Crossover cable wiring refers to a specific type of Ethernet cable used to connect two devices directly without the need for a switch or hub. A typical usage scenario is connecting two computers for data transfer or troubleshooting network issues. The cable features a unique wiring configuration where the transmit pins on one end are connected to the receive pins on the other, and vice versa.
Crossover cables are especially relevant for situations where a direct connection between devices is required and no network infrastructure is available. They offer benefits such as simplicity, ease of setup, and cost-effectiveness. Historically, crossover cables played a crucial role in the early days of networking, enabling direct peer-to-peer communication before the widespread adoption of switches and routers.
This article delves into the technical aspects of crossover cable wiring, including its pinout diagram, cable specifications, and compatibility with different network devices. It also explores advanced topics such as auto-MDIX technology and how it has made crossover cables less necessary in modern networking environments. By understanding the principles of crossover cable wiring, network administrators and technicians can effectively troubleshoot and manage network connectivity issues.
Understanding the essential aspects of crossover cable wiring is crucial for effective network management and troubleshooting. These aspects encompass:
- Pinout configuration
- Cable specifications
- Network compatibility
- Direct device connection
- Simplified setup
- Cost-effectiveness
- Auto-MDIX technology
- Legacy networking
Each of these aspects plays a vital role in the functionality and application of crossover cables. For instance, the pinout configuration defines the specific wiring scheme that enables direct communication between two devices. Cable specifications determine the transmission speed and distance limitations, while network compatibility ensures seamless integration with different types of network devices. Auto-MDIX technology has significantly simplified crossover cable usage by automatically detecting and configuring the correct pinout. By delving into these key aspects, network professionals can gain a comprehensive understanding of crossover cable wiring and its relevance in modern networking environments.
Pinout configuration
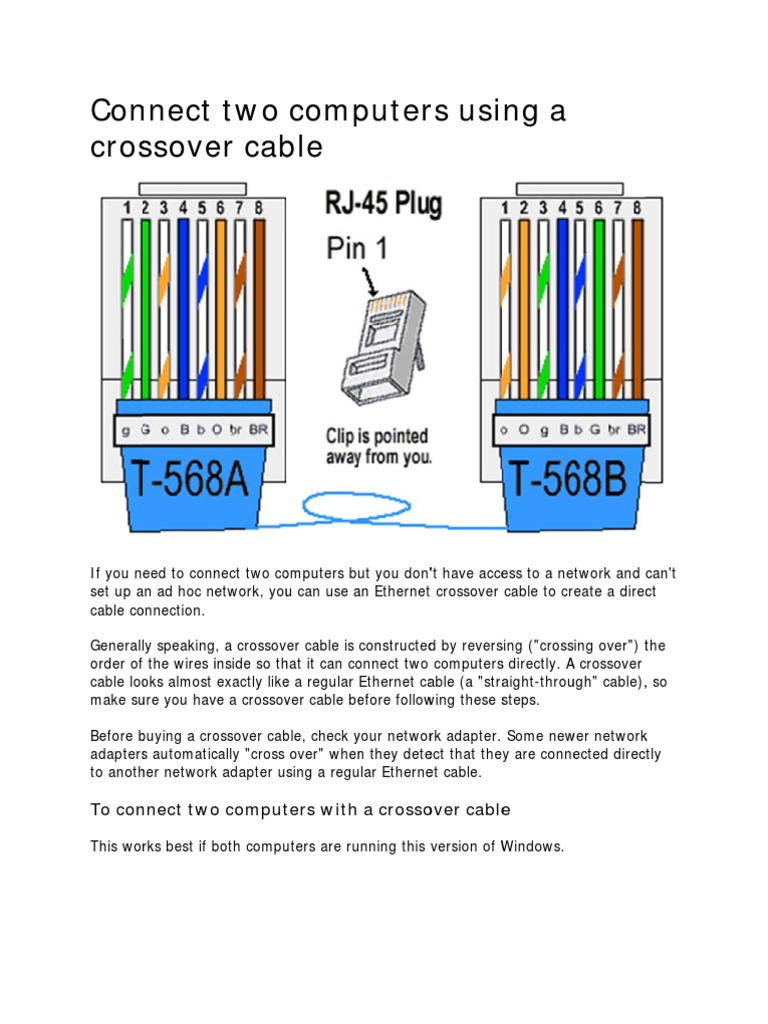
Pinout configuration plays a fundamental role in crossover cable wiring, determining the specific arrangement of wires within the cable and the connections between the transmit and receive pins on each end. Without the correct pinout configuration, crossover cables would not be able to facilitate direct communication between two devices. The pinout defines which wire is connected to which pin on the RJ-45 connectors at both ends of the cable, ensuring that the transmit pins on one end are connected to the receive pins on the other, and vice versa.
Understanding the pinout configuration is crucial for troubleshooting and maintaining crossover cables. If the wires are not properly connected according to the pinout, the devices connected by the cable will not be able to communicate. For instance, if the transmit and receive pins are not correctly crossed over, data transmission will not occur, and the devices will not be able to establish a connection. Therefore, it is essential for network professionals to be familiar with the pinout diagram of crossover cables.
