Basic Wiring For Light Switch is fundamental to electrical systems, allowing users to control lighting circuits manually. This involves connecting a single-pole switch between a power source, the light fixture, and a neutral wire, forming a closed circuit when the switch is turned on, completing the electrical path and illuminating the light.
For example, in a living room, a light switch permits household members to brighten or dim the ambiance by activating the lights as needed. Its simplicity and reliability make it an essential component of electrical installations.
Basic Wiring For Light Switch serves as a critical aspect of safeguarding against electrical hazards and maintaining efficient energy consumption. Historically, the invention of the snap switch in the 1920s revolutionized lighting control, improving safety and convenience. Through continuous advancements, modern switches now incorporate energy-saving features and remote operation capabilities.
This article will delve deeper into the intricacies of Basic Wiring For Light Switch, providing a comprehensive guide to its proper installation, troubleshooting techniques, and latest technological innovations in the realm of lighting control.
Understanding the fundamental aspects of Basic Wiring For Light Switch is critical for ensuring safety, functionality, and energy efficiency in electrical systems. These aspects encompass various dimensions related to the installation, operation, and maintenance of lighting circuits.
- Circuit Design: Planning the layout of electrical wiring, including wire sizing, switch placement, and circuit protection.
- Wire Selection: Choosing the appropriate wire type, gauge, and insulation for the specific application.
- Switch Types: Understanding the different types of light switches available, including single-pole, double-pole, and three-way switches.
- Connection Techniques: Mastering the proper methods for connecting wires to switches and light fixtures.
- Safety Regulations: Adhering to electrical codes and standards to ensure safe and compliant installations.
- Troubleshooting: Identifying and resolving common electrical issues related to light switches.
- Energy Efficiency: Utilizing energy-saving lighting techniques and switch technologies.
- Smart Lighting: Exploring the integration of smart switches and home automation systems for enhanced convenience and efficiency.
In-depth knowledge of these aspects empowers electricians, homeowners, and DIY enthusiasts to confidently handle lighting projects, ensuring the proper functioning and longevity of electrical systems. By understanding the underlying principles and best practices, individuals can contribute to a safer and more efficient electrical environment.
Circuit Design
In the realm of Basic Wiring For Light Switch, Circuit Design stands as a cornerstone, dictating the efficiency, safety, and functionality of lighting circuits. It encompasses a meticulous planning process that involves selecting appropriate wire sizes, strategically placing switches, and implementing circuit protection measures to safeguard against electrical hazards.
- Wire Sizing: Determining the correct wire gauge is critical for ensuring adequate current flow and preventing overheating. Factors such as circuit load, wire length, and insulation type influence wire sizing decisions.
- Switch Placement: Switches should be positioned for convenient operation and accessibility. Proper placement considers factors like room layout, traffic flow, and the intended use of the lighting.
- Circuit Protection: Overcurrent protection devices, such as fuses or circuit breakers, play a crucial role in safeguarding circuits from excessive current flow. Selecting the appropriate amperage rating for these devices is essential to prevent electrical fires.
- Grounding: Establishing a proper grounding system provides a safe path for fault currents, minimizing the risk of electrical shock and equipment damage.
By adhering to sound circuit design principles, electricians can ensure that lighting circuits operate safely, efficiently, and in compliance with electrical codes. These considerations form the foundation for reliable and long-lasting electrical systems.
Wire Selection
In the realm of Basic Wiring For Light Switch, wire selection plays a pivotal role in ensuring the safe and efficient operation of lighting circuits. Proper selection encompasses choosing the appropriate wire type, gauge, and insulation for the specific application, considering factors such as current carrying capacity, voltage rating, and environmental conditions.
- Wire Type: Common wire types used in lighting circuits include solid copper, stranded copper, and aluminum. Solid copper offers higher current carrying capacity and is often used in fixed installations, while stranded copper provides greater flexibility and is suitable for applications where movement is anticipated. Aluminum wire, though less common in residential settings, is employed in certain industrial and commercial applications.
- Wire Gauge: Wire gauge, denoted by AWG (American Wire Gauge), determines the cross-sectional area of the wire and its current carrying capacity. Thicker wires with lower AWG numbers can handle higher currents, while thinner wires with higher AWG numbers have lower current carrying capacities.
- Insulation: Wire insulation serves as a protective layer, preventing electrical shock and short circuits. Common insulation materials for lighting circuits include PVC (polyvinyl chloride), THHN (thermoplastic high heat resistant nylon), and UF (underground feeder). Each type offers varying degrees of protection against moisture, heat, and abrasion.
