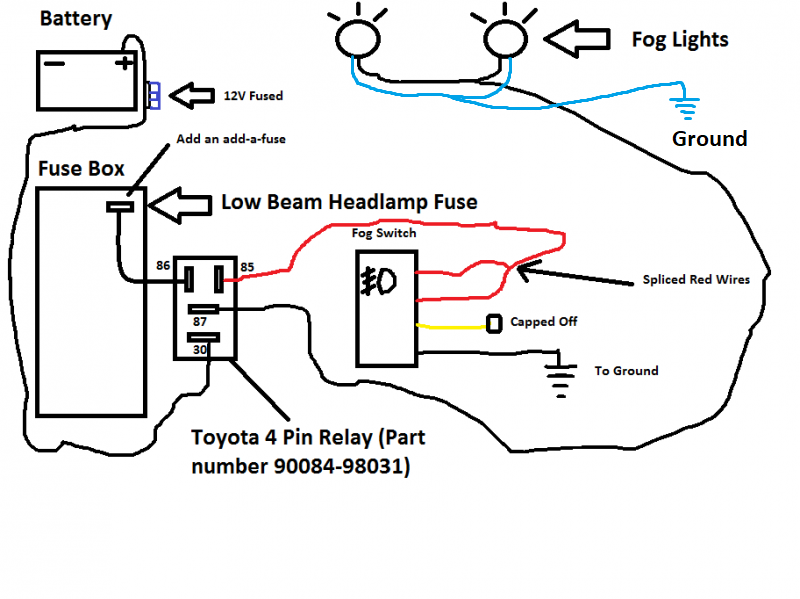
Fog Light Relay Wiring is the electrical circuitry that powers fog lamps, using a relay to increase the amount of current that can be supplied to the lamps. For instance, in automotive applications, the relay allows for higher wattage fog lamps to be used without overloading the vehicle’s electrical system.
This wiring arrangement is important as it enables fog lamps to operate at their optimal brightness, providing improved visibility and safety in foggy conditions. Relay wiring also reduces the risk of electrical fires by preventing excessive current draw through the vehicle’s wiring.
A key historical development in fog light relay wiring was the advent of solid-state relays in the 1970s. These electronic relays offered improved reliability and faster switching speeds, enhancing the overall performance of fog lamp systems.
In the following article, we will delve into the technical aspects of fog light relay wiring, discussing circuit design, component selection, and installation techniques to ensure optimal performance and safety.
Fog Light Relay Wiring plays an essential role in powering fog lamps, enhancing visibility and safety in challenging weather conditions. To fully grasp its significance, it is vital to examine the following key aspects:
- Circuit Design
- Relay Selection
- Wiring Gauge
- Fuse Protection
- Switch Compatibility
- Grounding
- Routing and Protection
- Maintenance and Inspection
These aspects are interconnected, ensuring that fog light relay wiring functions reliably and safely. Circuit design determines the proper flow of current, while relay selection ensures that sufficient power is supplied to the fog lamps. Wiring gauge, fuse protection, and proper grounding protect the electrical system from overloads and shorts. Switch compatibility allows for seamless integration with the vehicle’s controls, and routing and protection safeguard the wiring from damage and corrosion. Regular maintenance and inspection ensure optimal performance and longevity of the fog light relay wiring.
Circuit Design
Circuit Design is a fundamental aspect of Fog Light Relay Wiring, determining the proper flow of current to power the fog lamps. Careful consideration of circuit components and their arrangement is essential for optimal performance and safety.
-
Power Source
The circuit must draw power from the vehicle’s electrical system, typically through a fused connection to the battery or an ignition-switched source. -
Relay Control
A switching mechanism, often a relay, is used to control the flow of current to the fog lamps. This allows for high-power fog lamps to be operated without overloading the vehicle’s wiring. -
Lamp Wiring
The circuit must provide a path for current to reach the fog lamps. Proper wire gauge and connections are crucial to minimize voltage drop and ensure reliable operation. -
Grounding
A solid ground connection is essential for completing the electrical circuit and preventing electrical faults. The circuit design must incorporate a reliable grounding point for the fog light system.
By carefully designing the circuit, considering these components and their interactions, it is possible to ensure that the Fog Light Relay Wiring system operates safely and effectively, providing enhanced visibility in inclement weather conditions.
Relay Selection
Relay Selection is a critical aspect of Fog Light Relay Wiring, directly impacting the system’s performance, reliability, and safety. Selecting an appropriate relay involves careful consideration of several key parameters and their implications.
