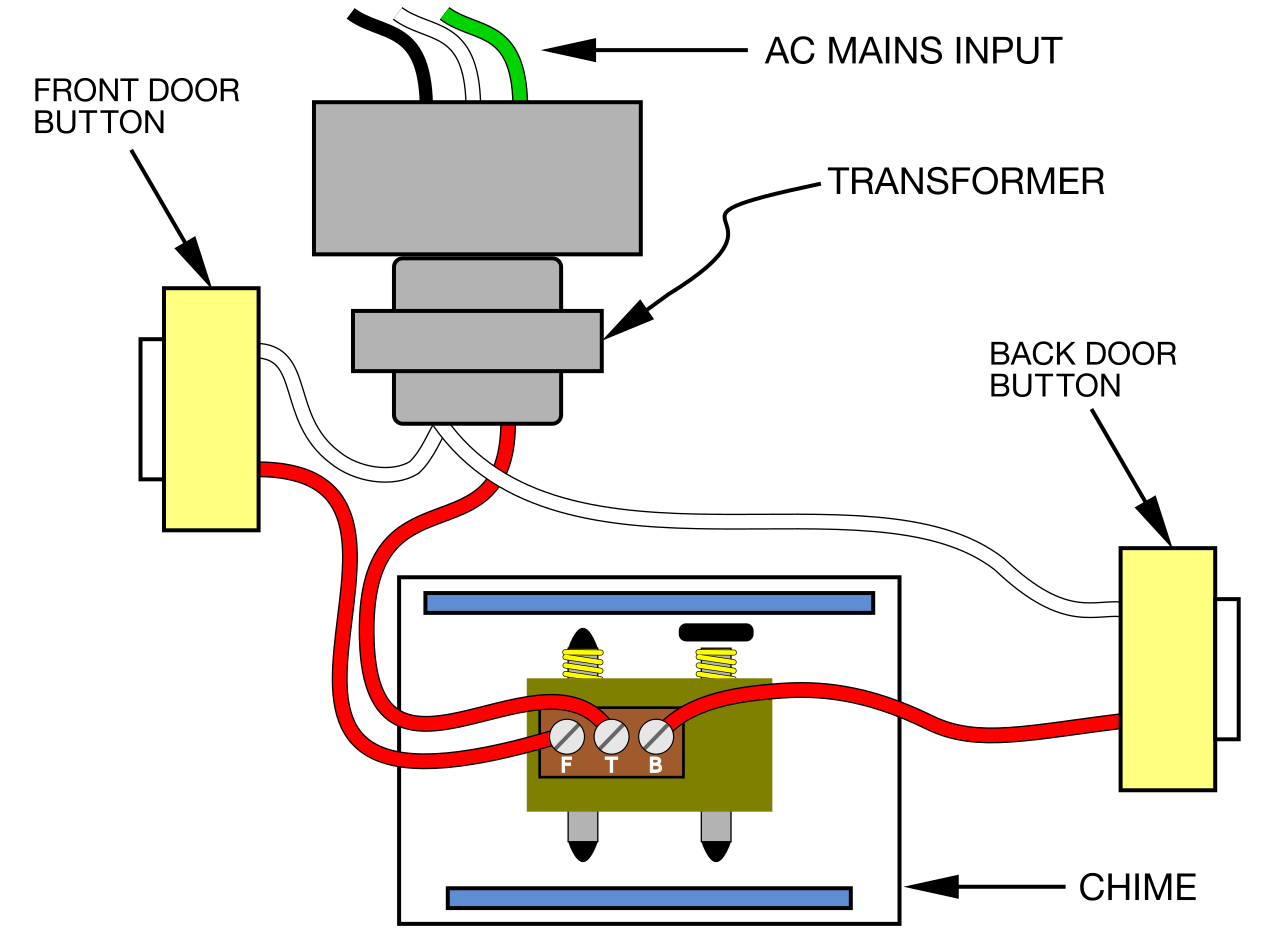
A Doorbell Chime Wiring Diagram is a schematic representation of the electrical connections required to install and operate a doorbell chime system. It provides a visual guide for electricians and homeowners, ensuring that the chime is wired correctly and functions properly. For instance, a basic doorbell chime wiring diagram might show the connection between the doorbell button, transformer, and chime unit.
Wiring diagrams are crucial for ensuring electrical safety and system reliability. They help identify the proper wire gauges, circuit protection devices, and connection points. Historically, the invention of the doorbell transformer in the early 1900s revolutionized doorbell systems, allowing them to operate on lower voltages, making them safer and more convenient.
