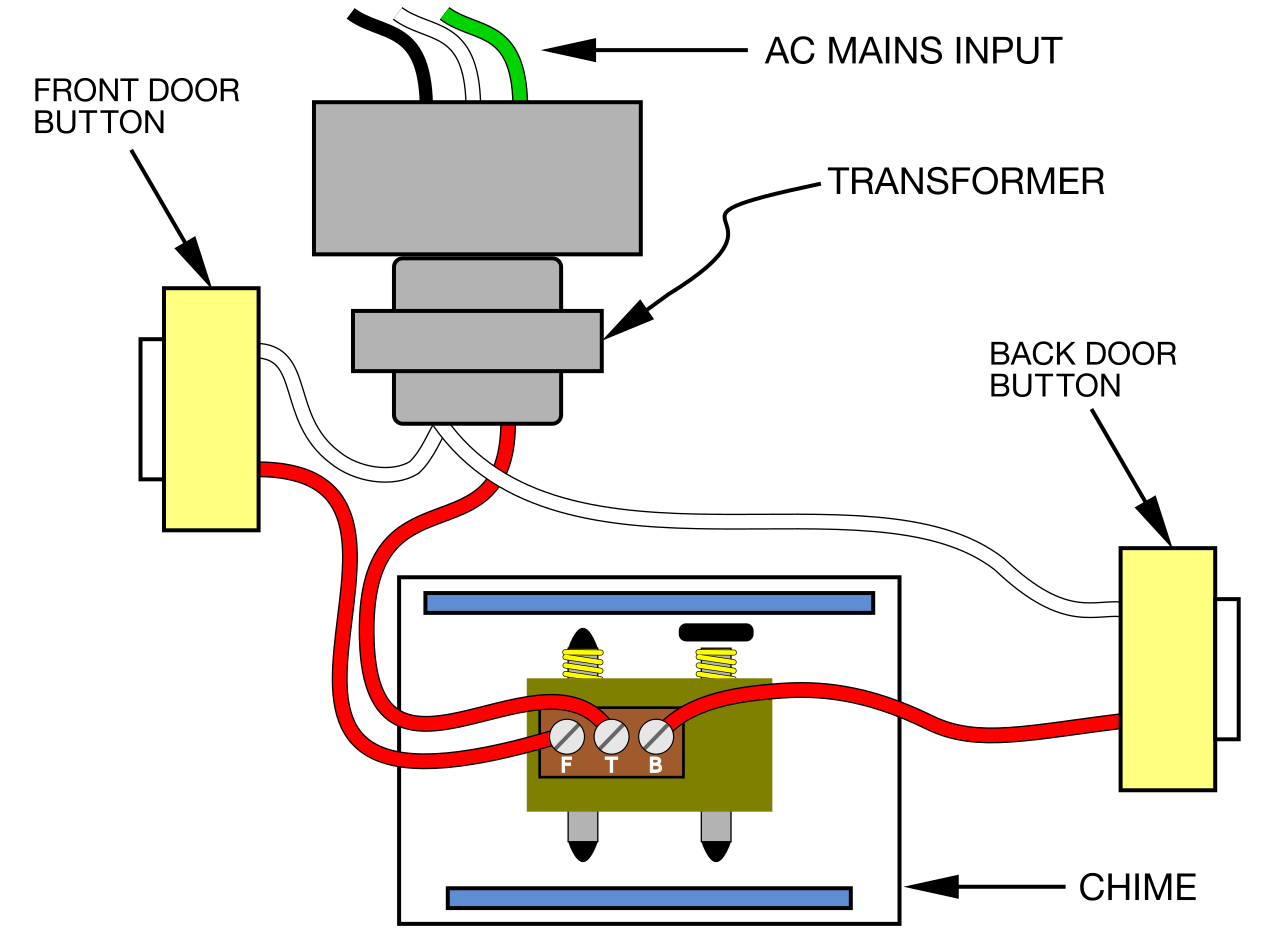
Traditional Doorbell Wiring Diagram: A configuration that connects a doorbell button and chime using electrical wiring, typically consisting of two wires, one carrying power and the other completing the circuit when the button is pressed. An example is the “Parallel Wiring Diagram,” where the button and chime are connected in parallel, allowing for multiple buttons to ring the same chime.
