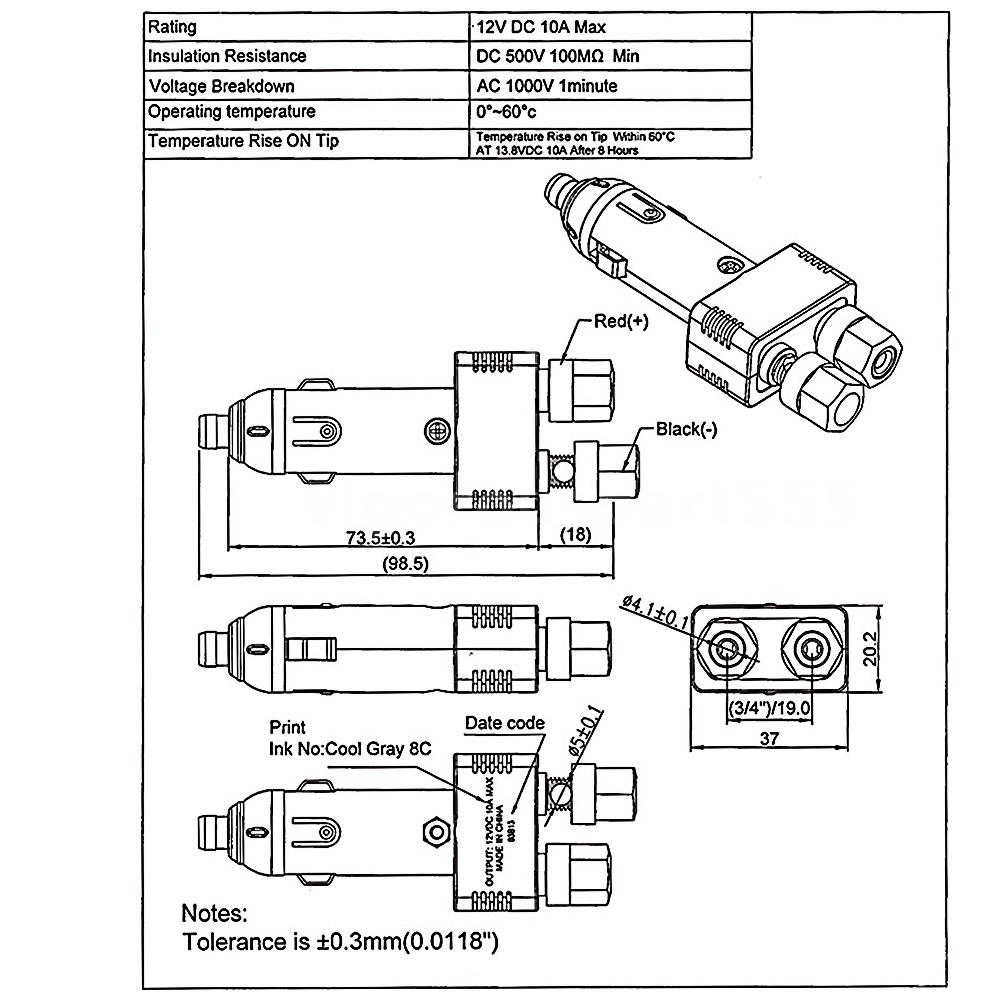
A Cigarette Socket Wiring Diagram provides detailed instructions on how to correctly connect and wire a cigarette socket, typically found in vehicles. It outlines the electrical connections necessary between the socket, power source (e.g., vehicle battery), and any associated devices (e.g., phone charger, GPS unit). Following the diagram ensures proper functionality and prevents electrical hazards.
Cigarette sockets are relevant in vehicles as they offer a convenient way to power or charge electronic devices while on the go. Benefits include easy accessibility, standardized design, and the ability to use a variety of compatible devices. A key historical development was the introduction of USB ports in cigarette sockets, allowing for broader and more efficient device charging.
This article delves into the components, wiring techniques, safety considerations, and troubleshooting tips related to Cigarette Socket Wiring Diagrams. It provides comprehensive guidance for both professional and DIY vehicle enthusiasts seeking to install or maintain this electrical feature.
A Cigarette Socket Wiring Diagram outlines the steps for connecting and wiring a cigarette socket in a vehicle. Understanding these key aspects is essential for proper installation and functionality.
- Electrical Connections: Proper wiring of the socket to the power source and devices ensures safe and efficient operation.
- Safety Measures: Following guidelines for insulation, grounding, and fuse protection minimizes electrical hazards.
- Socket Compatibility: Choosing the correct socket type and amperage rating prevents overheating and device damage.
- Power Source: Identifying the vehicle’s electrical system and selecting the appropriate power source for the socket is crucial.
- Wire Gauge and Type: Using the correct wire gauge and insulation ensures adequate current flow and prevents voltage drop.
