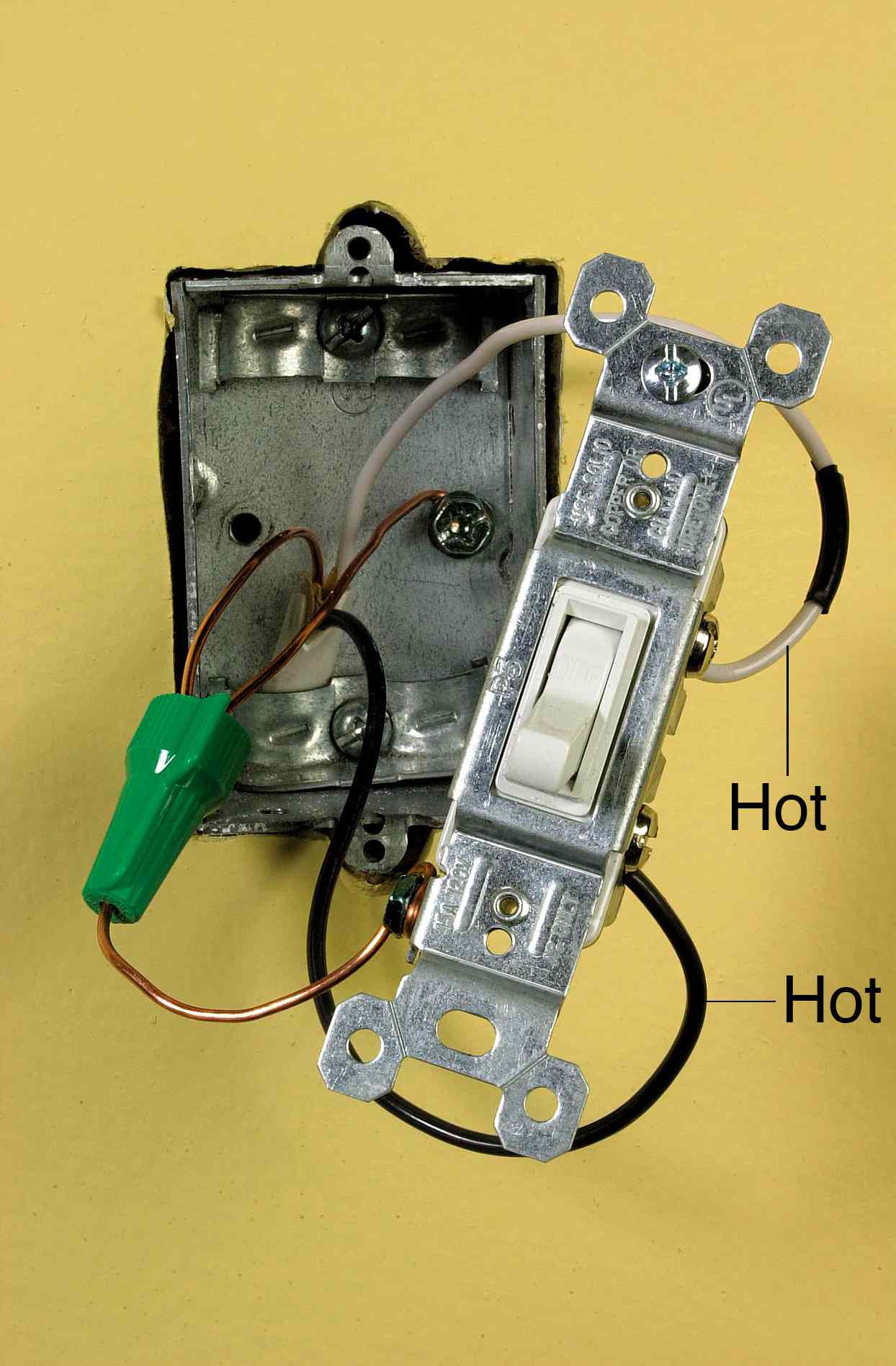
Wiring in a light switch involves connecting electrical wires to a switch that controls the flow of electricity to a light fixture. For instance, when wiring a single-pole switch to a ceiling light, an electrician would connect the power line to the terminal screw on the switch and extend the line to the light fixture. This allows the user to turn the light on or off by flipping the switch.
Wiring in light switches is crucial as it enables the convenient control of lighting in homes, offices, and various buildings. It enhances safety by allowing users to turn off lights when leaving a room, reducing fire hazards. The key historical development was the invention of the first light switch by John Henry Holmes in 1884, revolutionizing electrical systems and home lighting.
This article will delve deeper into the types of light switches, techniques for wiring them, and essential safety considerations when working with electrical systems.
