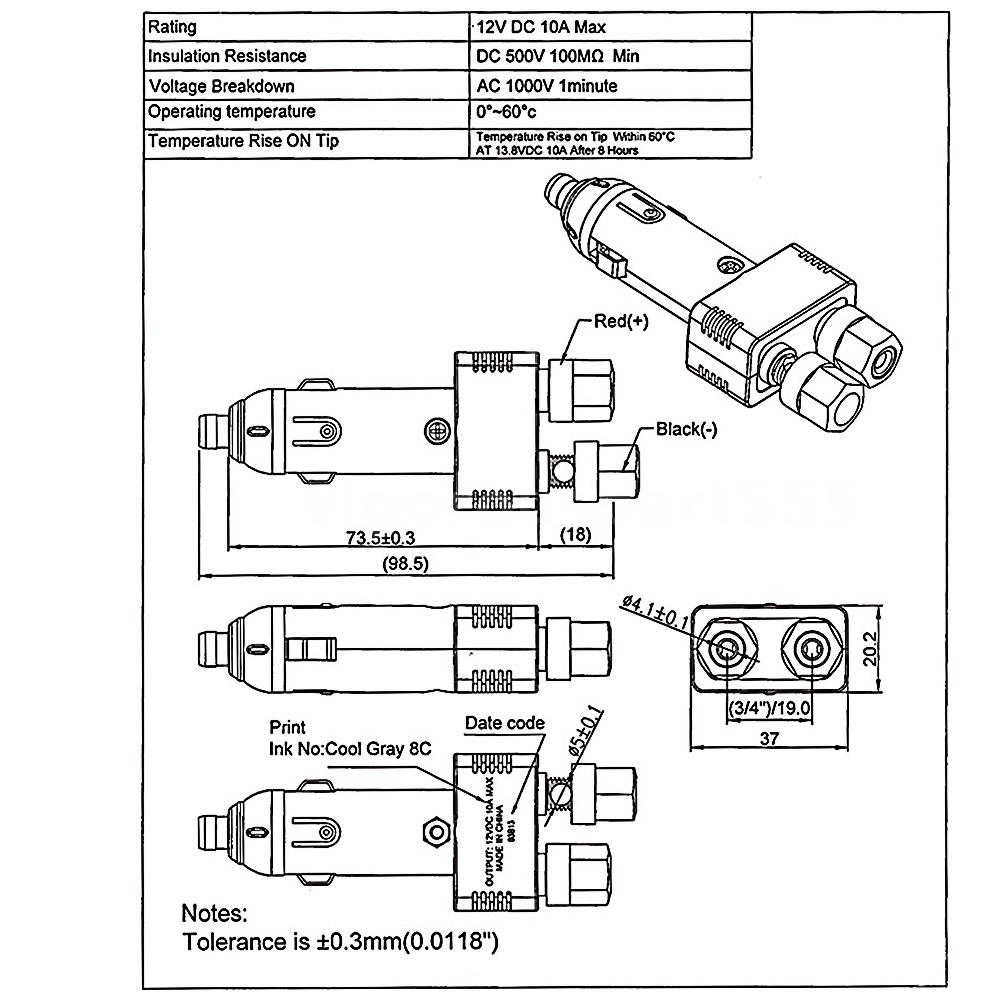
A Cigarette Plug Wiring Diagram illustrates the electrical connections within a cigarette plug, a type of connector used to provide power to electronic devices from a vehicle’s electrical system. It guides users through the proper wiring arrangement, ensuring a secure and functional connection.
The diagram details the specific wiring colors and their corresponding terminals, helping to eliminate confusion and prevent incorrect connections. Benefits include reduced risk of electrical shorts, improved compatibility with different devices, and enhanced charging efficiency. The advent of standardized cigarette plugs and wiring diagrams has played a crucial role in their widespread adoption across various industries and applications.
This article will delve deeper into the components of a cigarette plug wiring diagram, examine its practical applications and safety considerations, and explore recent advancements in cigarette plug technology. Prepare to gain insights into the intricacies of this essential electrical connection.
Understanding the essential aspects of a “Cigarette Plug Wiring Diagram” is crucial for a comprehensive grasp of this electrical connection. As a noun phrase, the term encompasses various components and their interrelationships, which play a vital role in the proper functioning of the device.
- Connector Type: The type of connector used in the cigarette plug, such as male or female, affects its compatibility with different devices.
- Voltage and Current Ratings: The voltage and current capacity of the cigarette plug determine the types of devices it can safely power.
- Wiring Color Coding: Standardized color coding of the wires ensures correct connection and prevents electrical hazards.
- Terminal Connections: The diagram specifies the specific terminals where each wire should be connected, ensuring proper electrical flow.