- Circuit Protection: Implementing fuses or circuit breakers protects the socket and connected devices from electrical overloads.
- Grounding: Proper grounding provides a safe path for electrical current to return to the vehicle’s chassis, preventing electrical shocks.
- Switch Control: Integrating a switch allows for controlling the power supply to the socket when not in use.
- Socket Placement: Choosing a suitable location for the socket ensures accessibility, safety, and aesthetic considerations.
- Compatibility with Devices: Ensuring compatibility between the socket and the devices being powered prevents damage and optimizes charging.
These aspects are interconnected and contribute to the safe and effective operation of a Cigarette Socket Wiring Diagram. Proper wiring and installation are crucial for preventing electrical issues, ensuring device compatibility, and maximizing the functionality of this essential vehicle feature.
Electrical Connections
Electrical connections are a fundamental aspect of Cigarette Socket Wiring Diagrams, ensuring the safe and efficient operation of the socket and connected devices. Proper wiring practices minimize electrical hazards, prevent damage to components, and optimize power flow.
- Power Source Connection: The socket must be correctly connected to the vehicle’s electrical system, typically via the fuse box or directly to the battery. This connection provides the necessary power supply for the socket.
- Socket Wiring: The socket itself requires proper wiring to ensure current flow and prevent overheating. The wire gauge and type should be appropriate for the amperage rating of the socket and the connected devices.
- Device Compatibility: Devices plugged into the socket should be compatible with its voltage and amperage output. Mismatched devices can lead to damage or malfunction.
- Grounding: Proper grounding of the socket and connected devices provides a safe path for electrical current to return to the vehicle’s chassis, preventing electrical shocks and ensuring stable operation.
These electrical connections are crucial for the functionality and safety of Cigarette Socket Wiring Diagrams. By understanding and adhering to proper wiring practices, vehicle owners can ensure the reliable operation of their electronic devices while on the go.
Safety Measures
Within the context of Cigarette Socket Wiring Diagrams, safety measures play a critical role in minimizing electrical hazards and ensuring the safe operation of the socket and connected devices. These measures include proper insulation, grounding, and fuse protection, each contributing to the overall safety of the electrical system.
Proper insulation of wires prevents electrical shocks and short circuits by ensuring that current flows only through the intended paths. Grounding provides a safe path for electrical current to return to the vehicle’s chassis, preventing voltage spikes and potential shocks. Fuse protection safeguards the socket and connected devices from damage caused by electrical overloads or short circuits by interrupting the current flow when it exceeds a predetermined safe level.
Real-life examples of these safety measures in Cigarette Socket Wiring Diagrams include:
- Insulated wires used to connect the socket to the power source and devices.
- A grounding wire connected to the socket and the vehicle’s chassis.
- A fuse or circuit breaker installed in the circuit to protect against overloads.
Understanding the connection between safety measures and Cigarette Socket Wiring Diagrams is crucial for ensuring the safe and reliable operation of electronic devices in vehicles. By adhering to proper safety guidelines, vehicle owners can minimize the risk of electrical hazards, protect their devices, and maintain a safe electrical environment.
Socket Compatibility
Within the context of Cigarette Socket Wiring Diagrams, socket compatibility plays a critical role in preventing overheating and device damage. It ensures that the socket can safely handle the electrical load of the connected devices and operates within its intended parameters.
Cause and Effect:Choosing an incompatible socket can lead to excessive current draw, which can cause overheating, melting of the socket or wiring, and potential damage to connected devices. Conversely, using a compatible socket ensures that the current flow is within safe limits, preventing these hazards.
Critical Component:Socket compatibility is a crucial component of Cigarette Socket Wiring Diagrams as it directly impacts the safety and functionality of the electrical system. Selecting the correct socket type and amperage rating is essential to prevent overheating and device damage.
Real-Life Examples:– Choosing a 12V socket with an amperage rating compatible with the connected device (e.g., GPS unit, phone charger).
Practical Applications:Understanding the importance of socket compatibility empowers vehicle owners and installers to make informed decisions when selecting and installing cigarette sockets. This knowledge helps prevent electrical hazards, ensures reliable operation of devices, and extends the lifespan of both the socket and connected electronics.
Summary:Socket compatibility is a vital aspect of Cigarette Socket Wiring Diagrams, directly influencing the safety and functionality of the electrical system in vehicles. Choosing the correct socket type and amperage rating prevents overheating, device damage, and potential electrical hazards. By understanding this critical connection, vehicle owners and installers can ensure the safe and effective operation of electronic devices while on the go.
Power Source
Within the context of Cigarette Socket Wiring Diagrams, identifying the vehicle’s electrical system and selecting the appropriate power source for the socket are critical steps that ensure the safe and efficient operation of the socket and connected devices. Selecting an incompatible power source can lead to electrical hazards, damage to the socket or devices, or insufficient power supply.
