as oxygen-free copper, reduces electrical resistance and ensures efficient signal transmission. Proper insulation materials, such as polyethylene or Teflon, provide excellent dielectric properties, preventing signal leakage and maintaining signal integrity.
Real-life examples of the impact of quality on headphone jack wiring can be found in the noticeable difference in sound quality between headphones with low-quality and high-quality wiring. Low-quality wiring can introduce noise, distortion, and other artifacts into the audio signal, diminishing the listening experience. In contrast, high-quality wiring preserves the purity of the audio signal, allowing the listener to fully appreciate the nuances and details of the music.
Understanding the connection between quality and headphone jack wiring is essential for manufacturers, audio engineers, and consumers alike. By selecting high-quality materials and employing precise manufacturing techniques, manufacturers can produce headphone jack wiring that delivers superior audio performance and durability. Consumers, on the other hand, can make informed decisions when choosing headphones, knowing that high-quality wiring ensures a more enjoyable and immersive listening experience.
Durability
In the realm of headphone jack wiring, durability plays a critical role in ensuring the longevity and reliability of headphones. Headphone jack wiring is subjected to various forms of wear and tear during everyday use, such as bending, twisting, and exposure to sweat and moisture. Durable headphone jack wiring can withstand these rigors without compromising its functionality or audio quality, extending the lifespan of the headphones.
The durability of headphone jack wiring is largely determined by the materials used and the construction methods employed. High-quality materials, such as robust polymers and reinforced conductors, can withstand repeated bending and flexing without breaking or losing their integrity. Proper strain relief measures, such as reinforced connectors and flexible cable jackets, protect the wiring from damage at the points where it is most vulnerable to stress. Real-life examples of durable headphone jack wiring can be found in heavy-duty headphones designed for professional use, such as studio monitoring headphones or DJ headphones. These headphones often feature rugged construction, reinforced cables, and durable connectors to withstand the demanding conditions of professional environments.
Understanding the connection between durability and headphone jack wiring is essential for manufacturers, consumers, and anyone involved in the design, production, or repair of headphones. By incorporating durable materials and construction techniques into headphone jack wiring, manufacturers can create headphones that can withstand the rigors of everyday use and provide a long-lasting listening experience. Consumers, on the other hand, can make informed decisions when choosing headphones, knowing that durable wiring ensures the longevity and reliability of their investment.
History
The history of headphone jack wiring is closely intertwined with the evolution of headphones themselves. The first headphones, invented in the late 19th century, were simple electroacoustic transducers that converted electrical signals into sound waves. These early headphones used a variety of different connectors, including simple two-conductor plugs and more complex multi-pin connectors. As headphones became more popular and sophisticated, the need for a standardized connector became apparent.
In the 1950s, the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) developed the 3.5mm TRS (tip, ring, sleeve) connector as a standard for headphone jacks. This connector quickly became the de facto standard for portable audio devices, and it remains the most common type of headphone jack in use today. The 3.5mm TRS connector has three conductors: the tip carries the left audio channel, the ring carries the right audio channel, and the sleeve is the common ground. This simple but effective design has ensured the compatibility of headphones with a wide range of audio devices for over half a century.
In recent years, the 3.5mm TRS connector has been supplemented by other types of connectors, such as the 2.5mm TRRS (tip, ring, ring, sleeve) connector and the USB-C connector. These newer connectors offer additional features, such as support for microphone input and digital audio transmission. However, the 3.5mm TRS connector remains the most widely used type of headphone jack, and it is likely to continue to be used for many years to come.
Understanding the history of headphone jack wiring is important for several reasons. First, it helps us to appreciate the evolution of headphone technology and the challenges that engineers have faced in developing a standardized connector. Second, it helps us to understand the different types of headphone jacks that are available and the compatibility issues that can arise when using different types of headphones with different types of audio devices. Finally, it helps us to make informed decisions about the type of headphone jack that is best for our needs.
Future trends
As the realm of personal audio continues to evolve, headphone jack wiring stands at the cusp of significant advancements and innovations. These emerging trends promise to reshape the way we connect and interact with our headphones, enhancing the overall listening experience and pushing the boundaries of audio technology.
- Wireless Connectivity: Bluetooth and other wireless technologies have revolutionized headphone connectivity, eliminating the need for physical wires. This freedom of movement and convenience is transforming the headphone experience, making it more portable and versatile.
- Active Noise Cancellation: Advanced noise cancellation algorithms and specialized hardware are enabling headphones to effectively block out external noise, creating an immersive and distraction-free listening environment. This innovation is particularly valuable in noisy environments, such as during commutes or in public spaces.
- High-Resolution Audio: The proliferation of high-resolution audio formats is driving the demand for headphones capable of reproducing the full spectrum of sound with exceptional clarity and detail. Future headphone jack wiring will need to support these higher bandwidth requirements to deliver the best possible audio quality.
- Smart Features: Headphones are becoming increasingly intelligent, incorporating features such as voice control, touch controls, and fitness tracking. These smart features enhance the user experience by providing greater control and convenience, making headphones more than just audio playback devices.
These future trends in headphone connectivity will undoubtedly have a profound impact on headphone jack wiring. As wireless connectivity becomes more prevalent, headphone jacks may become less common in portable devices. However, the need for high-quality wired connections will remain in professional audio applications and for enthusiasts who demand the best possible sound quality. The continued evolution of headphone jack wiring will ensure that headphones remain an essential part of our audio experience, offering a seamless and enjoyable connection to our music, movies, and other audio content.








Related Posts








