Wiring 24v Trolling Motor refers to the electrical procedures and techniques involved in connecting and installing a 24-volt (V) trolling motor to a boat’s electrical system, battery, and other components. For instance, a common wiring setup for a 24V trolling motor consists of connecting it to two 12V batteries wired in series, ensuring that the voltage output matches the motor’s requirements.
Wiring a 24V trolling motor offers advantages such as increased power and torque for improved boat propulsion, enabling smoother trolling speeds and enhanced maneuvering capabilities in various water conditions. Historically, the development of efficient and reliable 24V trolling motors was a significant step forward for the fishing industry, providing anglers with greater control and performance while on the water.
In this article, we will delve deeper into the wiring process for 24V trolling motors, covering essential components, safety considerations, and troubleshooting tips to ensure a successful installation and optimize the performance of your boat’s electrical system.
To effectively wire a 24V trolling motor, it is essential to understand the various aspects involved in the process. These aspects not only affect the performance and efficiency of the motor but also ensure the safety and reliability of your boat’s electrical system.
- Voltage: Matching the motor’s voltage requirements (24V) with the appropriate battery configuration.
- Battery Capacity: Selecting batteries with sufficient capacity (amp-hours) to support the motor’s power consumption.
- Wiring Gauge: Usingavoid voltage drop and ensure efficient current flow.
- Connections: Making secure and properly insulated electrical connections to prevent shorts and malfunctions.
- Circuit Protection: Incorporating fuses or circuit breakers to protect the motor and electrical system from overloads.
- Grounding: Establishing a proper grounding system to prevent electrical hazards and ensure the stability of the motor’s operation.
- Switch: Installing a switch to conveniently control the power supply to the motor.
- Propeller: Selecting the appropriate propeller size and pitch for optimal performance and efficiency.
- Maintenance: Regularly checking and servicing the motor’s electrical components to ensure continued reliability.
These aspects are interconnected and play a crucial role in the successful wiring and operation of a 24V trolling motor. Understanding and properly addressing each aspect will contribute to a safe, efficient, and enjoyable boating experience.
Voltage
When wiring a 24V trolling motor, it is crucial to ensure that the motor’s voltage requirements are met by selecting the appropriate battery configuration. This aspect plays a vital role in the performance, efficiency, and longevity of the motor and the overall electrical system of the boat.
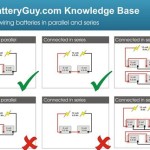
- Battery Voltage: Trolling motors are designed to operate at a specific voltage, typically 12V, 24V, or 36V. For a 24V trolling motor, two 12V batteries must be connected in series to provide the required voltage.
- Battery Capacity: The capacity of the batteries, measured in amp-hours (Ah), determines how long the motor can run on a single charge. Higher capacity batteries will provide longer run times, especially when powering a 24V motor with its higher power consumption.
- Series Connection: Connecting batteries in series increases the overall voltage while maintaining the same amp-hour capacity. In the case of a 24V trolling motor, two 12V batteries connected in series will provide the necessary 24 volts.
- Parallel Connection: Connecting batteries in parallel increases the overall amp-hour capacity while maintaining the same voltage. This type of connection is not suitable for powering a 24V trolling motor, as it will not provide the required voltage.
Matching the motor’s voltage requirements with the appropriate battery configuration ensures that the motor receives the correct amount of power to operate efficiently. It also prevents damage to the motor and batteries due to over-voltage or under-voltage conditions. Proper battery selection and wiring are essential for a well-functioning 24V trolling motor system.
Battery Capacity
When wiring a 24V trolling motor, selecting batteries with sufficient capacity (amp-hours) is critical to ensure optimal performance and endurance. Battery capacity directly affects the motor’s ability to deliver consistent power and operate for extended periods without draining the batteries prematurely.
The amp-hour (Ah) rating of a battery indicates the amount of current it can deliver over a specific period. For instance, a 100Ah battery can provide 1 amp of current for 100 hours or 10 amps of current for 10 hours. When powering a 24V trolling motor, which typically consumes several amps of current, a higher amp-hour capacity battery is essential to sustain the motor’s operation for longer durations.
Insufficient battery capacity can lead to several issues. If the batteries are undersized for the motor’s power consumption, they may drain rapidly, resulting in shorter run times and potential damage to the motor due to over-discharging. Additionally, undersized batteries may struggle to provide sufficient power, leading to reduced motor performance and efficiency.
Selecting batteries with sufficient capacity ensures that the motor has an adequate power supply to operate effectively and reliably. It extends the motor’s run time, allowing anglers to spend more time fishing without worrying about battery depletion. Moreover, proper battery capacity selection contributes to the longevity of the batteries and the overall electrical system of the boat.
