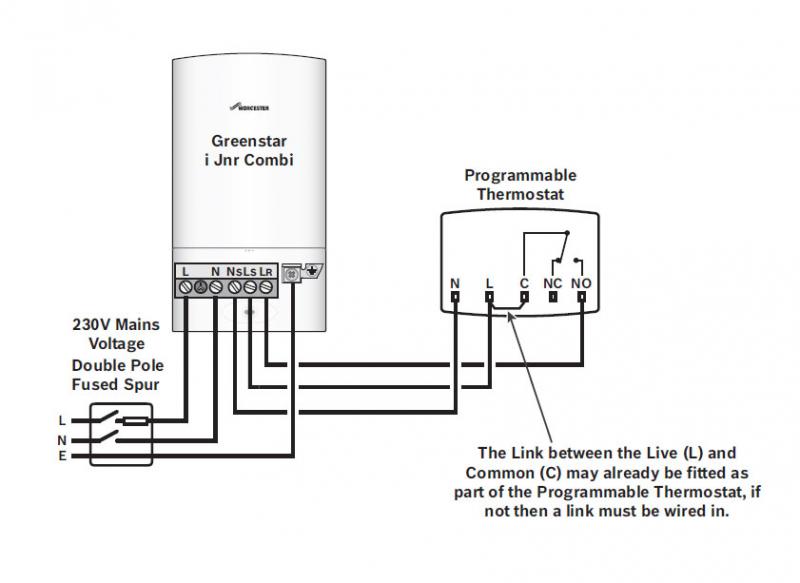
Boiler Thermostat Wiring refers to the electrical connections between a boiler and its thermostat, enabling the thermostat to control the boiler’s operation. For instance, in a residential setting, a thermostat’s wiring can regulate a gas-fired boiler to maintain a desired room temperature.
This wiring is crucial for ensuring the boiler’s efficiency and safety. Benefits include precise temperature control, reduced energy consumption, and improved indoor comfort. One important historical development is the introduction of wireless thermostats, eliminating the need for physical wiring and offering greater flexibility.
This article delves deeper into boiler thermostat wiring, its intricacies, and its impact on efficient home heating systems.
Boiler Thermostat Wiring plays a crucial role in ensuring the efficient operation of boiler systems, encompassing various essential aspects:
- Compatibility: Matching the thermostat’s specifications with the boiler’s capabilities.
- Safety: Adhering to electrical codes and safety regulations for proper installation.
- Efficiency: Optimizing energy consumption through precise temperature control.
- Convenience: Enabling remote or programmable control for user comfort.
- Compatibility: Ensuring compatibility between the thermostat and the boiler’s voltage and current requirements.
- Compatibility: Selecting the correct wire gauge and type for the specific application.
- Compatibility: Identifying the appropriate thermostat terminals for wiring connections.
- Testing: Verifying the accuracy and functionality of the wiring before system operation.
- Maintenance: Inspecting and servicing the wiring periodically to ensure longevity.
- Troubleshooting: Diagnosing and resolving any issues related to the wiring.
These aspects are interconnected, ensuring the safe, efficient, and convenient operation of boiler thermostat wiring systems. Understanding and addressing these aspects is crucial for the optimal performance of boiler heating systems.
Compatibility
Compatibility between the thermostat and the boiler is the cornerstone of effective boiler thermostat wiring. Mismatched components can lead to system malfunctions, safety hazards, and suboptimal performance.
-
Voltage and Current Requirements
The thermostat’s voltage and current output must align with the boiler’s input requirements. Mismatches can damage the thermostat or the boiler.
-
Control Type
The thermostat’s control type (e.g., on/off, modulating) must be compatible with the boiler’s operation. Incompatible control types can result in inefficient or unsafe system operation.
-
Wiring Configuration
The thermostat’s wiring configuration must match the boiler’s terminal layout. Incorrect wiring can lead to malfunctions or even electrical hazards.
-
Communication Protocol
In the case of smart or wireless thermostats, compatibility in communication protocols is essential for proper communication and control.