This article will delve into the various types of doorbell chime wiring diagrams, their applications, and essential considerations for proper installation. By understanding the fundamentals of doorbell chime wiring, readers can ensure the efficient and safe operation of their home security systems.
Understanding the essential aspects of Doorbell Chime Wiring Diagrams is crucial for ensuring the proper installation and operation of doorbell chime systems. These diagrams provide a visual representation of the electrical connections required, helping electricians and homeowners alike to avoid potential hazards and ensure the system’s reliability.
- Components: Doorbell button, transformer, chime unit, wires
- Connections: How the components are electrically connected
- Circuit Protection: Fuses or circuit breakers to protect against electrical faults
- Voltage: Typically 12-24 volts for safety and compatibility
- Wire Gauge: Thickness of the wires used, affecting current capacity
- Chime Types: Mechanical, electronic, wireless chimes with different tones and features
- Wiring Methods: Surface mount, concealed wiring, wireless options
- Troubleshooting: Identifying and resolving common issues with doorbell chime systems
These aspects are interconnected and play a vital role in the functionality of a doorbell chime system. For example, the voltage and wire gauge must be compatible to ensure sufficient power delivery, while proper circuit protection safeguards against electrical hazards. Understanding these aspects enables informed decision-making during installation and maintenance, ensuring a reliable and effective doorbell chime system.
Components
Components such as the doorbell button, transformer, chime unit, and wires are indispensable elements of a Doorbell Chime Wiring Diagram. These components work in conjunction to create a functional doorbell system, enabling communication between the doorbell button and the chime unit, which produces an audible alert when the button is pressed. A comprehensive understanding of the relationship between these components is critical for proper installation and maintenance of doorbell chime systems.
The doorbell button initiates the system’s operation. When pressed, it completes an electrical circuit, sending a signal to the transformer. The transformer reduces the voltage from the main power supply to a safer level, typically 12-24 volts, making the system safer and more energy-efficient. The reduced voltage is then supplied to the chime unit, which converts the electrical signal into an audible chime.
The proper selection and installation of these components are crucial. The doorbell button should be rated for outdoor use and weather-resistant. The transformer must be compatible with the chime unit’s voltage requirements and have sufficient power capacity to handle the load. The chime unit should be placed in an easily audible location and have adjustable volume and tone settings. The wires used for connections should be of appropriate gauge to prevent voltage drop and ensure reliable signal transmission.
In summary, the components of a Doorbell Chime Wiring Diagram, including the doorbell button, transformer, chime unit, and wires, play interdependent roles in the system’s operation. A clear understanding of their connections and functions is essential for proper installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting, ensuring a reliable and effective doorbell chime system.
Connections
In a Doorbell Chime Wiring Diagram, the connections between the components play a critical role in determining the system’s functionality and reliability. The proper electrical connections ensure that the doorbell button, transformer, and chime unit communicate effectively, resulting in the desired audible alert when the doorbell is pressed.
The connections begin at the doorbell button, which is typically a momentary switch that completes an electrical circuit when pressed. This sends a signal to the transformer, which steps down the voltage from the main power supply to a safer level, usually 12-24 volts. The reduced voltage is then supplied to the chime unit, which converts the electrical signal into an audible chime.
The connections between these components must be secure and follow the manufacturer’s instructions to prevent malfunctions or safety hazards. Incorrect wiring can lead to the system not functioning correctly, producing a weak or no chime sound, or even posing electrical risks. Therefore, it is essential to pay meticulous attention to the connections when installing or troubleshooting a doorbell chime system.
Understanding the connections between the components of a Doorbell Chime Wiring Diagram empowers individuals to troubleshoot and maintain their systems effectively. By identifying loose connections, faulty wires, or incorrect voltage levels, they can quickly resolve common issues, ensuring the system’s optimal performance. This knowledge is particularly valuable for homeowners, landlords, or anyone responsible for the upkeep of residential or commercial buildings.
Circuit Protection
In the context of Doorbell Chime Wiring Diagrams, circuit protection plays a critical role in safeguarding the system and preventing electrical hazards. Fuses or circuit breakers are essential components that protect against electrical faults by interrupting the flow of electricity in the event of an overload or short circuit. Without proper circuit protection, excessive current can flow through the wiring, potentially leading to overheating, electrical fires, or damage to the doorbell chime system’s components.