This diagram is relevant as it remains the foundation for doorbell wiring in most residential and commercial buildings. Its benefits include simplicity, ease of installation, and low cost. A key historical development was the introduction of wireless doorbells in the 1990s, which eliminated the need for wiring and provided greater flexibility in doorbell placement.
As we delve deeper into doorbell systems, this article will explore advanced wiring diagrams, troubleshooting techniques, and the latest innovations in doorbell technology.
Understanding the essential aspects of “Traditional Doorbell Wiring Diagram” is crucial for effective content creation. These aspects encompass the core concepts and characteristics that define this topic.
- Components: Button, chime, wires
- Wiring Diagram: Parallel, series
- Power Source: Battery, transformer
- Installation: Basic electrical skills
- Maintenance: Loose connections, button malfunction
- Safety: Electrical hazards
- Troubleshooting: Continuity testing, voltage measurement
- Modernization: Wireless doorbells, smart home integration
- Code Compliance: Electrical codes, building regulations
These aspects provide a comprehensive framework for exploring the traditional doorbell wiring diagram. They encompass the technical components, installation procedures, troubleshooting techniques, safety considerations, and modern advancements related to this topic. A thorough understanding of these aspects enables effective content creation that caters to the diverse needs of readers.
Components: Button, chime, wires
The components of a doorbell system are essential to its functionality. They comprise a button, chime, and wires, each playing a vital role in the operation of the system.
- Button: The button is the component that initiates the doorbell’s operation. It is typically installed near the entrance of a building and consists of a push-button that completes an electrical circuit when pressed.
- Chime: The chime is the component that produces the audible sound when the button is pressed. It is typically installed inside the building and consists of an electromagnet that strikes a metal gong.
- Wires: The wires are the components that connect the button to the chime. They typically consist of two insulated wires, one carrying power from the transformer to the button and the other completing the circuit back to the chime.
These components work together to provide a simple and effective way to announce visitors to a building. The button initiates the electrical signal, the wires transmit the signal to the chime, and the chime produces the audible sound. Understanding the components of a doorbell system is essential for proper installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting.
Wiring Diagram: Parallel, series
Within the context of traditional doorbell wiring diagrams, the choice between parallel and series wiring is a critical decision that affects the functionality and reliability of the system. Understanding the relationship between these two wiring methods is essential for proper installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting.
In a parallel wiring diagram, the button and chime are connected in parallel to the power source. This means that each component has its own direct connection to the power source, creating two independent circuits. The advantage of parallel wiring is that if one component fails, the other component will continue to function. For example, if the button fails, the chime will still ring if the button is bypassed. Additionally, parallel wiring allows for multiple buttons to be connected to the same chime, making it suitable for buildings with multiple entrances.
In a series wiring diagram, the button and chime are connected in series to the power source. This means that the current flows through the button first and then through the chime before returning to the power source. The disadvantage of series wiring is that if one component fails, the entire circuit will fail. For example, if the button fails, the chime will not ring. However, series wiring is simpler to install and requires less wire than parallel wiring.
The choice between parallel and series wiring depends on the specific requirements of the doorbell system. Parallel wiring is more reliable and versatile, while series wiring is simpler and less expensive. Understanding the cause-and-effect relationship between wiring diagrams and doorbell functionality empowers individuals to make informed decisions during installation and maintenance.
Power Source: Battery, transformer
In traditional doorbell wiring diagrams, the power source plays a crucial role in providing the necessary electrical energy to operate the system. The choice between a battery or transformer as the power source has a direct impact on the design, installation, and maintenance of the doorbell system.
Batteries are commonly used in doorbell systems due to their portability and ease of installation. They provide a convenient and self-contained power source, eliminating the need for external wiring. However, batteries have a limited lifespan and require periodic replacement, which can be a disadvantage in high-traffic areas or for systems that require continuous operation.
Transformers, on the other hand, provide a more stable and reliable power source for doorbell systems. They convert alternating current (AC) to low-voltage AC, which is suitable for powering the doorbell button and chime. Transformers require external wiring to connect to the power grid, but they offer a longer lifespan and do not require frequent replacement. Additionally, transformers can power multiple doorbells simultaneously, making them suitable for larger buildings or multi-unit dwellings.