Wiring Gauge
In the context of wiring a 24V trolling motor, selecting the appropriate wire gauge is a fundamental aspect that directly influences the motor’s performance and overall electrical system efficiency. It ensures that the motor receives adequate power while minimizing voltage drop and potential energy loss.
Voltage drop is the reduction in voltage that occurs when electrical current flows through a conductor, such as a wire. It is primarily caused by the resistance of the wire, which impedes the flow of current and results in a voltage loss. In the case of a trolling motor, voltage drop can negatively impact the motor’s speed, torque, and overall efficiency.
Using an appropriate wire gauge helps mitigate voltage drop by reducing the resistance in the electrical circuit. A thicker wire gauge, indicated by a lower gauge number, has a larger cross-sectional area, allowing for better current flow and reducing resistance. This ensures that the motor receives the necessary voltage to operate effectively, even over longer wire runs.
For instance, if a 24V trolling motor draws 50 amps of current and the wire run from the battery to the motor is 20 feet long, using a 10 AWG wire will result in a voltage drop of approximately 1.5 volts. Upgrading to a thicker wire, such as a 8 AWG wire, will reduce the voltage drop to around 0.8 volts, providing the motor with more power and improved performance.
Choosing the appropriate wire gauge for wiring a 24V trolling motor is crucial for several reasons. It ensures efficient power delivery, minimizes voltage drop, and prevents overheating due to excessive resistance. By carefully selecting the wire gauge based on the motor’s power consumption and wire run length, anglers can optimize the performance and longevity of their trolling motor system.
Connections
When wiring a 24V trolling motor, making secure and properly insulated electrical connections is paramount to ensure the motor’s reliable operation and prevent potential hazards. In this context, connections refer to the physical joining of wires, terminals, and other components within the electrical circuit.
- Proper Crimping: Crimping is a technique used to create a secure and reliable connection between wires and terminals. Using a crimping tool, the wire is compressed around a terminal, ensuring a tight fit and good electrical contact. This prevents loose connections that can lead to arcing, overheating, and potential damage to the motor or electrical system.
- Insulation: Electrical insulation is crucial to prevent short circuits and ensure the safe operation of the trolling motor. Wires should be properly insulated to avoid contact with other wires or components, which could lead to electrical faults. Heat shrink tubing, electrical tape, and other insulating materials are commonly used to cover exposed wires and terminals.
- Waterproof Connections: In marine environments, it is essential to make waterproof connections to protect the electrical system from moisture and corrosion. Waterproof connectors, heat shrink tubing with adhesive lining, and marine-grade electrical tape can be used to seal connections and prevent water intrusion.
- Grounding: Grounding the trolling motor’s electrical system is essential for safety. The negative terminal of the battery should be connected to the boat’s grounding system, which provides a path for electrical current to safely return to the source. Proper grounding helps prevent electrical shocks and ensures the stable operation of the motor.
By meticulously making secure and properly insulated electrical connections, anglers can ensure the reliable and safe operation of their 24V trolling motor system, preventing potential shorts, malfunctions, and hazards that could compromise the motor’s performance or safety on the water.
Circuit Protection
In the context of wiring a 24V trolling motor, circuit protection plays a crucial role in safeguarding the motor and the entire electrical system from potential damage caused by overloads. Overloads occur when excessive current flows through the circuit, which can result from various factors such as short circuits, faulty wiring, or overloading the motor beyond its capacity.
To mitigate the risks associated with overloads, incorporating fuses or circuit breakers into the wiring of a 24V trolling motor is essential. These protective devices act as safety switches, interrupting the electrical circuit when the current exceeds a predetermined threshold. By doing so, they prevent damage to the motor’s electrical components, wiring, and the boat’s electrical system as a whole.
Real-life examples of circuit protection in 24V trolling motor wiring include the use of inline fuses or circuit breakers installed between the battery and the motor. These devices monitor the current flow and trip if the current exceeds a safe level, effectively isolating the motor and preventing damage. Additionally, some trolling motors have built-in circuit protection features, such as thermal overload protection, which automatically shuts off the motor if it overheats due to excessive current draw.
The practical significance of understanding the importance of circuit protection in wiring a 24V trolling motor lies in ensuring the longevity and reliability of the motor and the boat’s electrical system. Overloads, if left unchecked, can lead to burned-out motor windings, damaged wiring, and even fires. By incorporating appropriate circuit protection measures, anglers can safeguard their investment and prevent potentially hazardous situations on the water.
Grounding
When wiring a 24v trolling motor, grounding plays a crucial role in ensuring the safe and stable operation of the motor and the entire electrical system. A proper grounding system provides a path for electrical current to return to the source, preventing electrical hazards and potential damage to the motor and other components.
- Electrical Safety: Grounding provides a low-resistance path for stray electrical current to flow back to the battery, preventing the buildup of voltage on the motor and other components. This reduces the risk of electrical shocks and short circuits, enhancing the overall safety of the electrical system.