- Voltage Rating: The voltage rating of a wire indicates the maximum voltage it can safely withstand. Lighting circuits typically operate at 120 volts or 240 volts, and the wire selected must have a voltage rating that meets or exceeds the circuit voltage.
Understanding and applying the principles of wire selection is essential for ensuring the proper functioning and longevity of lighting circuits. By carefully considering the specific requirements of each application, electricians can select the most appropriate wire type, gauge, and insulation, ensuring a safe and reliable electrical system.
Switch Types
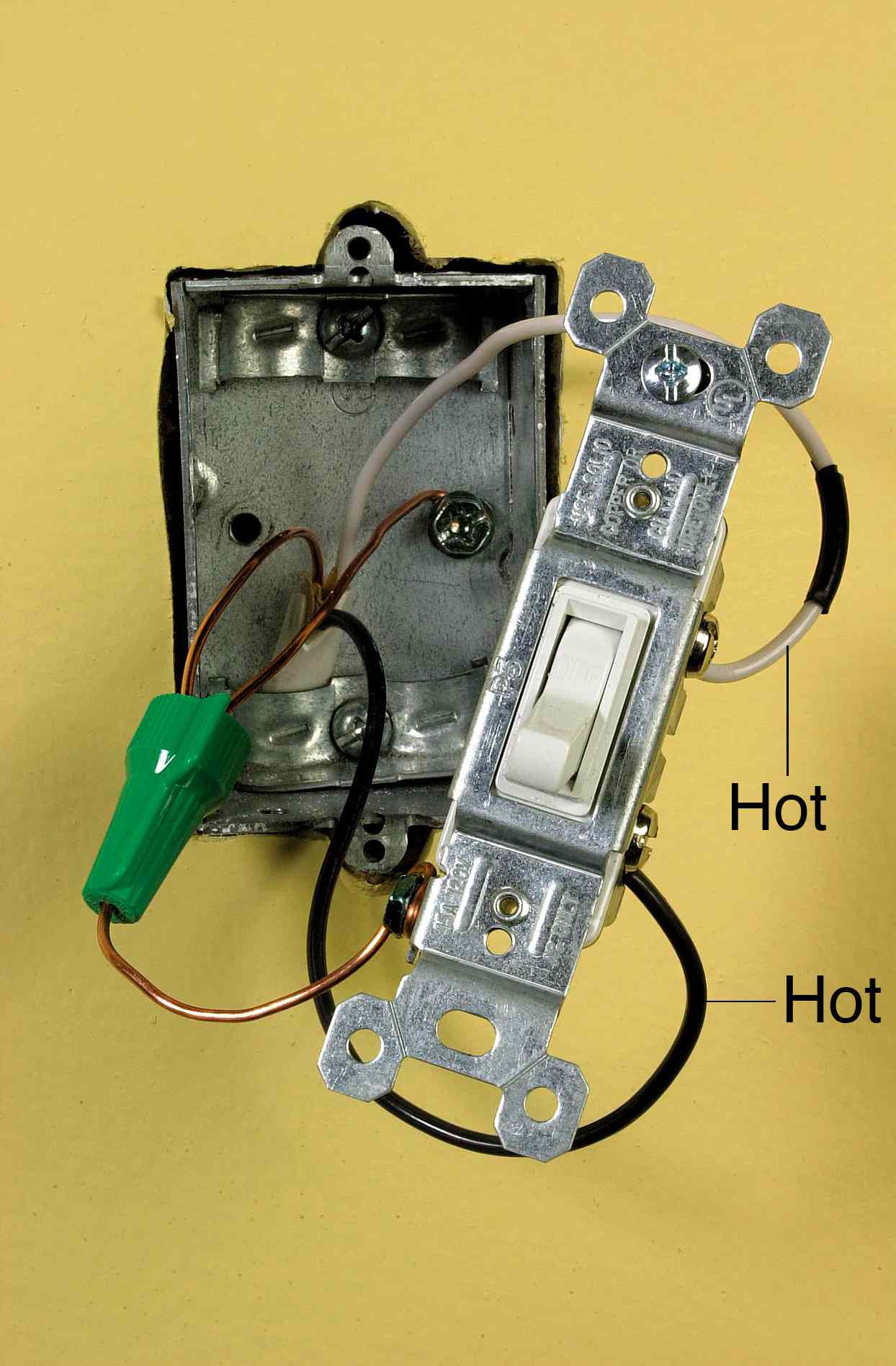
In the realm of “Basic Wiring For Light Switch,” switch types play a critical role in controlling lighting circuits. Understanding the different types of switches available, including single-pole, double-pole, and three-way switches, is essential for proper circuit design and installation.
