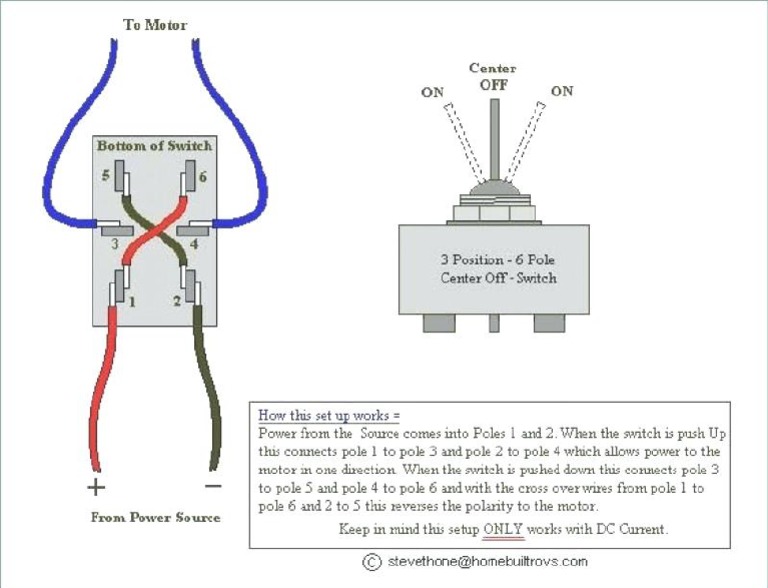
A 3-position switch wiring diagram outlines the electrical connections for a switch with three distinct positions. It provides a visual guide to wire the switch correctly, ensuring proper operation and safety.
3-position switches are commonly used in various applications, such as lighting control, fan speed regulation, and appliance operation. Their relevance lies in the ability to select among three different states or functions, making them versatile and efficient.
Historically, 3-position switches have played a crucial role in electrical systems. Their development has enabled more sophisticated control over electrical devices, improving convenience and functionality.
The article will delve deeper into the specific wiring configurations, connections, and applications of 3-position switches. It will also explore advanced features, recent developments, and practical examples to provide a comprehensive understanding of this versatile electrical component.
Understanding the essential aspects of a 3-position switch wiring diagram is critical for its effective implementation. These aspects encompass the fundamental characteristics, functions, and applications of the switch.
- Components: Terminal screws, switch body, actuator.
- Connections: Line, load, and neutral wires.
- Positions: Off, on, and momentary.
- Wiring Configurations: Single-pole, double-pole, three-way.
- Applications: Lighting control, fan speed regulation, appliance operation.
- Safety Precautions: Electrical code compliance, proper insulation.
- Troubleshooting: Identifying and resolving common issues.
- Advanced Features: Illuminated switches, timed switches.
- Historical Development: From simple toggles to modern smart switches.
These aspects are interconnected and play vital roles in the overall functionality of a 3-position switch wiring diagram. By understanding each aspect, electricians and homeowners can ensure the safe and efficient operation of electrical systems utilizing these switches, enabling control and convenience in various applications.
Components
In the context of a 3-position switch wiring diagram, the components play a crucial role in establishing and maintaining electrical connections. These components include terminal screws, switch body, and actuator, each with distinct functions and implications.
-
Terminal Screws
Terminal screws are responsible for securing the electrical wires to the switch. They provide a reliable connection point, ensuring proper current flow and preventing loose connections that could lead to electrical hazards. -
Switch Body
The switch body houses the internal mechanism of the switch, including the contacts and terminals. It provides insulation and protection for the electrical components, ensuring safe operation and preventing external influences from affecting the switch’s functionality. -
Actuator
The actuator is the part of the switch that is physically manipulated to change its position. It can be a lever, a rocker, or a push button, depending on the switch design. The actuator triggers the internal mechanism to switch between different positions, controlling the flow of electricity.
Understanding the components of a 3-position switch wiring diagram is essential for proper installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting. By ensuring that each component is correctly connected and functioning as intended, electricians and homeowners can guarantee the reliable and safe operation of electrical systems utilizing these switches.
Connections
In the realm of 3-position switch wiring diagrams, understanding the connections between line, load, and neutral wires is paramount. These connections form the backbone of the electrical circuit, ensuring proper functionality and safety. Here’s a breakdown of the individual components and their implications:
-
Line Wire
The line wire, typically black or red, carries the incoming power from the electrical panel to the switch. It serves as the source of electricity for the circuit. -
Load Wire
The load wire, usually black or blue, connects the switch to the electrical device being controlled, such as a light fixture or fan. It carries the electricity from the switch to the load. -
Neutral Wire
The neutral wire, generally white or gray, provides a path for the current to complete the circuit. It connects the electrical device back to the electrical panel, creating a closed loop for the electricity to flow. -
Ground Wire
In many modern wiring systems, a ground wire (usually green or bare copper) is also included for safety. It provides a low-resistance path for any stray electrical current, protecting against electrical shock and potential damage.