-
Current Capacity
The relay must be able to handle the current draw of the fog lamps without overheating or failing. This requires selecting a relay with a current rating that exceeds the combined amperage of the fog lamps. -
Coil Voltage
The relay’s coil voltage determines the type of power source it can use. Common coil voltages include 12V (for automotive applications) and 24V (for heavy-duty vehicles). It is crucial to match the relay’s coil voltage to the available power source. -
Contact Configuration
The relay’s contact configuration refers to the arrangement and number of its contacts. For fog light applications, a single-pole, single-throw (SPST) relay is typically sufficient. -
Mounting Type
Relays come in various mounting types, such as blade-type, panel-mount, and DIN-rail mount. The mounting type should be compatible with the available space and installation requirements.
By carefully considering these factors, it is possible to select a relay that meets the specific requirements of the Fog Light Relay Wiring system, ensuring reliable operation and enhanced visibility in challenging weather conditions.
Wiring Gauge
Wiring Gauge is a critical aspect of Fog Light Relay Wiring as it determines the thickness and current-carrying capacity of the wires used in the circuit. The appropriate gauge ensures that the wires can safely handle the electrical load while minimizing voltage drop and power loss.
-
Conductor Material
Copper is the most common conductor material due to its excellent conductivity and durability. However, aluminum can also be used, offering a lighter and more cost-effective option. -
Wire Size
The wire size is inversely proportional to its resistance. Thicker wires have lower resistance and can carry more current without excessive voltage drop. -
Insulation Rating
The wire insulation must be rated for the voltage and temperature range of the circuit. It protects the conductors from short circuits and prevents current leakage. -
Stranding
Stranded wires, composed of multiple smaller wires twisted together, offer greater flexibility and resistance to fatigue compared to solid wires.
By carefully selecting the appropriate wiring gauge, considering factors such as conductor material, wire size, insulation rating, and stranding, it is possible to ensure that the Fog Light Relay Wiring system operates safely and effectively, providing enhanced visibility and safety in inclement weather conditions.
Fuse Protection
Fuse protection is a critical component of fog light relay wiring, safeguarding the electrical system from potential damage caused by overcurrent conditions. A fuse is a sacrificial device designed to interrupt the flow of current when it exceeds a predetermined safe level. This protects the wiring, relay, and fog lamps from overheating and potential fire hazards.
In fog light relay wiring, the fuse is typically placed in line with the power supply to the relay. When an excessive current draw occurs, such as a short circuit or a fault in the fog lamp circuit, the fuse “blows,” severing the connection and preventing further current flow. This immediate interruption prevents the overcurrent from damaging the wiring or components.
Real-life examples of fuse protection in fog light relay wiring include:
- In-line fuse holders: These are commonly used to hold and protect the fuse in the power supply line to the relay.
- Integrated fuses: Some relays have built-in fuses, providing a compact and convenient solution for fuse protection.
- Fuse panels: In complex fog light relay wiring systems, a fuse panel may be used to house multiple fuses, providing centralized protection for various circuits.
Understanding the connection between fuse protection and fog light relay wiring is crucial for ensuring the safe and reliable operation of the fog lighting system. By incorporating appropriate fuse protection measures, it is possible to prevent electrical faults, minimize the risk of damage, and enhance the overall effectiveness of the fog light relay wiring system.
Switch Compatibility
Switch compatibility plays a critical role in fog light relay wiring, ensuring seamless integration between the control switch and the relay. The compatibility between the two components determines the ability to activate and deactivate the fog lamps reliably and efficiently.
When selecting a switch for fog light relay wiring, several factors must be considered. Firstly, the switch must be rated to handle the electrical load of the fog lamps. Using a switch with an insufficient current rating can lead to overheating, damage to the switch, or even electrical fires. Secondly, the switch must be compatible with the type of relay being used. Different relays have different activation mechanisms, such as momentary or latching, and the switch must be able to provide the appropriate signal.
Real-life examples of switch compatibility in fog light relay wiring include:
- Rocker switches: These switches are commonly used in automotive applications and are compatible with a wide range of relays.
- Push-button switches: These switches are often used in custom fog light installations and require relays with momentary activation.
- Toggle switches: Toggle switches are another option for controlling fog lights and are compatible with latching relays.