Wiring in light switches is a fundamental aspect of electrical systems in buildings, enabling the convenient control of . Various key aspects are involved in this process, each contributing to the safety, functionality, and efficiency of lighting systems.
- Safety: Wiring must adhere to electrical codes and standards to prevent electrical hazards.
- Compatibility: Switches must be compatible with the type of lighting fixtures and electrical systems.
- Functionality: Switches must operate smoothly and reliably to control lighting effectively.
- Location: Switches should be placed in convenient and accessible locations for ease of use.
- Circuitry: Wiring must be planned to ensure proper circuit protection and load balancing.
- Materials: High-quality wires, switches, and terminals are essential for durability and safety.
- Tools: Appropriate tools are necessary for safe and efficient wiring.
- Codes: Compliance with electrical codes is crucial to ensure safety and adherence to regulations.
- Maintenance: Regular inspection and maintenance are important to prevent issues and ensure optimal performance.
- Troubleshooting: Understanding basic troubleshooting techniques can help identify and resolve common problems.
These aspects collectively contribute to the effective and safe operation of lighting systems. Proper wiring in light switches ensures the reliable control of lighting, reduces the risk of electrical hazards, and enhances the overall functionality of electrical systems.
Safety
When wiring in light switches, adhering to electrical codes and standards is paramount for safety. Electrical codes provide specific guidelines for wiring practices, ensuring that electrical systems are installed and maintained safely. These codes address various aspects, including wire size, insulation requirements, grounding, and circuit protection. By following these codes, electricians can minimize the risk of electrical fires, shocks, and other hazards.
For instance, using the correct wire size is crucial to prevent overheating and potential fires. Proper insulation prevents electrical shocks and short circuits. Grounding provides a safe path for fault currents to flow, protecting equipment and. Circuit protection devices, such as fuses or circuit breakers, safeguard circuits from overcurrents that could lead to electrical fires.
Neglecting safety measures when wiring in light switches can have severe consequences. Loose connections, improper grounding, and overloaded circuits can lead to electrical fires, shocks, or electrocution. Adhering to electrical codes ensures that these hazards are minimized, protecting buildings, occupants, and electrical systems.
In summary, safety is a critical aspect of wiring in light switches. By following electrical codes and standards, electricians can ensure that lighting systems are installed and maintained safely, reducing the risk of electrical hazards and promoting the well-being of building occupants.
Compatibility
In the context of “Wiring In Light Switch”, compatibility plays a crucial role in ensuring the proper functioning and safety of lighting systems. Compatibility encompasses various aspects, including the switch’s ability to handle the electrical load of the lighting fixture, the voltage requirements, and the type of dimming or control system used.
- Electrical Load: The switch must be rated to handle the electrical load of the lighting fixture. If the switch is not rated for the load, it may overheat and pose a fire hazard.
- Voltage Requirements: The switch must be compatible with the voltage of the electrical system. Using a switch that is not rated for the correct voltage can damage the switch or the lighting fixture.
- Dimming and Control Systems: If a dimming or control system is being used, the switch must be compatible with that system. Using an incompatible switch may result in flickering, buzzing, or other problems.
- Physical Compatibility: The switch must be physically compatible with the mounting box and the lighting fixture. This includes factors such as the size, shape, and mounting mechanism.
Ensuring compatibility between switches, lighting fixtures, and electrical systems is essential for safe and effective lighting control. By selecting compatible components, electricians can prevent potential hazards, ensure optimal performance, and enhance the overall functionality of lighting systems.
Functionality
In the context of “Wiring In Light Switch,” functionality encompasses the ability of switches to operate smoothly and reliably, ensuring effective lighting control. This facet is paramount for ensuring that lighting systems function as intended, providing users with convenient and efficient control over their lighting environment.
- Electrical Contacts: The electrical contacts within the switch must be clean and properly aligned to ensure good electrical conductivity. Poor contact can lead to flickering lights, switch failure, or even electrical arcing.
- Mechanical Operation: The switch mechanism should operate smoothly and without any sticking or jamming. A faulty mechanical operation can make it difficult to turn the lights on or off, or may even cause the switch to break.
- Durability: Switches should be durable enough to withstand repeated use and the rigors of everyday operation. A flimsy or poorly constructed switch may wear out quickly, requiring frequent replacement.
- Safety: The switch must be designed and constructed to prevent electrical shocks or other safety hazards. This includes features such as proper insulation and grounding.
By ensuring that switches operate smoothly and reliably, electricians can contribute to the overall functionality and safety of lighting systems. Properly functioning switches provide users with convenient and efficient control over their lighting environment, enhancing the usability and enjoyment of spaces.