Correctly connecting these wires is essential for the safe and effective operation of a 3-position switch wiring diagram. By adhering to electrical codes and industry standards, electricians can ensure that the electrical circuit functions as intended, providing reliable control and safety in various electrical applications.
Positions
In the context of 3-position switch wiring diagrams, the switch positionsoff, on, and momentarydefine the switch’s operation and behavior when it is in each position. Understanding these positions is crucial for proper installation, functionality, and safety in electrical systems.
-
Off Position
In the off position, the switch breaks the electrical circuit, preventing current flow between the line and load wires. This position is typically used to turn off a light or appliance, cutting off power to the device.
-
On Position
The on position establishes a closed circuit, allowing current to flow from the line wire through the switch to the load wire. This position is used to turn on a light or appliance, providing power to the device.
-
Momentary Position
The momentary position is a spring-loaded position that completes the circuit only while the actuator is physically held in that position. When the actuator is released, the switch returns to the off position, breaking the circuit. This position is commonly used for momentary functions such as doorbells or garage door openers.
-
Additional Positions
Some 3-position switches may have additional positions beyond off, on, and momentary, depending on their specific design and application. These additional positions may provide specialized functions or control multiple circuits.
The positions of a 3-position switch determine its functionality and allow for versatile control in various electrical applications. By understanding the off, on, and momentary positions, electricians and homeowners can effectively design and implement 3-position switch wiring diagrams, ensuring safe and efficient operation of electrical systems.
Wiring Configurations
In the realm of electrical systems, wiring configurations play a pivotal role in determining the functionality and control of electrical circuits. Within the context of 3-position switch wiring diagrams, the choice of wiring configuration significantly impacts the switch’s behavior and application.
Single-pole, double-pole, and three-way wiring configurations represent the fundamental types used with 3-position switches. Each configuration serves a distinct purpose and is tailored to specific electrical requirements:
- Single-pole: A single-pole configuration is the most basic and commonly used wiring method for 3-position switches. It involves controlling a single circuit, typically used for simple on/off switching of lights or appliances.
- Double-pole: A double-pole configuration is employed when it is necessary to control two separate circuits simultaneously with a single switch. This configuration is often used for controlling lights or appliances in different locations or for safety purposes.
- Three-way: A three-way configuration is utilized when controlling a light or appliance from multiple locations is desired. This configuration involves using two or more 3-position switches wired together to achieve multi-point control.
Understanding the different wiring configurations and their compatibility with 3-position switch wiring diagrams is essential for designing and implementing electrical systems effectively. Proper selection and implementation of these configurations ensure that electrical circuits function as intended, providing safe and efficient control in various applications.
Applications
3-position switch wiring diagrams find practical applications in controlling various electrical devices, including lighting, fans, and appliances. These applications stem from the ability of 3-position switches to provide multiple control options within a single electrical circuit.
In lighting control, 3-position switch wiring diagrams are commonly used to provide on/off/dimming functionality. This allows users to adjust the brightness of lights to suit different needs and preferences. The switch’s three positions correspond to off, low light, and high light, offering versatility in lighting control.
Fan speed regulation is another common application of 3-position switch wiring diagrams. By connecting a 3-position switch to a fan, users can control the fan’s speed in three distinct levels: low, medium, and high. This flexibility enables users to adjust the airflow to achieve optimal comfort levels.
Appliance operation also benefits from the versatility of 3-position switch wiring diagrams. For example, a 3-position switch can be used to control a water pump, with the three positions corresponding to off, low flow, and high flow. This allows users to regulate the water flow rate to meet specific requirements.
Understanding the connection between 3-position switch wiring diagrams and their applications in lighting control, fan speed regulation, and appliance operation is crucial for electrical professionals and homeowners alike. It enables the design and implementation of efficient and user-friendly control systems for various electrical devices.
Safety Precautions
When working with electrical systems, adhering to safety precautions is paramount. In the context of 3-position switch wiring diagrams, electrical code compliance and proper insulation play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and reliability of the electrical installation.
-
Electrical Code Compliance
Electrical codes provide a set of regulations and standards that govern the installation and maintenance of electrical systems. These codes aim to minimize the risk of electrical fires, shocks, and other hazards. When wiring a 3-position switch, it is essential to follow the electrical code requirements for your specific location, ensuring that the installation meets the necessary safety standards.