Single-pole switches are the most common type, used to control a single light fixture from one location. They have two terminals, one for the incoming power and one for the outgoing power to the light. Double-pole switches are used to control two separate circuits or two different light fixtures from one location. They have four terminals, two for each circuit.
Three-way switches are used to control a single light fixture from two different locations. They have three terminals, one for the incoming power and two for the outgoing power to the light. Three-way switches are typically used in conjunction with a four-way switch, which allows for control of the light from three or more locations.
Selecting the appropriate switch type for a specific application is crucial for ensuring proper functionality and safety. For instance, in a bedroom, a single-pole switch may be sufficient to control the overhead light. In a hallway, a three-way switch may be necessary to control the light from both ends of the hallway.
Understanding switch types and their applications empowers electricians and homeowners to design and install lighting circuits that meet specific requirements. Proper switch selection contributes to efficient lighting control, enhanced convenience, and overall electrical safety in residential and commercial settings.
Connection Techniques
Connection Techniques are integral to the successful implementation of Basic Wiring for Light Switch. Mastering these methods ensures safe, reliable, and efficient operation of lighting circuits. This involves understanding the different types of wire connectors, proper wire stripping techniques, and adhering to electrical codes and standards.
- Wire Connectors: Choosing the appropriate wire connectors, such as wire nuts, solderless connectors, or terminal blocks, is crucial for secure and long-lasting connections. Each type has its own advantages and applications.
- Wire Stripping: Correctly stripping the insulation from wires is essential to ensure proper contact and prevent short circuits. Using the right tools and techniques, such as wire strippers or a utility knife, is important for precise and safe stripping.
- Electrical Codes and Standards: Adhering to established electrical codes and standards, such as the National Electrical Code (NEC), is paramount for ensuring the safety and compliance of lighting circuits. These regulations dictate proper wiring practices, grounding requirements, and circuit protection measures.
- Testing and Inspection: Once connections are made, thorough testing and inspection are necessary to verify circuit integrity and functionality. This includes using voltage testers, continuity testers, and visual inspections to identify any potential issues.
By mastering proper Connection Techniques, electricians and homeowners can confidently execute lighting circuit installations. These techniques contribute to the overall safety, reliability, and efficiency of electrical systems, ensuring the proper functioning of lighting fixtures and switches.
Safety Regulations
In the realm of Basic Wiring For Light Switch, adherence to safety regulations is paramount. Electrical codes and standards, such as the National Electrical Code (NEC), serve as essential guidelines for the design, installation, and maintenance of electrical systems, including lighting circuits.
By adhering to these regulations, electricians and homeowners can minimize the risk of electrical hazards, such as electrical fires, shocks, and electrocution. These regulations dictate proper wiring practices, grounding requirements, and circuit protection measures, ensuring the safe operation of lighting circuits.
For example, proper grounding, as mandated by electrical codes, provides a safe path for fault currents to flow, preventing the buildup of dangerous voltages on electrical equipment. Similarly, the use of overcurrent protection devices, such as fuses or circuit breakers, safeguards circuits from excessive current flow, reducing the risk of electrical fires.
Understanding and implementing safety regulations in Basic Wiring For Light Switch is not only a legal requirement but also a fundamental aspect of responsible electrical practices. It ensures that lighting circuits are installed and maintained in a manner that prioritizes the safety of individuals and property.
Troubleshooting
In the realm of Basic Wiring For Light Switch, troubleshooting electrical issues related to light switches is a crucial aspect of maintaining safe and functional lighting circuits. Troubleshooting involves identifying the root cause of electrical problems, such as flickering lights, unresponsive switches, or complete loss of power, and implementing appropriate solutions to restore proper operation.
Troubleshooting is an essential component of Basic Wiring For Light Switch, as it enables electricians and homeowners to diagnose and resolve electrical issues effectively. By understanding the fundamental principles of light switch wiring and the potential causes of malfunctions, individuals can approach troubleshooting systematically and efficiently.
For instance, a common electrical issue is a flickering light, which can be caused by loose connections, faulty wiring, or a failing light bulb. By inspecting the switch connections, examining the wiring for damage, and replacing the light bulb, the issue can be identified and rectified.