Location
In the context of “Wiring In Light Switch,” the placement of switches plays a crucial role in enhancing the usability and functionality of lighting systems. Switches should be positioned in convenient and accessible locations to allow users to easily control lighting, promote safety, and optimize the overall user experience.
- Proximity to Lighting Fixtures: Switches should be placed in close proximity to the lighting fixtures they control, ensuring convenient and direct control over the lighting. This placement minimizes the need for users to walk across the room or search for switches in dimly lit areas.
- Clear Visibility: Switches should be positioned in clearly visible locations to facilitate easy identification and operation. This is especially important in dark or unfamiliar environments where fumbling for switches can be hazardous.
- Height and Reach: Switches should be installed at an appropriate height that allows for comfortable and effortless operation. This typically involves placing switches at around elbow height for most adults, ensuring they can be easily reached and activated without strain.
- Clearance and Obstructions: Switches should be positioned in areas free from obstructions such as furniture, artwork, or other objects that may hinder access or operation. Adequate clearance around switches prevents accidental activation or difficulty in finding and using them.
By carefully considering the location of switches and adhering to these guidelines, electricians can enhance the functionality, safety, and user-friendliness of lighting systems. Proper switch placement contributes to a positive user experience, promotes efficient lighting control, and ensures that switches are conveniently accessible when needed.
Circuitry
Within the context of “Wiring In Light Switch,” the aspect of “Circuitry: Wiring must be planned to ensure proper circuit protection and load balancing” plays a critical role in ensuring the safety, reliability, and efficiency of lighting systems. By carefully planning the circuitry, electricians can prevent electrical hazards, distribute electrical loads evenly, and enhance the overall functionality of lighting systems.
- Circuit Protection: Circuit protection devices such as fuses or circuit breakers are essential components of electrical circuits. These devices protect wires and equipment from damage caused by overcurrent conditions, preventing electrical fires and other hazards.
- Load Balancing: Proper load balancing ensures that electrical loads are evenly distributed across different circuits, preventing overloading and potential power outages. This involves calculating the electrical load of each circuit and ensuring that it does not exceed the circuit’s capacity.
- Wire Sizing: The size of electrical wires used in a circuit must be appropriate for the amount of current that will flow through them. Using undersized wires can lead to overheating and electrical fires, while oversized wires can be wasteful and expensive.
- Grounding: Grounding provides a safe path for electrical current to flow in the event of a fault, preventing electrical shocks and damage to equipment. Proper grounding involves connecting all metal parts of an electrical system to a grounding electrode.
By considering these facets of circuitry and adhering to established electrical codes and standards, electricians can ensure that lighting systems are safe, reliable, and efficient, minimizing the risk of electrical hazards and maximizing the performance of lighting installations.
Materials
When discussing “Wiring In Light Switch”, the aspect of “Materials: High-quality wires, switches, and terminals are essential for durability and safety” holds paramount importance. Utilizing top-notch components ensures longevity, reliability, and minimizes potential hazards within electrical systems.
- Wire Gauge and Insulation: Electrical wires come in varying gauges, indicating their thickness and current-carrying capacity. Selecting wires with appropriate gauge and insulation is crucial to prevent overheating, voltage drop, and electrical fires.
- Switch Mechanisms: Light switches are subjected to frequent operation, making their internal mechanisms prone to wear and tear. High-quality switches employ robust materials and precise engineering to ensure smooth operation over an extended lifespan.
- Terminal Connections: Terminals provide secure connections between wires and electrical devices. Loose or poorly crimped terminals can lead to arcing, overheating, and potential fire hazards. Using high-quality terminals ensures reliable electrical contact and longevity.
- Durability and Corrosion Resistance: Electrical components are often exposed to moisture, dust, and other environmental factors. Durable materials, such as brass or stainless steel, resist corrosion and maintain optimal performance even in challenging conditions.
By prioritizing high-quality materials throughout the wiring process, electricians lay the foundation for safe, reliable, and long-lasting lighting systems. Compromising on material quality can lead to premature failures, increased maintenance costs, and potential safety risks. Therefore, selecting and utilizing top-notch wires, switches, and terminals is a non-negotiable aspect of responsible electrical installations.
Tools
In the context of “Wiring In Light Switch,” the availability and utilization of appropriate tools play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and efficiency of the wiring process. Employing the right tools enables electricians to complete electrical tasks with accuracy, minimize the risk of accidents, and enhance overall productivity.
- Safety Gear: Personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, safety glasses, and non-conductive mats safeguards electricians from electrical shocks, arc flashes, and other potential hazards.