-
Proper Insulation
Proper insulation is crucial for preventing electrical shocks and short circuits. All electrical wires and connections should be properly insulated to prevent accidental contact with live conductors. In the context of 3-position switch wiring diagrams, it is essential to use wires with the appropriate insulation rating for the voltage and current involved. Additionally, wire nuts or other approved methods should be used to securely insulate and protect the connections.
-
Grounding
Grounding provides a safe path for electrical current to flow in the event of a fault or short circuit. In a 3-position switch wiring diagram, the switch box and all electrical components should be properly grounded to prevent electrical shocks and protect against electrical fires.
-
Circuit Protection
Circuit protection devices, such as fuses or circuit breakers, are essential for protecting electrical circuits from overloads and short circuits. In a 3-position switch wiring diagram, the circuit feeding the switch should be protected by an appropriately sized circuit breaker or fuse to prevent damage to the switch or other electrical components.
By adhering to these safety precautions, electricians and homeowners can ensure that 3-position switch wiring diagrams are implemented safely and in accordance with electrical codes. This helps to minimize the risk of electrical hazards, protect against damage to electrical equipment, and ensure the reliable operation of electrical systems.
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting is an essential aspect of working with 3-position switch wiring diagrams, as it allows electricians and homeowners to identify and resolve common issues that may arise during installation or operation. By understanding the potential problems that can occur and the steps to take to address them, it is possible to ensure the reliable and safe functioning of 3-position switch wiring systems.
One of the most common issues with 3-position switch wiring diagrams is incorrect wiring. This can occur due to various reasons, such as loose connections, faulty components, or incorrect switch configuration. Troubleshooting involves carefully examining the wiring diagram, checking for loose connections, and ensuring that all components are properly connected. Additionally, testing the switch with a multimeter can help identify any electrical faults or continuity issues.
Another common issue is switch malfunction. This can be caused by wear and tear, dirt accumulation, or internal damage. Troubleshooting switch malfunction involves inspecting the switch for any visible damage, cleaning the contacts, and testing the switch’s functionality. If the switch is found to be faulty, it may need to be replaced.
Understanding how to troubleshoot 3-position switch wiring diagrams is crucial for ensuring the proper functioning of electrical systems. By identifying and resolving common issues, electricians and homeowners can prevent potential hazards, maintain electrical safety, and ensure the reliable operation of electrical devices.
Advanced Features
Within the realm of 3-position switch wiring diagrams, advanced features such as illuminated switches and timed switches enhance functionality and provide greater control over electrical systems. These features offer additional capabilities beyond basic on/off switching, enabling customization and automation to meet specific requirements.
-
Illuminated Switches
Illuminated switches incorporate a small light source that glows when the switch is in the on position. This feature provides visual indication of the switch’s state, making it easier to locate in dimly lit areas or during nighttime. Illuminated switches are commonly used in bedrooms, hallways, and other areas where quick and easy identification of the switch is desired.
-
Timed Switches
Timed switches allow for automated control of electrical devices by turning them on or off at predetermined times. These switches are equipped with a timer that can be set to specific intervals, enabling devices to be turned on or off without manual intervention. Timed switches are commonly used to control lighting, fans, and other appliances, providing convenience and energy savings.
The advanced features of illuminated switches and timed switches extend the capabilities of 3-position switch wiring diagrams, providing greater flexibility, convenience, and control over electrical systems. These features cater to specific needs and preferences, enhancing the functionality and user experience of electrical installations.
Historical Development
The evolution of electrical switches, from simple toggles to advanced smart switches, has significantly influenced the design and functionality of 3-position switch wiring diagrams. In this exploration, we will delve into the connection between the historical development of switches and the impact on modern wiring diagrams.
Initially, switches were basic toggle mechanisms that simply turned circuits on or off. These early switches, while effective in their simplicity, lacked the versatility and control offered by modern counterparts. The advent of 3-position switches introduced the concept of controlling circuits in multiple states, allowing for expanded functionality and user convenience.
The introduction of illuminated switches further enhanced the usability of 3-position switch wiring diagrams by providing visual indication of the switch’s state. This feature is particularly beneficial in dimly lit environments or during nighttime, making it easier to locate and operate the switch as desired.
The latest advancement in switch technology is the emergence of smart switches. These switches integrate advanced electronics and connectivity features, enabling remote control, scheduling, and automation capabilities. Smart switches seamlessly integrate with 3-position switch wiring diagrams, providing unparalleled control and energy efficiency.
Understanding the historical development of electrical switches is crucial for fully appreciating the capabilities and applications of modern 3-position switch wiring diagrams. By tracing the evolution from simple toggles to smart switches, electrical professionals and homeowners alike can gain valuable insights into the design, functionality, and practical significance of these essential electrical components.








Related Posts