- Fuse Protection: The inclusion of a fuse protects the circuit from overcurrent conditions, preventing damage to the plug or connected devices.
- Insulation: Proper insulation of the wires and terminals prevents electrical shorts and ensures safe handling.
- Strain Relief: Strain relief mechanisms prevent damage to the wiring due to bending or pulling, ensuring a durable connection.
- Environmental Protection: The diagram may consider environmental factors such as moisture and temperature resistance.
- Compliance Standards: Adherence to industry standards ensures compatibility and safety.
- Troubleshooting Guide: The diagram may include troubleshooting tips to assist in diagnosing and resolving common issues.
These key aspects collectively define the functionality and safety of a cigarette plug wiring diagram, making it an essential guide for electrical installations and device compatibility. Understanding these aspects enables proper wiring, ensuring reliable power transmission and preventing potential hazards.
Connector Type
Within the context of “Cigarette Plug Wiring Diagram”, the connector type plays a pivotal role in ensuring compatibility with various devices. It determines the physical and electrical mating characteristics of the plug, influencing its ability to establish a secure and functional connection.
- Gender: The gender of the connector, whether male or female, dictates its counterpart’s gender for proper mating. Male connectors typically have prongs that insert into female receptacles.
- Size and Shape: The physical dimensions and shape of the connector, including the number and arrangement of terminals, vary depending on the specific type. This ensures proper alignment and mating with compatible devices.
- Keying: Keying mechanisms prevent incorrect mating by ensuring that the connector can only be inserted in one orientation. This feature enhances safety and prevents damage to devices.
- Locking Mechanisms: Some cigarette plugs incorporate locking mechanisms to provide a secure connection, preventing accidental disconnection during operation.
Understanding the connector type is essential for selecting the appropriate cigarette plug for a particular application. Mismatched connector types can lead to poor electrical contact, overheating, and potential damage to devices. By carefully considering the connector type, users can ensure compatibility, reliability, and safe operation.
Voltage and Current Ratings
Within the context of “Cigarette Plug Wiring Diagram”, voltage and current ratings play a crucial role in ensuring the safe and effective operation of electronic devices powered through the cigarette plug. These ratings directly influence the types of devices that can be safely connected and the amount of power that can be drawn without causing damage or electrical hazards.
The voltage rating of a cigarette plug typically ranges from 12 to 24 volts DC, matching the voltage supplied by most vehicle electrical systems. Devices designed to operate within this voltage range can be safely connected to the cigarette plug without risk of damage due to over-voltage. Exceeding the voltage rating can lead to overheating, component failure, or even fire.
Similarly, the current rating of a cigarette plug determines the maximum amount of current that can be drawn without overloading the circuit. Common current ratings for cigarette plugs range from 10 to 20 amps. Devices with high current requirements, such as laptop chargers or power inverters, should be carefully matched to the current capacity of the cigarette plug to prevent overheating or damage to the wiring.
Understanding the voltage and current ratings of a cigarette plug is essential for selecting compatible devices and ensuring safe operation. Mismatched voltage or current ratings can lead to a variety of problems, including:
- Overheating and potential fire hazards
- Damage to connected devices
- Diminished performance or reduced battery life
- Electrical shorts or circuit failures
By carefully considering the voltage and current ratings of both the cigarette plug and the intended device, users can make informed decisions about compatibility and minimize the risks associated with improper power connections.
Wiring Color Coding
Within the context of “Cigarette Plug Wiring Diagram”, standardized wiring color coding plays a vital role in ensuring the safe and reliable operation of electrical devices connected to a vehicle’s electrical system. By adhering to established color conventions, manufacturers and users can easily identify the purpose of each wire, facilitating correct connections and minimizing the risk of electrical hazards.
- Power Wire: Typically colored red, the power wire carries the positive voltage from the vehicle’s battery to the cigarette plug. Proper identification of the power wire is crucial to avoid short circuits and damage to connected devices.
- Ground Wire: Usually black or white, the ground wire provides a return path for electrical current to complete the circuit. Establishing a solid ground connection is essential for ensuring proper device operation and preventing electrical shocks.
- Accessory Wire (Optional): Some cigarette plugs incorporate a third wire, often yellow or blue, which provides switched power. This wire is typically used to control accessories such as lights or USB chargers, allowing them to be turned on or off with the ignition.
- Fuse Protection: Many cigarette plugs incorporate an inline fuse to protect the circuit from overcurrent conditions. The fuse is typically located on the power wire and should be replaced if it blows, indicating a potential electrical fault.
Standardized wiring color coding in cigarette plug wiring diagrams enables consistent and safe electrical connections. It facilitates troubleshooting, prevents misconnections, and minimizes the risk of electrical fires or damage to connected devices. By following these color conventions, users can ensure the proper functioning of their electrical systems and enhance overall safety.