- Electrical System Compatibility: The vehicle’s electrical system (12V or 24V) must match the voltage requirements of the socket and connected devices. Using an incompatible voltage can damage the socket or devices.
- Power Source Options: Vehicles may offer multiple power sources, such as the battery, fuse box, or dedicated power outlets. Selecting the appropriate source ensures sufficient power supply and prevents overloading.
- Fuse or Circuit Breaker Protection: Installing a fuse or circuit breaker in the circuit protects the socket and devices from overcurrent conditions that could cause damage or electrical fires.
- Wire Gauge and Length: The wire gauge and length used to connect the socket to the power source should be appropriate for the amperage draw of the socket and devices, ensuring minimal voltage drop and safe current flow.
Understanding the critical nature of power source selection in Cigarette Socket Wiring Diagrams empowers vehicle owners and installers to make informed decisions. By carefully considering the electrical system compatibility, power source options, protection measures, and wire specifications, they can ensure the safe and reliable operation of their electronic devices while on the go.
Wire Gauge and Type
In the context of Cigarette Socket Wiring Diagrams, selecting the correct wire gauge and type is essential for ensuring adequate current flow and preventing voltage drop, which can impact the performance and safety of the electrical system.
- Wire Gauge: The wire gauge, measured in American Wire Gauge (AWG), determines the thickness of the wire and its current-carrying capacity. A thicker wire (lower AWG number) allows for higher current flow with less voltage drop.
- Insulation: The insulation around the wire prevents electrical shorts and ensures safe operation. Different types of insulation materials offer varying levels of protection against heat, abrasion, and chemicals.
- Voltage Drop: Voltage drop occurs when there is resistance in the wire, causing a decrease in voltage at the socket. Using a wire with an appropriate gauge and insulation minimizes voltage drop, ensuring that devices receive the necessary voltage.
- Real-Life Example: In a Cigarette Socket Wiring Diagram, a 12-gauge wire with high-temperature insulation is recommended for connecting the socket to the power source, as it can safely handle the current draw of most devices and withstand the heat generated.
Understanding the importance of wire gauge and type empowers individuals to make informed decisions when installing or modifying Cigarette Socket Wiring Diagrams. By selecting the correct wire specifications, they can ensure the reliable operation of electronic devices, prevent electrical hazards, and maintain a safe and efficient electrical system in their vehicles.
Circuit Protection
Circuit protection is a crucial aspect of Cigarette Socket Wiring Diagrams, safeguarding the socket, connected devices, and the vehicle’s electrical system from potential damage caused by electrical overloads. Implementing fuses or circuit breakers in the circuit provides a controlled and safe response to excessive current flow, preventing hazardous situations.
- Fuse Protection: A fuse is a sacrificial device that interrupts the circuit when the current exceeds a predetermined safe level. It consists of a thin wire that melts and breaks the circuit, preventing further current flow and protecting the socket and devices.
- Circuit Breaker Protection: A circuit breaker is a resettable device that automatically switches off the circuit when an overload occurs. It contains a bimetallic strip that bends due to excessive current, tripping the breaker and interrupting the circuit. Once the overload is removed, the circuit breaker can be manually reset.
- Current Rating: Fuses and circuit breakers are rated for specific current capacities. Choosing the correct rating is essential to ensure that the protective device operates appropriately without nuisance tripping or failing to protect in the event of an overload.
- Wiring Considerations: Proper wiring practices are crucial for effective circuit protection. The wire gauge and type must be appropriate for the current draw of the socket and devices, minimizing voltage drop and preventing overheating.
Understanding circuit protection in Cigarette Socket Wiring Diagrams empowers individuals to implement safety measures that prevent electrical hazards, protect their devices, and extend the lifespan of the electrical system. By incorporating fuses or circuit breakers into the circuit, they can ensure a safe and reliable electrical environment for their vehicles and connected electronic devices.
Grounding
In the context of Cigarette Socket Wiring Diagrams, grounding plays a critical role in ensuring the safe operation of the electrical system. Proper grounding provides a safe path for electrical current to return to the vehicle’s chassis, preventing electrical shocks and potential hazards.
- Ground Wire: A grounding wire connects the socket’s metal housing to the vehicle’s chassis, providing a dedicated path for current to flow back to the negative terminal of the battery.
- Chassis Ground: The vehicle’s chassis acts as a common ground point, providing a reference for all electrical circuits and ensuring that stray currents are safely dissipated.
- Reduced Electrical Resistance: Proper grounding reduces electrical resistance in the circuit, allowing for efficient current flow and minimizing the risk of overheating or voltage drop.