The choice between a battery or transformer as the power source depends on the specific requirements of the doorbell system. Batteries are ideal for portable or temporary installations, while transformers are preferred for permanent and high-traffic applications. Understanding the cause-and-effect relationship between the power source and the doorbell wiring diagram enables informed decision-making during system design and installation.
Installation: Basic electrical skills
In the realm of traditional doorbell wiring diagrams, the significance of basic electrical skills cannot be overstated. These skills serve as the cornerstone upon which a functional and reliable doorbell system is built, dictating the proper execution of installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting procedures.
The cause-and-effect relationship between basic electrical skills and traditional doorbell wiring diagrams is undeniable. Without a fundamental understanding of electrical principles, attempting to install or modify a doorbell system can lead to electrical hazards, improper connections, and system malfunctions. Basic electrical skills empower individuals to navigate the electrical components, wiring configurations, and power sources involved in doorbell wiring diagrams, ensuring safe and effective system operation.
Real-life examples abound, underscoring the critical role of basic electrical skills in traditional doorbell wiring diagrams. For instance, proper wire selection and connection techniques are essential to prevent short circuits and ensure reliable signal transmission. Additionally, the ability to identify and address loose connections, faulty switches, and inadequate power supply is crucial for maintaining a functional doorbell system.
The practical applications of understanding this connection are far-reaching. Homeowners and DIY enthusiasts can confidently tackle doorbell installation and repairs, saving time and expenses associated with hiring an electrician. Moreover, basic electrical skills enable proactive maintenance, extending the lifespan of the doorbell system and preventing minor issues from escalating into significant problems.
In conclusion, basic electrical skills are indispensable for traditional doorbell wiring diagrams. They provide a foundation for safe and effective system installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting. By embracing these skills, individuals can ensure the and uninterrupted operation of their doorbell systems, contributing to a more secure and convenient living environment.
Maintenance: Loose connections, button malfunction
Maintenance plays a crucial role in ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of traditional doorbell wiring diagrams. Two common issues that arise during maintenance are loose connections and button malfunctions. These issues can lead to intermittent or complete failure of the doorbell system, causing inconvenience and security concerns.
- Loose Wire Connections: These occur when the wires connecting the button, chime, and power source become loose or disconnected. Loose connections prevent the flow of electricity, resulting in a non-functional doorbell. Regular inspection and tightening of connections is essential to maintain proper operation.
- Button Sticking or Malfunction: The doorbell button may stick due to dirt, debris, or wear and tear, preventing it from making proper contact. Additionally, the button mechanism itself may malfunction, leading to intermittent or complete failure. Cleaning and replacing the button as needed is crucial for maintaining a responsive doorbell system.
- Faulty Chime: The chime may malfunction due to internal component failures or loose connections. This can result in the chime not producing any sound or producing a distorted sound. Replacing the chime or repairing loose connections can resolve these issues.
- Power Source Issues: Traditional doorbells rely on batteries or transformers for power. Depleted batteries or faulty transformers can disrupt the power supply to the doorbell system. Regular battery replacement or transformer inspection and replacement are necessary to ensure continuous operation.
By understanding the causes and implications of loose connections and button malfunctions, individuals can proactively maintain their doorbell systems. Regular inspections, proper connections, and timely repairs help prevent these issues from occurring, ensuring the reliable and secure operation of traditional doorbell wiring diagrams.
Safety: Electrical hazards
In the realm of traditional doorbell wiring diagrams, safety emerges as a paramount concern, demanding meticulous attention to electrical hazards. These hazards, if overlooked or mishandled, can lead to severe consequences, jeopardizing the well-being of individuals and the integrity of the electrical system.
- Exposed Wires: Loose connections or damaged insulation can expose live wires, creating a risk of electric shock or short circuits. Exposed wires should be promptly addressed to prevent accidental contact.
- Overloading: Connecting too many devices to a single circuit can overload the system, causing overheating and potential electrical fires. Proper circuit planning and load balancing are crucial.
- Improper Grounding: Inadequate grounding provides an alternative path for electrical current, increasing the risk of shock or electrocution. Grounding must be properly installed and maintained.
- Water Damage: Moisture can penetrate electrical components, causing corrosion and increasing the risk of electrical hazards. Doorbell systems should be protected from water exposure.
Understanding these electrical hazards and implementing appropriate safety measures are essential for the safe and reliable operation of traditional doorbell wiring diagrams. Regular inspections, proper installation techniques, and adherence to electrical codes help mitigate these hazards, ensuring the safety of individuals and the integrity of the electrical system.