Electrical faults can occur due to various reasons, such as faulty wiring, damaged insulation, or power surges. When a fault occurs, a fuse or circuit breaker acts as a sacrificial device, sacrificing itself to protect the rest of the system. Fuses are one-time-use devices that blow out and need to be replaced, while circuit breakers can be reset after the fault is resolved. By interrupting the circuit, these protective devices prevent the buildup of excessive heat and potential damage to the doorbell chime system or even the entire electrical system of the building.
In practical terms, incorporating circuit protection into Doorbell Chime Wiring Diagrams is essential to ensure the safety and reliability of the system. By choosing appropriate fuses or circuit breakers with the correct amperage rating, homeowners and electricians can prevent electrical hazards and protect their property. Additionally, regular inspection and testing of the circuit protection devices ensure they are functioning correctly and provide adequate protection against electrical faults.
In summary, circuit protection is a crucial aspect of Doorbell Chime Wiring Diagrams, safeguarding the system and preventing electrical hazards. Fuses or circuit breakers act as sacrificial devices, interrupting the flow of electricity in the event of a fault, preventing overheating, electrical fires, and damage to the system. Understanding the importance of circuit protection and incorporating it into wiring diagrams is essential for safe and reliable operation of doorbell chime systems.
Voltage
In the context of Doorbell Chime Wiring Diagrams, the specified voltage range of 12-24 volts plays a critical role in ensuring the safety and compatibility of the system. This voltage level is carefully chosen to balance two important considerations: safety and compatibility with various doorbell chime units.
From a safety perspective, using a low voltage range of 12-24 volts significantly reduces the risk of electrical shock or fire hazards. Doorbell systems operate in close proximity to people, and a higher voltage could pose a safety risk, especially if there are any electrical faults or improper installations. By limiting the voltage to a safe range, the risk of harm to individuals or damage to property is minimized.
Compatibility is another key reason for using 12-24 volts in Doorbell Chime Wiring Diagrams. Different doorbell chime units have varying voltage requirements, and using a voltage within this range ensures compatibility with a wide range of models. By adhering to this voltage standard, homeowners and electricians have the flexibility to choose from a variety of chime units without worrying about compatibility issues.
In real-life applications, Doorbell Chime Wiring Diagrams typically incorporate a transformer to step down the voltage from the main power supply to the specified 12-24 volt range. This transformer acts as a safety measure, ensuring that the voltage supplied to the doorbell chime unit is within the safe and compatible range.
Understanding the connection between voltage and Doorbell Chime Wiring Diagrams is essential for several reasons. Firstly, it emphasizes the importance of electrical safety in doorbell system installations. Secondly, it highlights the need for compatibility between different components of the system, ensuring that the doorbell chime unit functions correctly. Lastly, it provides practical guidance on selecting appropriate transformers and wiring materials to meet the voltage requirements.
Wire Gauge
Within the context of Doorbell Chime Wiring Diagrams, the selection of appropriate wire gauge is crucial to ensure the system’s safe and efficient operation. Wire gauge refers to the thickness of the wires used in the diagram, which directly affects their current-carrying capacity and overall performance of the doorbell chime system.
-
Electrical Resistance
Thicker wires have lower electrical resistance, allowing for better current flow and reducing power loss. This is particularly important for longer wire runs, where thinner wires can result in noticeable voltage drop and diminished chime volume.
-
Current Capacity
The wire gauge determines the maximum amount of current that can safely pass through the wire without overheating. Using wires below the recommended gauge can lead to excessive current draw, overheating, and potential fire hazards.
-
Voltage Drop
As current flows through a wire, some voltage is lost due to resistance. Thicker wires have less resistance and experience lower voltage drop, ensuring that the chime unit receives sufficient voltage to operate properly.
-
Code Compliance
Electrical codes specify minimum wire gauge requirements for doorbell chime systems based on factors such as wire length and insulation type. Adhering to these requirements ensures compliance with safety standards and prevents potential electrical issues.
Considering these factors, it is evident that proper wire gauge selection is essential for a well-functioning Doorbell Chime Wiring Diagram. By choosing the appropriate wire thickness, electricians and homeowners can optimize current flow, minimize voltage drop, ensure safety, and ensure the reliable operation of their doorbell chime systems.
Chime Types
In the context of Doorbell Chime Wiring Diagrams, the selection of chime type plays a significant role in determining the system’s functionality, aesthetics, and user experience. Chimes can be broadly categorized into three main types: mechanical, electronic, and wireless, each with its own unique characteristics and implications for the wiring diagram.