- Safety Feature: Grounding serves as a safety feature, protecting users from electrical shocks. Without proper grounding, current could flow through unintended paths, increasing the risk of shocks or electrical fires.
Understanding the importance of grounding in Cigarette Socket Wiring Diagrams is crucial for ensuring a safe and reliable electrical system in vehicles. Proper grounding practices prevent electrical hazards, protect users, and extend the lifespan of electronic devices. By adhering to recommended grounding techniques, vehicle owners and installers can ensure that their electrical systems operate as intended, providing a safe and convenient way to power and charge devices while on the go.
Switch Control
Within the context of Cigarette Socket Wiring Diagrams, switch control is a critical component that enables users to conveniently manage the power supply to the socket. Integrating a switch in the circuit provides several advantages and enhances the overall user experience.
Cause and Effect: Incorporating a switch allows for manual control of the power supply to the socket. When the switch is in the “off” position, the socket is de-energized, preventing power flow to connected devices. This feature is particularly useful when the socket is not in immediate use, as it helps conserve power and prevents unnecessary battery drain.
Real-Life Examples: In practice, switch control is commonly implemented in Cigarette Socket Wiring Diagrams to provide users with the flexibility to turn the socket on or off as needed. For instance, in vehicles, a switch can be installed on the dashboard or center console, allowing the driver or passengers to conveniently control the power supply to the socket.
Practical Applications: Understanding the connection between switch control and Cigarette Socket Wiring Diagrams empowers vehicle owners and installers to design and implement electrical systems that meet their specific needs. By incorporating a switch, they can enjoy the benefits of controlled power supply, extending the lifespan of connected devices and enhancing overall convenience.
Summary: Switch control is an integral part of Cigarette Socket Wiring Diagrams, providing users with the ability to manually manage the power supply to the socket. This feature allows for efficient power consumption, prevents battery drain, and enhances the user experience by enabling convenient control of connected devices.
Socket Placement
Socket placement plays a crucial role in the design and implementation of Cigarette Socket Wiring Diagrams. Choosing a suitable location for the socket is essential to ensure accessibility, safety, and aesthetic compatibility within the vehicle.
- Accessibility: The socket’s location should provide convenient access for users to plug and unplug devices without causing discomfort or distraction while driving. Common placement areas include the dashboard, center console, or armrest.
- Safety: The socket should be positioned to minimize the risk of electrical hazards. It should not be located near flammable materials or in areas where it could be easily damaged by spills or impact. Proper mounting and insulation are crucial to prevent short circuits or electrical fires.
- Aesthetics: The socket’s placement should also consider the vehicle’s interior design. It should complement the overall aesthetics and not appear out of place or visually distracting. Factors such as color, shape, and finish should be taken into account.
- Ergonomics: The socket’s location should be ergonomic, allowing users to easily reach and operate it without straining or compromising their driving posture. This is especially important for sockets that will be frequently used while driving.
By carefully considering these aspects of socket placement, vehicle owners and installers can ensure that their Cigarette Socket Wiring Diagrams meet the highest standards of functionality, safety, and aesthetics. Proper socket placement enhances the user experience, promotes safe operation, and maintains the vehicle’s overall design integrity.
Compatibility with Devices
In the context of Cigarette Socket Wiring Diagrams, compatibility between the socket and the powered devices is paramount. Choosing incompatible devices can lead to damage to the socket, devices, or both, as well as hinder optimal charging performance.
Cause and Effect: Using an incompatible device with a cigarette socket can result in excessive current draw, leading to overheating, melting of the socket or wiring, and potential damage to the device. Conversely, using compatible devices ensures that the current flow is within safe limits, preventing these hazards and ensuring efficient charging.
Importance as a Component: Compatibility with devices is a critical component of Cigarette Socket Wiring Diagrams as it directly impacts the safety and functionality of the electrical system. Selecting compatible devices prevents electrical hazards, protects the socket and devices from damage, and optimizes charging efficiency.
Real-Life Examples:
- Using a phone charger specifically designed for use with cigarette sockets, ensuring compatibility with the socket’s voltage and amperage output.
- Choosing a GPS unit with a cigarette socket adapter that matches the socket’s electrical specifications.
Practical Applications: Understanding the connection between compatibility and Cigarette Socket Wiring Diagrams empowers vehicle owners and installers to make informed decisions when selecting and using devices with cigarette sockets. This knowledge helps prevent electrical hazards, ensures reliable device operation, and maximizes charging efficiency.
Conclusion: Compatibility between cigarette sockets and powered devices is a vital aspect of Cigarette Socket Wiring Diagrams, directly influencing the safety and functionality of the electrical system in vehicles. By understanding this critical connection, vehicle owners and installers can ensure the safe and effective operation of electronic devices while on the go.








Related Posts