Another common problem is an unresponsive switch, which may indicate a faulty switch, a broken wire, or a tripped circuit breaker. Troubleshooting involves testing the switch with a voltage tester, checking for continuity in the wiring, and resetting the circuit breaker if necessary.
Understanding troubleshooting techniques empowers individuals to address electrical issues promptly, ensuring the safety and reliability of lighting circuits. It also fosters a proactive approach to electrical maintenance, as regular inspection and troubleshooting can prevent minor issues from escalating into more significant problems.
In summary, Troubleshooting: Identifying and resolving common electrical issues related to light switches is an integral part of Basic Wiring For Light Switch, providing essential knowledge and skills to diagnose and resolve electrical problems effectively. By understanding troubleshooting techniques, electricians and homeowners can maintain safe and functional lighting circuits, contributing to the overall safety and reliability of electrical systems.
Energy Efficiency
In the realm of Basic Wiring For Light Switch, incorporating energy-saving lighting techniques and switch technologies plays a critical role in promoting energy efficiency and sustainability. Energy-efficient lighting measures not only reduce energy consumption but also contribute to cost savings and environmental conservation.
One key aspect of energy efficiency in Basic Wiring For Light Switch involves utilizing energy-efficient light sources, such as LED (light-emitting diode) or CFL (compact fluorescent lamp) bulbs. These bulbs consume significantly less energy compared to traditional incandescent bulbs while providing comparable or even better illumination. By switching to energy-efficient bulbs, individuals can substantially reduce their energy consumption without compromising lighting quality.
Another important consideration is the use of occupancy sensors or motion detectors in conjunction with lighting circuits. These devices automatically turn lights off when a room is unoccupied, preventing unnecessary energy wastage. Occupancy sensors are particularly effective in areas like hallways, closets, and storage rooms, where lights are often left on inadvertently.
Furthermore, modern light switches offer advanced features that contribute to energy efficiency. Dimmer switches allow users to adjust the brightness of lights, reducing energy consumption when full illumination is not required. Smart switches, connected to home automation systems, provide remote control and scheduling capabilities, enabling users to optimize lighting usage and minimize energy waste.
In summary, incorporating energy-saving lighting techniques and switch technologies into Basic Wiring For Light Switch is a crucial step towards energy efficiency and sustainability. By utilizing energy-efficient light sources, implementing occupancy sensors, and leveraging advanced switch features, individuals can significantly reduce their energy consumption, save costs, and contribute to a greener environment.
Smart Lighting
In the evolving landscape of electrical systems, “Smart Lighting: Exploring the integration of smart switches and home automation systems for enhanced convenience and efficiency” represents a significant advancement that complements the foundation laid by “Basic Wiring For Light Switch.”
Smart Lighting systems leverage smart switches and home automation to elevate lighting control beyond traditional manual operation. By seamlessly integrating with home networks, smart lighting allows users to control lights remotely via smartphones, tablets, or voice assistants. This integration introduces a plethora of benefits, including:
Enhanced Convenience: Smart Lighting eliminates the need for physical interaction with light switches, offering remote control from anywhere within or outside the home. This convenience is particularly valuable for individuals with limited mobility or in situations where accessing light switches is challenging.Automated Lighting: Smart Lighting systems can be programmed to automate lighting based on predefined schedules, occupancy detection, or environmental conditions. This automation optimizes energy consumption by ensuring lights are only used when necessary, leading to cost savings and reduced environmental impact.Scene Setting: Smart Lighting allows users to create and recall custom lighting scenes that suit different moods or activities. With a single command, users can transform the ambiance of a room, creating the perfect atmosphere for relaxation, entertainment, or work.
Real-life examples of Smart Lighting applications within Basic Wiring For Light Switch include:
Smart Switches: These switches replace traditional switches and connect to a home network, enabling remote control and automation features.Motion Sensors: Motion sensors can be integrated into lighting circuits to automatically turn lights on or off based on movement, providing hands-free lighting control and enhanced security.Smart Bulbs: Smart bulbs incorporate LED technology and wireless connectivity, allowing for remote control, color adjustment, and scheduling.
Understanding the connection between Smart Lighting and Basic Wiring For Light Switch empowers individuals to create intelligent and efficient lighting systems. By incorporating smart lighting components, homeowners and businesses can unlock a world of convenience, energy savings, and enhanced living experiences.









Related Posts