Mechanical chimes, the traditional type, utilize a physical hammer to strike metal rods or bells, producing a classic and nostalgic chime sound. They typically require more complex wiring, as they involve multiple wires for the hammer mechanism and solenoid. Electronic chimes, on the other hand, employ electronic circuits and speakers to generate chime sounds. They offer a wider range of tones and melodies, and their wiring is generally simpler, involving connections to power and the doorbell button.
Wireless chimes, gaining popularity in recent years, operate without any physical wires between the chime unit and the doorbell button. They utilize radio frequency (RF) or Wi-Fi technology to transmit signals, providing greater flexibility in placement and installation. However, their wiring diagrams may include additional components such as a receiver and transmitter, depending on the specific system design.
Understanding the different chime types and their implications is crucial for creating effective Doorbell Chime Wiring Diagrams. The choice of chime type influences the wiring complexity, power requirements, and overall functionality of the system. By carefully considering the desired chime features, aesthetics, and installation constraints, electricians and homeowners can select the appropriate chime type and design a wiring diagram that meets their specific needs.
Wiring Methods
In the context of Doorbell Chime Wiring Diagrams, the choice of wiring method directly influences the system’s physical appearance, ease of installation, and overall functionality. The three primary wiring methods are surface mount, concealed wiring, and wireless options.
Surface mount wiring involves running wires along the surface of walls or baseboards, typically using plastic conduits or cable trays. This method is relatively easy to install and provides easy access for future maintenance or modifications. However, it can be less aesthetically pleasing, especially in visible areas. Concealed wiring, on the other hand, involves hiding the wires within walls or ceilings. It offers a cleaner and more discreet appearance but requires more extensive installation effort and may disrupt existing structures.
Wireless options, gaining popularity in recent years, eliminate the need for physical wires between the chime unit and the doorbell button. They utilize radio frequency (RF) or Wi-Fi technology to transmit signals, providing maximum flexibility in placement and installation. Wireless chimes are particularly suitable for retrofitting existing homes or in areas where running wires would be impractical.
Understanding the different wiring methods and their implications is crucial for creating effective Doorbell Chime Wiring Diagrams. The choice of wiring method depends on factors such as aesthetics, ease of installation, maintenance considerations, and the specific layout of the building. By carefully assessing these factors, homeowners and electricians can select the most appropriate wiring method and design a wiring diagram that meets their unique requirements.
Troubleshooting
In the context of Doorbell Chime Wiring Diagrams, troubleshooting plays a crucial role in ensuring the system’s optimal performance and longevity. Troubleshooting involves identifying and resolving common issues that may arise during the installation, operation, or maintenance of a doorbell chime system. A comprehensive Doorbell Chime Wiring Diagram serves as a valuable tool for effective troubleshooting, providing a clear visual representation of the system’s electrical connections.
When troubleshooting doorbell chime systems, the wiring diagram serves as a roadmap, guiding electricians and homeowners through the system’s components and connections. By analyzing the diagram, potential issues can be identified and traced back to their source. Common problems such as loose connections, faulty wires, or incorrect voltage levels can be easily spotted, allowing for targeted troubleshooting and repairs.
Real-life examples of troubleshooting using Doorbell Chime Wiring Diagrams abound. For instance, a weak or intermittent chime sound may indicate a loose connection between the chime unit and the transformer. By referring to the wiring diagram, the electrician can quickly locate the connection point and tighten the terminals, resolving the issue. Another common problem is a chime that does not sound at all, which could be caused by a blown fuse or tripped circuit breaker. The wiring diagram helps identify the location of the fuse or circuit breaker, enabling a quick replacement or reset.
The practical applications of understanding the connection between troubleshooting and Doorbell Chime Wiring Diagrams extend to both residential and commercial settings. For homeowners, it empowers them to perform basic troubleshooting tasks, saving time and expenses on professional repairs. For electricians, it provides a systematic approach to identify and resolve issues efficiently, ensuring customer satisfaction and building a reputation for quality workmanship.
In summary, troubleshooting is an integral part of Doorbell Chime Wiring Diagrams. By utilizing the wiring diagram as a diagnostic tool, electricians and homeowners can effectively identify and resolve common issues, ensuring the reliable operation and longevity of doorbell chime systems.






Related Posts