- Voltage Testers: These devices are essential for verifying the presence and absence of voltage in electrical circuits, ensuring that circuits are de-energized before any work is performed.
- Hand Tools: Pliers, screwdrivers, and wire strippers are indispensable tools for manipulating wires, tightening connections, and removing insulation, facilitating efficient and precise wiring.
- Specialized Tools: Depending on the complexity of the wiring task, specialized tools like fish tapes, conduit benders, and crimping tools may be necessary for routing wires, bending conduits, and creating secure connections.
The use of appropriate tools goes beyond mere convenience; it is a fundamental aspect of responsible electrical practices. By equipping themselves with the right tools and utilizing them correctly, electricians can minimize the risk of accidents, ensure the integrity of electrical installations, and contribute to the overall safety and efficiency of “Wiring In Light Switch” projects.
Codes
In the context of “Wiring In Light Switch,” compliance with electrical codes is paramount. These codes establish a set of rules and regulations governing the design, installation, and maintenance of electrical systems, including lighting switches. Adhering to these codes is not only a legal requirement but also a fundamental aspect of ensuring safety and reliability in electrical installations.
- Safety Standards: Electrical codes incorporate safety standards that aim to minimize the risk of electrical fires, shocks, and other hazards. These standards specify requirements for wire sizing, circuit protection, grounding, and other aspects of electrical systems.
- Inspection and Approval: Electrical codes often require inspections and approvals by qualified authorities to ensure that electrical installations meet the required safety standards. This process helps identify and address any potential issues before the system is energized.
- Insurance and Liability: Compliance with electrical codes is often a requirement for obtaining insurance coverage for electrical systems. Insurance companies may deny claims or limit coverage if an electrical fire or accident is caused by non-compliant wiring.
- Building Permits and Occupancy: In many jurisdictions, obtaining building permits and certificates of occupancy may require compliance with electrical codes. This ensures that the electrical system meets the minimum safety standards required for the intended use of the building.
By adhering to electrical codes, electricians and homeowners can help ensure that lighting switches and the overall electrical system are installed, maintained, and operated safely and reliably. Neglecting or violating electrical codes can compromise safety, lead to costly repairs, and potentially result in legal consequences.
Maintenance
In the context of “Wiring In Light Switch,” regular inspection and maintenance play a critical role in ensuring the longevity, safety, and optimal performance of lighting systems. Neglecting maintenance can lead to various issues, affecting both the functionality of light switches and the overall electrical system.
One of the primary reasons for regular maintenance is to identify and address potential problems early on. Loose connections, worn-out components, and accumulated dust or debris can all contribute to switch malfunctions, flickering lights, and even electrical hazards if left unattended. By conducting periodic inspections and maintenance, electricians can proactively address these issues, minimizing the risk of more severe problems.
Moreover, regular maintenance helps ensure that light switches continue to operate efficiently, providing reliable control over lighting systems. Switches that are not properly maintained may become stiff or unresponsive, making it difficult to turn lights on or off. Regular cleaning and lubrication can help keep switches operating smoothly, extending their lifespan and enhancing the user experience.
In summary, regular inspection and maintenance are essential aspects of “Wiring In Light Switch.” By identifying and addressing potential issues early on, electricians can help prevent costly repairs, ensure optimal performance, and maintain a safe and reliable lighting system.
Troubleshooting
In the context of “Wiring In Light Switch,” understanding basic troubleshooting techniques is a valuable asset for electricians and homeowners alike. Electrical systems, including lighting switches, can occasionally encounter issues that require prompt attention to ensure safety and optimal performance.
Troubleshooting involves a systematic approach to identifying and resolving these issues. Electricians rely on their knowledge of electrical principles and utilize various tools and techniques to diagnose and rectify problems with lighting switches. For instance, if a light switch is not functioning correctly, a simple troubleshooting step would be to check if the power is reaching the switch using a voltage tester. By isolating the problem to the power source or the switch itself, electricians can quickly identify the root cause and implement the appropriate solution.
Moreover, basic troubleshooting techniques empower homeowners to address minor electrical issues safely and effectively. For example, if a light switch becomes loose or unresponsive, homeowners can tighten the screws or replace the switch faceplate without the need for professional assistance. Understanding the fundamental principles of troubleshooting empowers individuals to maintain their lighting systems, ensuring the safety and functionality of their homes.
In summary, troubleshooting skills play a crucial role in the effective wiring and maintenance of lighting switches. By understanding basic troubleshooting techniques, electricians and homeowners can diagnose and resolve common issues, ensuring the safety, reliability, and optimal performance of lighting systems.









Related Posts