- Motor Stability: A proper grounding system helps stabilize the motor’s operation by providing a reference point for the electrical circuit. It ensures that the motor receives a consistent voltage supply, preventing fluctuations that can affect its performance and reliability.
- Corrosion Protection: Grounding helps protect the motor and other electrical components from corrosion by providing a path for stray electrical currents to flow away from sensitive areas. This reduces the risk of electrolysis, which can damage metal components and lead to premature failure.
- Real-Life Example: In a typical 24v trolling motor installation, the negative terminal of the battery is connected to the boat’s grounding system, which is usually a metal plate or rod attached to the hull. This connection provides a low-resistance path for electrical current to return to the battery, completing the electrical circuit.
Understanding the importance of grounding and implementing a proper grounding system is essential for the safe and reliable operation of a 24v trolling motor. By providing a safe path for electrical current to flow, grounding helps prevent electrical hazards, ensures motor stability, and protects against corrosion, extending the lifespan of the motor and the entire electrical system.
Switch
In the context of wiring a 24v trolling motor, installing a switch plays a critical role in providing convenient control over the motor’s power supply. A switch acts as an intermediary between the battery and the motor, allowing anglers to effortlessly turn the motor on or off as needed, enhancing the user experience and safety.
The connection between installing a switch and wiring a 24v trolling motor is evident in the practical functionality it provides. By incorporating a switch into the wiring, anglers gain the ability to conveniently control the motor’s operation without having to disconnect and reconnect the battery each time. This ease of use is particularly valuable in situations where frequent adjustments or quick responses are necessary, such as when maneuvering the boat in tight spaces or navigating through changing water conditions.
Real-life examples of switch installation in 24v trolling motor wiring are commonly found in various types of fishing boats. Typically, a switch is mounted on the boat’s dashboard or control panel, providing easy access for the operator. When the switch is turned on, it completes the electrical circuit, allowing current to flow from the battery to the motor, thereby powering it up. Conversely, turning the switch off breaks the circuit, cutting off the power supply to the motor and stopping its operation.
Understanding the importance of installing a switch in wiring a 24v trolling motor extends beyond convenience. It also contributes to safety and efficiency. By having a dedicated switch, anglers can quickly shut off the motor in case of an emergency, such as if the propeller becomes entangled or if there is a need to make sudden adjustments. Additionally, a switch helps conserve battery power by allowing the motor to be turned off when not in use, preventing unnecessary power drain.
Propeller
When wiring a 24v trolling motor, selecting the appropriate propeller is essential for maximizing performance and efficiency. The propeller acts as the driving force, converting electrical energy into thrust to propel the boat. Choosing the right size and pitch ensures the motor operates at its optimum level, providing the desired speed, control, and battery life.
- Propeller Size: The diameter and blade area of the propeller determine the amount of thrust it generates. Larger propellers provide more thrust, suitable for heavier boats or faster speeds. Smaller propellers are more efficient at lower speeds and in shallower waters.
- Propeller Pitch: The pitch refers to the angle of the propeller blades. A higher pitch propeller “bites” into the water more, providing greater speed and efficiency at higher RPMs. A lower pitch propeller offers more torque and acceleration, ideal for slower speeds and heavier loads.
- Material and Design: Propellers can be made from various materials, such as aluminum, stainless steel, or composite. The choice of material affects durability, corrosion resistance, and weight. Additionally, blade design features like cupping or raking can influence performance.
- Real-Life Example: For a 24v trolling motor on a small fishing boat, a 12-inch, three-blade propeller with a medium pitch would provide a good balance of speed and efficiency. A larger, four-blade propeller with a higher pitch would be suitable for a heavier boat or higher desired speeds.
Selecting the appropriate propeller size and pitch for a 24v trolling motor optimizes the motor’s performance, ensuring it delivers the desired thrust, efficiency, and control. By considering the factors discussed above, anglers can make informed decisions to enhance their overall boating experience.
Maintenance
The connection between maintenance and wiring a 24v trolling motor lies in the critical role that regular maintenance plays in preserving the motor’s performance and longevity. By diligently checking and servicing the motor’s electrical components, anglers can proactively prevent potential issues and ensure continued reliability while on the water.
Neglecting maintenance can have detrimental effects on the motor’s electrical system, leading to decreased efficiency, reduced lifespan, and increased susceptibility to breakdowns. Regular maintenance, on the other hand, helps identify and address minor issues before they escalate into major problems, minimizing the likelihood of unexpected failures and costly repairs.
Real-life examples of maintenance tasks include
Understanding the importance of maintenance empowers anglers with the knowledge and skills to proactively care for their trolling motors, maximizing their performance and extending their lifespan. By incorporating regular maintenance into their routine, anglers can enjoy worry-free operation and peace of mind on every fishing trip.










Related Posts