In practice, the pinout configuration of crossover cables follows the TIA-568A or TIA-568B wiring standard. TIA-568A is the most commonly used standard, where the transmit and receive pairs are crossed over on pins 1 and 2, and pins 3 and 6. TIA-568B, on the other hand, uses a different pinout configuration where the transmit and receive pairs are crossed over on pins 1 and 2, and pins 3 and 5. By adhering to these standards, network professionals can ensure that crossover cables are wired correctly and function as intended.
In summary, pinout configuration is a critical aspect of crossover cable wiring, as it defines the connections between the transmit and receive pins on each end of the cable. Understanding the pinout diagram is essential for troubleshooting and maintaining crossover cables, and adhering to the TIA-568A or TIA-568B wiring standards ensures proper functionality.
Cable specifications
Cable specifications play a critical role in crossover cable wiring, determining the performance and capabilities of the cable. These specifications define various characteristics of the cable, such as the type of conductor material, the number of twisted pairs, the cable jacket material, and the overall cable length. Each of these specifications has a direct impact on the transmission speed, signal quality, and durability of the crossover cable.
One of the most important cable specifications is the conductor material. Copper is the most commonly used conductor material for crossover cables due to its excellent conductivity and cost-effectiveness. However, copper cables can be susceptible to signal loss over long distances. For longer runs, aluminum-clad copper (CCA) cables can be used as a more economical alternative, although they may have slightly higher signal loss than pure copper cables. Stranded conductors are also preferred over solid conductors for crossover cables, as they provide greater flexibility and durability.
Another important specification is the number of twisted pairs within the cable. Crossover cables typically use four twisted pairs, which are necessary for transmitting data at Gigabit Ethernet speeds. The twisting of the pairs helps to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk between the pairs, ensuring reliable signal transmission. The cable jacket material also plays a role in the durability and environmental resistance of the crossover cable. PVC (polyvinyl chloride) is a commonly used jacket material for indoor applications, while polyethylene (PE) is preferred for outdoor use due to its resistance to sunlight and moisture.
Understanding the cable specifications of crossover cables is essential for network professionals to select the appropriate cable for their specific application. By considering factors such as transmission speed, distance, and environmental conditions, they can choose a crossover cable that meets the performance and reliability requirements of their network.
Network compatibility
Network compatibility is a critical aspect of crossover cable wiring, as it determines whether the cable can successfully establish and maintain a connection between two devices. Without network compatibility, the devices will not be able to communicate with each other, regardless of the physical connection provided by the crossover cable.
One of the key factors affecting network compatibility is the network interface card (NIC) installed in each device. The NIC is responsible for managing the network connection and ensuring that data is transmitted and received in a compatible format. If the NICs in the two devices are not compatible, the crossover cable will not be able to facilitate communication between them.
Another important factor is the network protocol being used. The network protocol defines the rules and procedures for data transmission and reception. If the two devices are using different network protocols, they will not be able to communicate with each other, even if they have compatible NICs. Common network protocols include Ethernet, TCP/IP, and UDP.
Understanding network compatibility is essential for network professionals to troubleshoot and resolve connectivity issues. By verifying that the NICs and network protocols are compatible, they can eliminate one potential cause of network problems. Additionally, network compatibility should be considered when selecting crossover cables for specific applications. By choosing cables that are compatible with the devices and protocols being used, network professionals can ensure reliable and efficient network connectivity.
Direct device connection
In the realm of networking, direct device connection plays a pivotal role in enabling communication between devices without the need for intermediary network infrastructure. Crossover cable wiring serves as a crucial medium for establishing such direct connections, facilitating data transfer and troubleshooting.
-
Peer-to-peer communication
Crossover cables allow two devices, such as computers or network switches, to communicate directly with each other without the use of a router or hub. This peer-to-peer connection is particularly useful for data transfer, file sharing, and network diagnostics.
-
Troubleshooting
When troubleshooting network connectivity issues, crossover cables can be used to isolate the problem by connecting two devices directly and eliminating the possibility of issues with other network components, such as routers or switches.
-
Temporary connections
Crossover cables offer a simple and cost-effective solution for temporary network connections, such as connecting two laptops for data transfer or setting up a small network for a specific event.
-
Cost-effectiveness
Compared to using a switch or hub, crossover cables are a more economical option for establishing direct device connections, making them suitable for small-scale or temporary networking needs.
Direct device connection via crossover cable wiring provides numerous benefits, including simplified network setup, ease of troubleshooting, and cost-effectiveness. By understanding the various facets and applications of direct device connection, network professionals can effectively utilize crossover cables to meet their specific networking requirements.
Simplified setup
Within the realm of networking, “Simplified setup” stands as a cornerstone of “Crossover Cable Wiring,” enabling network professionals to establish direct connections between devices with minimal effort and configuration. This streamlined approach offers numerous advantages, ranging from reduced setup time to enhanced troubleshooting capabilities.
-
Elimination of Intermediary Devices
Unlike traditional networking setups that require switches or hubs, crossover cables allow direct device-to-device connections, removing the need for additional hardware and simplifying the overall network topology.