Ensuring compatibility between the thermostat and the boiler is crucial for the safety, efficiency, and reliability of the boiler thermostat wiring system. Careful consideration of these factors during system design and installation is essential for optimal performance.
Safety
Electrical safety is paramount in boiler thermostat wiring to prevent accidents, protect the equipment, and ensure reliable operation. Adhering to electrical codes and safety regulations during installation is a non-negotiable aspect of boiler thermostat wiring.
Electrical codes and safety regulations provide guidelines for proper wiring practices, component selection, and installation techniques. These regulations are established based on years of experience and research to minimize electrical hazards, such as short circuits, overloads, and electrical fires. By following these regulations, installers can ensure that the wiring is safe and meets the required standards.
Real-life examples of safety regulations in boiler thermostat wiring include:
- Using proper wire gauge and insulation for the specific current and voltage requirements.
- Securing all electrical connections with approved connectors and avoiding loose or exposed wires.
- Installing overcurrent protection devices (e.g., fuses or circuit breakers) to prevent damage from electrical overloads.
- Grounding the thermostat and boiler to provide a safe path for any stray electrical currents.
Understanding the connection between safety regulations and boiler thermostat wiring enables installers and homeowners to make informed decisions about the installation and maintenance of the system. By adhering to these regulations, they can help prevent electrical hazards, ensure the longevity of the equipment, and maintain a safe and comfortable indoor environment.
Efficiency
In the context of boiler thermostat wiring, efficiency is paramount, and precise temperature control plays a pivotal role in optimizing energy consumption. By leveraging advanced control algorithms and responsive sensors, modern thermostats can minimize energy waste and enhance overall system efficiency. Here are key aspects to consider:
-
Programmable Schedules
Programmable thermostats allow users to set heating schedules that align with their daily routines. This ensures that the boiler operates only when necessary, reducing energy consumption during unoccupied periods.
-
Temperature Setback
Temperature setback is a feature that automatically lowers the thermostat’s setpoint during periods of inactivity, such as sleep or work hours. This simple adjustment can yield significant energy savings.
-
Smart Sensors
Smart thermostats utilize sensors to detect occupancy and adjust temperatures accordingly. When no one is home, the thermostat can automatically switch to an energy-saving mode, further reducing energy consumption.
-
Zoning Control
Zoning control systems divide a building into separate heating zones, allowing for precise temperature control in each zone. This prevents unnecessary heating in unoccupied or less frequently used areas, leading to increased efficiency.
By incorporating these elements into boiler thermostat wiring, homeowners can harness the power of precise temperature control to optimize energy consumption, reduce their carbon footprint, and create a more comfortable and energy-efficient living environment.
Convenience
In the realm of boiler thermostat wiring, convenience has become a cornerstone, empowering users with remote and programmable control over their heating systems. This user-centric approach not only enhances comfort but also optimizes energy consumption.
-
Remote Access
Smart thermostats offer remote access via smartphones or tablets, allowing users to adjust temperatures, set schedules, and monitor energy usage from anywhere with an internet connection.
-
Programmable Schedules
Programmable thermostats enable users to create heating schedules that align with their daily routines, ensuring optimal comfort levels while minimizing energy waste.
-
Geolocation
Advanced thermostats leverage geolocation technology to automatically adjust temperatures based on the user’s location, providing energy savings when the home is unoccupied.
-
Voice Control
Integration with voice assistants such as Amazon Alexa or Google Home allows users to control their thermostats using simple voice commands, adding a layer of convenience and accessibility.
These facets of convenience, made possible through advancements in boiler thermostat wiring, translate into tangible benefits for users. Remote access empowers them to manage their heating systems from afar, ensuring comfort upon returning home or adjusting temperatures while away. Programmable schedules optimize energy consumption, reducing heating costs without compromising comfort. By embracing convenience in boiler thermostat wiring, homeowners can elevate their living experience and contribute to a more sustainable lifestyle.
Compatibility
In the context of boiler thermostat wiring, ensuring compatibility between the thermostat and the boiler’s voltage and current requirements is paramount for the safe and effective operation of the heating system. Mismatched components can lead to system malfunctions, safety hazards, and suboptimal performance.
