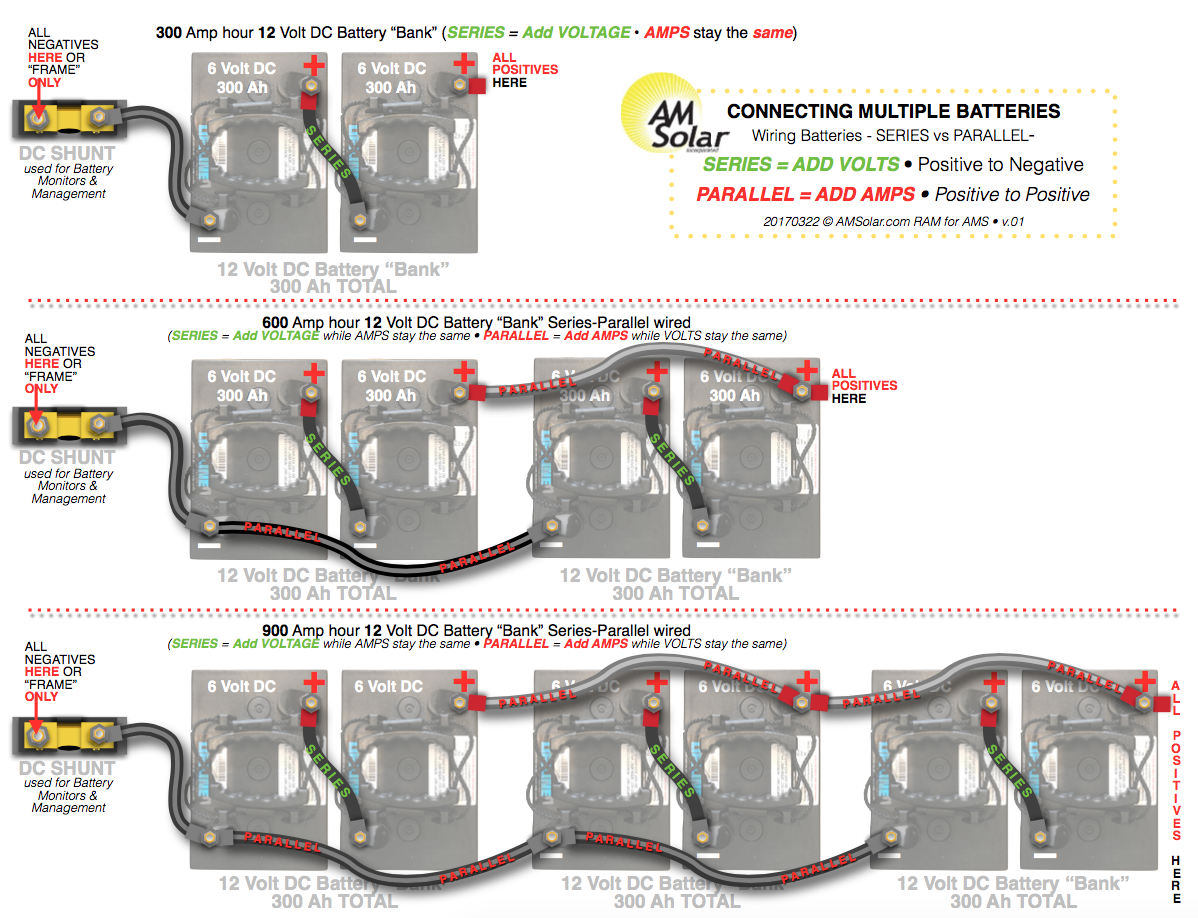
Battery Wiring Parallel or Series, a crucial aspect of battery management, involves connecting batteries in either parallel or series configurations to achieve specific electrical characteristics. In parallel wiring, batteries are connected side-by-side, with their positive terminals connected together and their negative terminals connected together. This configuration increases the overall current capacity and maintains the voltage of the individual batteries.
Conversely, in series wiring, batteries are connected end-to-end, with the positive terminal of one battery connected to the negative terminal of the next. This configuration increases the overall voltage while maintaining the current capacity of the individual batteries.
The choice between parallel or series wiring depends on the desired electrical output. Parallel wiring is suitable for applications requiring higher current, such as starting a car engine, while series wiring is appropriate for applications requiring higher voltage, such as powering high-intensity lighting.
Understanding the essential aspects of “Battery Wiring Parallel or Series” is crucial for optimizing battery performance and ensuring safe and efficient electrical systems. These aspects encompass both the technical and practical considerations involved in connecting batteries in various configurations.
- Parallel Wiring:
- Series Wiring:
- Voltage:
- Current:
- Capacity:
- Efficiency:
- Safety:
- Applications:
- Maintenance:
- Cost:
Parallel wiring increases current capacity while maintaining voltage, while series wiring increases voltage while maintaining current capacity. Understanding voltage, current, and capacity is essential for selecting the appropriate configuration and ensuring battery safety. Efficiency, safety, and cost are also important considerations, varying depending on the specific application and battery type. Regular maintenance is crucial to extend battery life and prevent potential hazards.








Related Posts