Terminal Connections
Within the context of “Cigarette Plug Wiring Diagram”, terminal connections play a pivotal role in establishing a secure and functional electrical pathway. The diagram provides precise instructions on which terminals to connect each wire, ensuring proper electrical flow and preventing potential hazards.
- Terminal Types: Cigarette plugs typically utilize screw terminals, push terminals, or spring terminals to establish electrical connections. Each type has its own advantages and is suited to specific applications.
- Wire Stripping: Before connecting wires to the terminals, it is crucial to strip the insulation to an appropriate length to ensure proper contact and prevent short circuits.
- Tightening Torque: Screw terminals require proper tightening to ensure a secure connection and prevent loose wires. Inadequate tightening can lead to increased resistance and potential overheating.
- Terminal Insulation: Terminals are often insulated to prevent accidental contact with other components or the chassis, minimizing the risk of electrical shocks or short circuits.
Understanding and adhering to the specified terminal connections are essential for ensuring the safe and reliable operation of electronic devices connected to a cigarette plug. Proper terminal connections minimize electrical resistance, prevent overheating, and enhance overall system stability. By carefully following the wiring diagram and exercising proper electrical practices, users can establish secure and efficient electrical connections.
Fuse Protection
Within the context of “Cigarette Plug Wiring Diagram”, fuse protection plays a critical role in ensuring the safety and reliability of the electrical system. A fuse acts as a sacrificial device, designed to break the circuit and prevent damage to the plug or connected devices in the event of an overcurrent condition.
Overcurrent conditions can arise from various factors, such as short circuits, faulty wiring, or excessive load. Without proper fuse protection, these conditions can lead to overheating, melting of wires, and even fire hazards. The inclusion of a fuse in the cigarette plug wiring diagram provides a controlled and safe way to protect the circuit and prevent catastrophic failures.
Real-life examples of fuse protection in cigarette plug wiring diagrams are prevalent in various industries and applications. In automotive electrical systems, cigarette plugs are commonly used to power accessories such as phone chargers, GPS devices, and portable refrigerators. The wiring diagrams for these installations typically include a fuse to protect the vehicle’s electrical system from potential overloads caused by faulty accessories or improper connections.
Understanding the importance of fuse protection in cigarette plug wiring diagrams is crucial for ensuring the safe and reliable operation of electronic devices. By incorporating fuses into the design, manufacturers and users can minimize the risks associated with electrical faults and enhance the overall safety of the electrical system.
Insulation
Within the context of “Cigarette Plug Wiring Diagram”, proper insulation of the wires and terminals plays a critical role in ensuring the safe and reliable operation of the electrical system. Insulation acts as a protective barrier, preventing electrical shorts and minimizing the risk of electrical shocks or fires.
Electrical shorts occur when two conductors with different electrical potential come into unintended contact, creating a low-resistance path for current flow. This can result in overheating, damage to components, and even fire hazards. Insulation prevents such occurrences by providing a non-conductive layer between the conductors, ensuring that current flows only through the intended pathways.
Real-life examples of insulation within cigarette plug wiring diagrams are evident in various industries and applications. In automotive electrical systems, cigarette plugs are commonly used to power accessories such as phone chargers, GPS devices, and portable refrigerators. The wiring diagrams for these installations incorporate insulation on all wires and terminals to prevent accidental contact with the vehicle’s chassis or other components, minimizing the risk of electrical shorts and ensuring safe operation.
Understanding the importance of insulation in cigarette plug wiring diagrams is crucial for ensuring the safety and reliability of electronic devices. By incorporating proper insulation, manufacturers and users can prevent electrical hazards, enhance system stability, and extend the lifespan of connected devices.
Strain Relief
In the context of “Cigarette Plug Wiring Diagram”, strain relief plays a critical role in ensuring the longevity and reliability of the electrical connection. Strain relief mechanisms are designed to prevent damage to the wiring caused by excessive bending or pulling, which can compromise the integrity of the connection and lead to electrical failures.
Strain relief is achieved through various methods, such as molded strain relief boots, cable ties, or specialized connectors. These mechanisms provide support and protection to the wiring at the point where it enters or exits the cigarette plug, preventing excessive movement and stress on the conductors.
Real-life examples of strain relief within cigarette plug wiring diagrams can be found in a wide range of applications. For instance, in automotive electrical systems, cigarette plugs are commonly used to power accessories such as GPS devices, phone chargers, and portable refrigerators. The wiring diagrams for these installations incorporate strain relief mechanisms to protect the wiring from damage caused by vibration, movement, or accidental pulling, ensuring a secure and reliable connection.