-
Plug-and-Play Functionality
Crossover cables often feature plug-and-play functionality, requiring minimal configuration or driver installation. Simply connecting the cable between two compatible devices typically establishes a functional network connection.
-
Cost-Effective Solution
Compared to more complex networking setups involving multiple devices and configurations, crossover cables offer a cost-effective solution for small-scale or temporary network connections.
-
Enhanced Troubleshooting
In troubleshooting network connectivity issues, crossover cables can be invaluable tools. By isolating direct connections between devices, network professionals can quickly identify and resolve problems without the interference of other network components.
The simplified setup offered by crossover cable wiring translates to significant advantages in terms of time savings, reduced complexity, and cost-effectiveness. These attributes make crossover cables an essential tool for network engineers, technicians, and even home users seeking to establish direct and reliable network connections.
Cost-effectiveness
Within the realm of networking, “Cost-effectiveness” stands as a primary consideration, particularly when exploring solutions such as “Crossover Cable Wiring.” This practicality-driven approach aims to optimize network functionality while minimizing financial outlay, making it an essential aspect of modern networking strategies.
Crossover cables, by design, embody the principles of cost-effectiveness. Their simple construction and direct connection approach eliminate the need for additional hardware components like switches or hubs, significantly reducing the overall cost of network setup. Moreover, the absence of complex configurations and minimal installation requirements further contribute to the cost-saving benefits of crossover cable wiring. Compared to more elaborate networking solutions, crossover cables offer a budget-friendly alternative, particularly for small-scale or temporary network deployments.
Real-life examples further underscore the cost-effectiveness of crossover cable wiring. In home networking scenarios, individuals seeking to establish a direct connection between two computers for data transfer or troubleshooting purposes can leverage crossover cables as a cost-efficient solution. Similarly, small businesses with limited budgets can utilize crossover cables to create simple and functional networks without incurring substantial expenses. The practicality of crossover cable wiring extends to educational institutions and non-profit organizations, where cost constraints often dictate networking choices.
Understanding the cost-effectiveness of crossover cable wiring empowers network professionals and users alike to make informed decisions when designing and implementing network solutions. By carefully considering the financial implications and comparing it with other available options, they can optimize network performance while adhering to budgetary limitations. This understanding also enables organizations to allocate resources wisely, prioritizing critical investments while leveraging cost-effective solutions like crossover cable wiring for non-essential or temporary networking needs.
Auto-MDIX technology
In the realm of networking, “Auto-MDIX technology” stands as a significant advancement that has revolutionized the use of “Crossover Cable Wiring.” By automatically detecting the cable type and configuring the network interface accordingly, Auto-MDIX technology has greatly simplified network setup and reduced the need for specialized crossover cables.
-
Automatic Crossover Detection
Auto-MDIX technology utilizes advanced circuitry to detect the type of cable connected to a network interface. It can automatically determine whether a straight-through cable or a crossover cable is being used, eliminating the need for manual configuration or the use of dedicated crossover cables.
-
Simplified Cabling
With Auto-MDIX technology, network administrators can use either straight-through cables or crossover cables interchangeably. The technology automatically adjusts the pin configuration to match the cable type, simplifying cable management and reducing the risk of misconfigurations.
-
Compatibility with Legacy Devices
Auto-MDIX technology is backward compatible with legacy network devices that do not support Auto-MDIX. This ensures seamless integration and interoperability between old and new devices, providing a smooth transition to modern networking standards.
-
Increased Flexibility
Auto-MDIX technology offers greater flexibility in network design and deployment. It allows network professionals to mix and match different cable types and devices without worrying about compatibility issues, making network setup and maintenance more efficient.
In summary, Auto-MDIX technology has significantly enhanced the functionality and usability of Crossover Cable Wiring. Its automatic crossover detection, simplified cabling, legacy device compatibility, and increased flexibility have made it an essential feature in modern networking environments. By eliminating the need for dedicated crossover cables and simplifying network setup, Auto-MDIX technology has contributed to the widespread adoption of twisted-pair Ethernet and the ease of network management.
Legacy networking
Legacy networking refers to the traditional methods and technologies used in computer networking before the widespread adoption of modern standards and protocols. These legacy systems often lack the advanced features and capabilities of contemporary networks but remain in use due to their compatibility with older devices and applications.
In the context of Crossover Cable Wiring, legacy networking plays a significant role. Crossover cables were originally designed to connect two network devices directly without the need for a switch or hub. This type of wiring was commonly used in early network setups and is still employed in specific scenarios today, such as troubleshooting, connecting older devices, or creating simple peer-to-peer networks.
Real-life examples of legacy networking within Crossover Cable Wiring include connecting two legacy computers to transfer files or share resources, or using a crossover cable to establish a direct connection between a computer and a network switch for diagnostic purposes. Understanding the relationship between legacy networking and Crossover Cable Wiring is crucial for network professionals who may encounter these technologies in their work.
In summary, legacy networking forms the foundation of Crossover Cable Wiring, providing a backward-compatible solution for connecting older devices and supporting specific networking scenarios. By understanding this connection, network engineers and administrators can effectively troubleshoot, maintain, and manage networks that incorporate legacy components.







Related Posts