-
Voltage Compatibility
The thermostat’s voltage output must match the boiler’s input voltage requirement. Incorrect voltage can damage the thermostat or the boiler.
-
Current Compatibility
The thermostat’s current output must be sufficient to handle the boiler’s current draw. Insufficient current can cause the thermostat to malfunction or fail.
-
Wiring Configuration
The thermostat’s wiring configuration must match the boiler’s terminal layout. Incorrect wiring can lead to malfunctions or even electrical hazards.
-
Fuse or Circuit Breaker Protection
The circuit supplying power to the thermostat and boiler should be protected by a fuse or circuit breaker of the appropriate amperage. This protection helps prevent electrical overloads and potential fires.
Ensuring compatibility between the thermostat and the boiler’s voltage and current requirements is a crucial aspect of boiler thermostat wiring. By carefully considering these factors during system design and installation, installers can help prevent electrical hazards, ensure the longevity of the equipment, and maintain a safe and comfortable indoor environment.
Compatibility
Within the context of “Boiler Thermostat Wiring,” selecting the correct wire gauge and type is crucial for ensuring safe, efficient, and reliable operation. Mismatched components can lead to system malfunctions, safety hazards, and suboptimal performance.
-
Wire Gauge
The wire gauge, denoted by AWG (American Wire Gauge), determines the thickness and current-carrying capacity of the wire. Using an undersized wire can lead to overheating and potential fire hazards, while an oversized wire may be unnecessary and more expensive.
-
Wire Type
Different types of wire, such as solid core or stranded, have varying degrees of flexibility and durability. Choosing the appropriate wire type ensures proper connections and longevity in specific installation environments.
-
Insulation Type
The insulation protects the wire from electrical shorts and prevents energy loss. Selecting the correct insulation type, such as PVC or Teflon, ensures the wire’s suitability for the operating temperature and environment.
-
Length
The wire length should be carefully considered to minimize voltage drop and ensure adequate signal transmission. Using excessively long wires can lead to signal loss and reduced efficiency.
By carefully considering these factors, installers can ensure that the wire gauge and type are compatible with the specific application, maximizing the safety, efficiency, and lifespan of the “Boiler Thermostat Wiring” system.
Compatibility
In the realm of “Boiler Thermostat Wiring,” compatibility plays a pivotal role, and identifying the appropriate thermostat terminals for wiring connections is a crucial aspect. Mismatched connections can lead to system malfunctions, safety hazards, and suboptimal performance.
Each terminal on a thermostat serves a specific function, such as providing power, controlling heating or cooling systems, or connecting to sensors. Correctly identifying and connecting these terminals to their corresponding counterparts on the boiler is essential for proper operation. For instance, reversing the connections for heating and cooling terminals can result in incorrect temperature regulation, compromising comfort and energy efficiency.
Practical applications of this understanding include preventing potential electrical hazards. Incorrectly connecting terminals can lead to short circuits, overheating, and even fires. Proper identification and connection ensure that the system operates safely and efficiently. Additionally, accurate wiring connections optimize energy consumption, as the thermostat can effectively manage the boiler’s operation based on the intended temperature settings.
In summary, understanding the need for compatibility and identifying the appropriate thermostat terminals for wiring connections are key to successful “Boiler Thermostat Wiring.” This understanding not only ensures the safety and efficiency of the system but also contributes to a comfortable and energy-conscious indoor environment.
Testing
In the context of “Boiler Thermostat Wiring,” testing is a critical component that ensures the accuracy and functionality of the entire system before it becomes operational. This process involves meticulous verification of each wire connection to guarantee proper signal transmission, power supply, and control functionality.
Testing is not merely an additional step; it is an essential safeguard against potential hazards and system failures. Without thorough testing, loose connections, incorrect polarity, or misidentified terminals can lead to malfunctions, safety issues, and suboptimal performance of the boiler thermostat wiring. By proactively identifying and rectifying any discrepancies, testing helps prevent electrical shorts, system breakdowns, and costly repairs.