Understanding the importance of strain relief in cigarette plug wiring diagrams is crucial for ensuring the safety and reliability of the electrical system. By incorporating proper strain relief mechanisms, manufacturers and users can prevent electrical faults, enhance system stability, and extend the lifespan of connected devices.
Environmental Protection
Within the context of “Cigarette Plug Wiring Diagram”, environmental protection plays a crucial role in ensuring the reliability and durability of the electrical connection, especially in harsh or demanding conditions. The diagram may incorporate design considerations and recommendations to protect the wiring and components from various environmental factors, including moisture and temperature extremes.
- Moisture Resistance: Cigarette plugs used in outdoor or marine applications may be exposed to moisture and humidity. The wiring diagram should specify moisture-resistant materials and sealing techniques to prevent corrosion and electrical shorts.
- High-Temperature Resistance: In high-temperature environments, such as under the hood of a vehicle, the wiring and components must withstand elevated temperatures without melting or degrading. The diagram should include guidelines for selecting heat-resistant materials and proper ventilation.
- Low-Temperature Resistance: In cold climates, the wiring and components must function reliably at low temperatures. The diagram should provide recommendations for using cold-weather lubricants and flexible materials to prevent cracking or damage.
- UV Resistance: Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation can degrade the insulation and outer casing of the cigarette plug. The diagram may suggest UV-resistant materials and coatings to protect against sun damage.
By considering environmental factors in the cigarette plug wiring diagram, manufacturers and users can ensure the longevity and reliability of the electrical connection in various operating conditions. Proper environmental protection prevents premature failure, enhances safety, and reduces maintenance costs.
Compliance Standards
Within the context of “Cigarette Plug Wiring Diagram”, compliance standards play a crucial role in ensuring the compatibility, safety, and reliability of cigarette plugs and their associated electrical systems. Adherence to established industry standards provides a framework for manufacturers and users to design, install, and operate cigarette plug wiring systems that meet specific requirements and best practices.
- Standardized Parts and Components: Compliance with industry standards ensures that cigarette plugs, terminals, and other components meet uniform specifications for size, shape, and performance. This standardization allows for interchangeability and compatibility between different manufacturers’ products, simplifying installation and replacement.
- Safety Features: Industry standards incorporate safety features into cigarette plug wiring diagrams to minimize the risk of electrical hazards. These features include proper insulation, strain relief mechanisms, and fuse protection to prevent short circuits, overheating, and electrical fires.
- Quality Assurance: Compliance with industry standards often involves quality assurance processes to verify that cigarette plug wiring systems meet the required specifications. This includes testing and certification to ensure that the products are safe, reliable, and perform as intended.
- Legal Implications: In many jurisdictions, adherence to industry standards is a legal requirement for the installation and use of electrical equipment. Compliance with these standards provides protection against liability in the event of accidents or electrical malfunctions.
Overall, compliance with industry standards in cigarette plug wiring diagrams is essential for ensuring the compatibility, safety, and reliability of these electrical systems. By following established guidelines and best practices, manufacturers and users can minimize risks, enhance performance, and ensure the safe and effective use of cigarette plugs in various applications.
Troubleshooting Guide
Within the context of “Cigarette Plug Wiring Diagram”, a troubleshooting guide plays a vital role in providing users with practical assistance in diagnosing and resolving common issues that may arise during installation, operation, or maintenance of the electrical system. By incorporating troubleshooting tips into the diagram, manufacturers empower users to address minor problems independently, minimizing downtime and enhancing overall system reliability.
- Symptom Identification: The troubleshooting guide helps users identify common symptoms associated with electrical faults, such as flickering lights, intermittent power supply, or blown fuses. This enables users to pinpoint the potential source of the problem more efficiently.
- Cause Analysis: The guide provides step-by-step instructions and diagnostic procedures to help users determine the underlying cause of the issue. It may include instructions for checking wire connections, testing components, and isolating faults.
- Solution Recommendations: Once the cause of the problem is identified, the troubleshooting guide offers specific recommendations for resolving the issue. These recommendations may involve simple repairs, such as tightening loose connections or replacing faulty components, or more complex procedures that require professional assistance.
- Safety Precautions: The guide emphasizes safety precautions that users should observe when troubleshooting electrical systems. It reminds users to disconnect the power supply, use appropriate tools, and avoid touching live wires to prevent electrical shocks or other hazards.
In conclusion, the troubleshooting guide included in the “Cigarette Plug Wiring Diagram” empowers users to diagnose and resolve common electrical issues effectively. By providing clear instructions and safety guidelines, the guide minimizes downtime, enhances system reliability, and promotes a safer operating environment for the electrical system.








Related Posts