Troubleshooting: Continuity testing, voltage measurement
Within the context of traditional doorbell wiring diagrams, troubleshooting techniques such as continuity testing and voltage measurement play a critical role in diagnosing and resolving system malfunctions. These techniques provide valuable insights into the electrical integrity of the wiring, components, and power source, enabling effective repair and maintenance.
Continuity testing involves using a multimeter to check for a complete electrical path between two points in the circuit. This test helps identify breaks in wires, loose connections, or faulty components. Voltage measurement, on the other hand, determines the presence and level of electrical voltage at specific points in the circuit. By comparing the measured voltage to expected values, one can pinpoint issues such as power supply problems or voltage drops.
Real-life examples abound, showcasing the practical significance of troubleshooting techniques in traditional doorbell wiring diagrams. For instance, if a doorbell button fails to activate the chime, continuity testing can isolate the fault to a break in the wire connecting the button to the chime. Similarly, voltage measurement can identify a faulty transformer if the voltage supplied to the doorbell is insufficient.
Understanding the connection between troubleshooting techniques and traditional doorbell wiring diagrams empowers individuals to diagnose and resolve doorbell system issues . This knowledge enables proactive maintenance, preventing minor problems from escalating into significant electrical hazards. Moreover, it fosters a deeper comprehension of electrical principles, contributing to overall electrical safety and competence.
Modernization: Wireless doorbells, smart home integration
The advent of wireless doorbells and smart home integration has revolutionized traditional doorbell wiring diagrams, introducing a new era of convenience, flexibility, and technological advancements. Wireless doorbells eliminate the need for complex wiring, simplifying installation and allowing for easy relocation. They operate on battery power or rechargeable batteries, providing greater freedom in doorbell placement and eliminating the constraints of wire runs.
Smart home integration further enhances the functionality of doorbells, connecting them to a network of smart devices within the home. This enables remote access and control of the doorbell through smartphones or voice assistants, allowing homeowners to answer the door, view live video footage, and receive notifications from anywhere. Smart doorbells also offer advanced features such as motion detection, facial recognition, and package tracking, integrating seamlessly with home security and automation systems.
The modernization of doorbell wiring diagrams through wireless doorbells and smart home integration presents numerous practical applications. Homeowners can benefit from increased convenience, enhanced security, and the ability to customize their doorbell experience to suit their specific needs. Moreover, these advancements have opened up new possibilities for accessibility, enabling individuals with limited mobility or sensory impairments to interact with their doorbells more easily. By embracing these modern technologies, traditional doorbell wiring diagrams have evolved to meet the demands of contemporary living, providing a more versatile and user-friendly doorbell experience.
Code Compliance: Electrical codes, building regulations
Within the context of “Traditional Doorbell Wiring Diagram,” adherence to electrical codes and building regulations is of paramount importance, ensuring the safety, reliability, and functionality of doorbell systems. These codes and regulations establish minimum standards for electrical installations, safeguarding individuals from electrical hazards and property from damage.
- Permits and Inspections: Electrical work, including doorbell installations, often requires permits and inspections by local authorities. These measures ensure that the installation complies with electrical codes and building regulations, minimizing the risk of electrical fires and accidents.
- Wire Selection and Sizing: Electrical codes specify the appropriate wire types and sizes for doorbell wiring, based on factors such as current carrying capacity and voltage drop. Using undersized or incorrect wires can lead to overheating, voltage loss, and potential fire hazards.
- Grounding and Bonding: Proper grounding and bonding are essential for electrical safety, providing a path for fault currents to flow safely to the ground. Electrical codes mandate the use of grounding wires and bonding straps to ensure the effective grounding of doorbell systems.
- Overcurrent Protection: Doorbell circuits should be protected by overcurrent protection devices such as fuses or circuit breakers. These devices prevent excessive current flow, which can damage doorbell components or cause electrical fires.
Compliance with electrical codes and building regulations not only ensures the safety and reliability of doorbell systems but also protects the property and its occupants from potential electrical hazards. By adhering to these regulations, homeowners and electricians can ensure that doorbell wiring diagrams meet the highest standards of electrical safety and functionality.









Related Posts