Real-life examples of testing in “Boiler Thermostat Wiring” include using a multimeter to measure voltage and continuity at various points in the circuit, inspecting wire connections for tightness and proper insulation, and simulating thermostat signals to verify the boiler’s response. These tests ensure that the wiring is not only correctly installed but also capable of handling the electrical load and transmitting control signals accurately.
The practical applications of this understanding are far-reaching. Proper testing not only ensures the safe and efficient operation of the boiler thermostat wiring but also contributes to the overall reliability and longevity of the heating system. It prevents costly breakdowns, reduces the risk of electrical hazards, and enhances the comfort and peace of mind of homeowners who rely on their boilers for warmth and hot water.
In summary, “Testing: Verifying the accuracy and functionality of the wiring before system operation” is an indispensable aspect of “Boiler Thermostat Wiring.” It is a crucial step that safeguards against potential hazards, optimizes system performance, and contributes to the overall reliability and longevity of the heating system.
Maintenance
Within the realm of “Boiler Thermostat Wiring,” “Maintenance: Inspecting and servicing the wiring periodically to ensure longevity” stands as a crucial aspect, safeguarding the system’s performance and extending its lifespan. Regular maintenance involves a comprehensive review of wire connections, terminals, and other components to identify and address potential issues before they escalate into costly repairs or system failures.
-
Connection Tightness
Loose wire connections are a common source of problems in “Boiler Thermostat Wiring.” Periodic inspection and tightening of all connections, including those at the thermostat, boiler, and any junction boxes, ensures optimal signal transmission and prevents overheating due to poor contact.
-
Terminal Condition
Over time, terminals can become corroded or damaged, leading to intermittent connections or complete failure. Regular inspection and cleaning of terminals, applying dielectric grease to prevent corrosion, helps maintain reliable electrical contact.
-
Wire Insulation
Damaged or frayed wire insulation can create electrical hazards and disrupt signal transmission. Inspecting the wiring for any signs of damage and replacing affected wires is essential to ensure safety and system integrity.
-
Environmental Factors
“Boiler Thermostat Wiring” is often exposed to harsh environmental conditions, such as extreme temperatures, moisture, or rodents. Regular inspection allows for the identification of any environmental stressors and the implementation of protective measures, such as conduit or wire insulation upgrades, to mitigate their impact.
By adhering to a regular maintenance schedule, homeowners and technicians can proactively address potential issues with “Boiler Thermostat Wiring,” extending its lifespan, preventing costly breakdowns, and ensuring the reliable and efficient operation of their heating system.
Troubleshooting
Within the realm of “Boiler Thermostat Wiring,” troubleshooting plays a pivotal role in maintaining the system’s functionality and ensuring the comfort and safety of its users. Troubleshooting involves identifying and resolving any issues related to the wiring, ranging from loose connections to faulty components.
Without effective troubleshooting, minor issues can escalate into major problems, leading to system failures, safety hazards, and costly repairs. It is a crucial component of “Boiler Thermostat Wiring,” as it enables technicians and homeowners to diagnose and rectify problems quickly and efficiently, minimizing downtime and maximizing the system’s lifespan.
Real-life examples of troubleshooting in “Boiler Thermostat Wiring” include situations where the boiler fails to respond to thermostat signals, erratic temperature fluctuations occur, or the system experiences intermittent power loss. By systematically checking wire connections, testing components, and analyzing system behavior, technicians can pinpoint the root cause of the issue and implement appropriate solutions.
The practical applications of troubleshooting in “Boiler Thermostat Wiring” are far-reaching. It helps prevent catastrophic system failures by identifying and resolving issues before they become more severe. It also enhances the overall efficiency and performance of the heating system, ensuring optimal comfort levels and energy savings. Furthermore, regular troubleshooting can extend the lifespan of the wiring and its components, reducing the need for costly replacements.
In summary, “Troubleshooting: Diagnosing and resolving any issues related to the wiring” is an essential aspect of “Boiler Thermostat Wiring,” safeguarding the system’s reliability, efficiency, and longevity. By understanding the importance of troubleshooting and its practical applications, technicians and homeowners can ensure the continued smooth operation of their boiler thermostat wiring systems.








Related Posts