Understanding the connection between switch compatibility and fog light relay wiring is crucial for ensuring the proper functioning of the fog light system. By selecting a compatible switch and relay, users can achieve reliable control over their fog lamps, enhancing visibility and safety in low-light conditions.
Grounding
Grounding is a crucial aspect of Fog Light Relay Wiring, ensuring a complete electrical circuit and preventing potential electrical faults. It involves establishing a low-resistance path between the negative terminal of the battery and various components of the fog light system, including the relay, fog lamps, and switch.
-
Chassis Ground:
The chassis of the vehicle often serves as the primary grounding point for the fog light relay wiring. A solid connection between the negative terminal of the battery and the chassis ensures a stable ground reference for the entire system.
-
Dedicated Ground Wire:
In some cases, a dedicated ground wire is run from the negative terminal of the battery to the fog light relay and/or fog lamps. This dedicated ground wire provides a more direct and reliable grounding path, minimizing the risk of voltage drop and ensuring optimal performance.
-
Ground Loops:
Ground loops occur when multiple ground connections create unwanted current paths, leading to electrical interference or malfunction. Proper grounding techniques, such as using a single grounding point and avoiding parallel ground paths, help prevent ground loops.
-
Electrical Safety:
Grounding plays a vital role in electrical safety by providing a safe path for excess current to flow in the event of a fault. Without proper grounding, electrical faults can lead to dangerous situations, such as electrical shocks, component damage, or even fires.
By ensuring proper grounding in Fog Light Relay Wiring, the electrical system operates safely and reliably, enhancing the effectiveness and longevity of the fog lighting system. Understanding the principles and components involved in grounding is essential for proper installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting of fog light relay wiring.
Routing and Protection
In the context of “Fog Light Relay Wiring”, “Routing and Protection” play a pivotal role in ensuring the safe, reliable, and effective operation of the fog lighting system. It encompasses various facets related to the physical placement, securing, and shielding of wiring components to optimize performance, prevent damage, and enhance longevity.
-
Wire Routing:
Careful planning and execution of wire routing are crucial to prevent interference with other electrical systems, mechanical components, and moving parts. Proper routing minimizes the risk of chafing, pinching, or damage due to vibration or exposure to heat and moisture.
-
Conduit and Sheathing:
Conduits and sheathing provide additional protection for wires against abrasion, crushing, and environmental hazards. They come in various materials, such as flexible plastic or corrugated metal, and can be used to bundle and protect multiple wires or critical sections.
-
Wire Connectors:
Reliable wire connectors are essential for secure and efficient electrical connections. Soldered, crimped, or heat-shrink connectors ensure proper contact and prevent corrosion or loose connections that could lead to voltage drop or system failure.
-
Fuses and Circuit Breakers:
Fuses and circuit breakers act as protective devices to safeguard the electrical system from overcurrent conditions. They interrupt the current flow in the event of a short circuit or excessive load, preventing damage to wiring, components, or even fire hazards.
By implementing proper “Routing and Protection” measures, “Fog Light Relay Wiring” systems can withstand the rigors of automotive environments, provide reliable illumination in adverse weather conditions, and contribute to overall vehicle safety and performance.
Maintenance and Inspection
Within the context of “Fog Light Relay Wiring”, “Maintenance and Inspection” play a crucial role in ensuring the sustained functionality, reliability, and safety of the fog lighting system. Regular maintenance and thorough inspections help identify potential issues, address minor problems before they escalate, and extend the lifespan of components. Here are some key aspects to consider:
-
Bulb Inspection:
Regularly inspect the fog light bulbs for any signs of damage, such as cracks, discoloration, or filament breakage. Replace damaged bulbs promptly to maintain optimal illumination. -
Relay Testing:
Periodically test the relay to ensure its proper operation. Use a multimeter to check for continuity and proper switching function. Replace the relay if it fails any of the tests. -
Wiring Inspection:
Inspect the wiring for any signs of damage, fraying, or corrosion, especially in areas prone to moisture or vibration. Repair or replace damaged wires to prevent electrical faults. -
Fuse Replacement:
Check the fuse in the fog light relay wiring and replace it if it has blown. A blown fuse indicates an overcurrent condition or a fault in the system, and replacing it restores the circuit’s protection.
By implementing a proactive approach to “Maintenance and Inspection”, owners of vehicles equipped with “Fog Light Relay Wiring” can enhance the safety and effectiveness of their fog lighting systems, ensuring reliable operation and improved visibility during adverse weather conditions.








Related Posts








