Wiring Outlet To Light Switch refers to the electrical connection between a power outlet and a light switch, allowing control of a light fixture from a convenient location. For instance, in a bedroom, wiring an outlet near the door to a switch by the bed enables turning off the light without getting out of bed.
This wiring method enhances convenience, safety by preventing accidental shocks from exposed wires, and energy efficiency by enabling easy light control. A significant historical development was the invention of the light switch in the late 1800s, revolutionizing home lighting and paving the way for today’s advanced electrical systems.
In this article, we will explore the steps involved in wiring an outlet to a light switch, necessary tools and materials, safety precautions, and troubleshooting tips. Whether you’re a homeowner or electrician, this guide will provide valuable insights into this practical electrical task.
Wiring an outlet to a light switch is a fundamental electrical task with several essential aspects to consider, ensuring safety, functionality, and code compliance. These aspects encompass various dimensions, from electrical theory to practical implementation.
- Circuit Planning: Determining the appropriate circuit for the wiring.
- Wire Selection: Choosing the correct wire gauge and type for the electrical load.
- Outlet Type: Selecting an outlet compatible with the intended use and location.
- Switch Type: Choosing a switch that matches the circuit requirements and desired functionality.
- Electrical Codes: Adhering to local and national electrical codes for safety and compliance.
- Tools and Materials: Gathering the necessary tools and materials for the wiring process.
- Safety Precautions: Understanding and implementing proper safety measures to prevent electrical hazards.
- Wiring Techniques: Employing proper wiring techniques for secure and reliable connections.
- Testing and Inspection: Thoroughly testing and inspecting the completed wiring for functionality and code compliance.
- Troubleshooting: Identifying and resolving common issues that may arise during or after wiring.
These aspects are interconnected and must be carefully considered to ensure a successful and safe wiring project. Understanding electrical principles, following code requirements, and employing proper techniques are crucial for reliable and long-lasting electrical systems. By considering these essential aspects, electricians and homeowners can confidently undertake outlet-to-switch wiring, enhancing convenience, safety, and energy efficiency in their homes.
Circuit Planning
Circuit planning is a critical component of wiring an outlet to a light switch, as it ensures the electrical system can safely and efficiently handle the load. The circuit’s amperage capacity must be adequate for the combined wattage of the outlet and light fixture. If the circuit is overloaded, it can trip the circuit breaker or blow a fuse, interrupting power to the outlet and light.
To determine the appropriate circuit, consider the following factors:
- Wattage of the light fixture: This information is typically found on the fixture’s packaging or label.
- Wattage of the outlet: If the outlet will be used to power other devices, add their wattage to the light fixture’s wattage.
- Circuit amperage: Most household circuits are rated for 15 or 20 amps. The circuit amperage can be found on the electrical panel.
Once you have determined the total wattage of the outlet and light fixture, divide it by the circuit amperage to get the circuit load. If the circuit load is less than 80% of the circuit amperage, the circuit can safely handle the load.
For example, if you have a 60-watt light fixture and a 15-amp circuit, the circuit load would be 4 amps (60 watts / 15 amps = 4 amps). This is well within the 80% limit, so the circuit can safely handle the load.
Proper circuit planning helps prevent electrical hazards, ensures reliable operation of the outlet and light switch, and meets electrical code requirements. By carefully considering the circuit load and selecting the appropriate circuit, you can ensure a safe and functional electrical system in your home.
Wire Selection
When wiring an outlet to a light switch, choosing the correct wire gauge and type is crucial for ensuring safety, functionality, and code compliance. The wire gauge, which refers to the thickness of the wire, determines its current-carrying capacity. Using a wire gauge that is too thin for the electrical load can lead to overheating, insulation damage, and potential fire hazards.
For example, if you are wiring a light fixture that draws 6 amps, you would need to use a wire gauge that is rated for at least 6 amps. Using a wire gauge that is rated for less than 6 amps could result in the wire overheating and becoming a fire hazard. The type of wire insulation also plays a role in its suitability for different applications. For instance, THHN wire is commonly used for indoor wiring, while UF wire is suitable for outdoor use.
Proper wire selection is critical in the context of wiring an outlet to a light switch, as it directly impacts the overall safety and functionality of the electrical system. By carefully considering the electrical load and selecting the appropriate wire gauge and type, you can prevent electrical hazards, ensure reliable operation, and meet electrical code requirements.
In summary, understanding the connection between wire selection and wiring an outlet to a light switch is essential for ensuring a safe and functional electrical installation. By choosing the correct wire gauge and type for the electrical load, you can prevent overheating, insulation damage, and potential fire hazards, contributing to a reliable and code-compliant electrical system.
Outlet Type
Outlet selection is a critical component of “Wiring Outlet To Light Switch”, directly influencing the safety, functionality, and code compliance of the electrical installation. Choosing an outlet compatible with the intended use and location ensures the outlet can safely handle the electrical load and meets specific environmental requirements.
For example, in a kitchen, where appliances draw high power, installing a 20-amp outlet is essential to prevent overloading and potential fire hazards. In outdoor locations, weather-resistant outlets are necessary to withstand moisture and temperature fluctuations. Understanding the electrical load and environmental conditions of the intended use and location is crucial for selecting the appropriate outlet type.
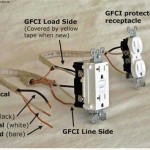
Furthermore, using outlets with built-in safety features, such as tamper-resistant receptacles or ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs), enhances electrical safety in homes and workplaces. GFCIs protect against electrical shocks by cutting off power when ground faults occur, reducing the risk of electrocution, particularly in areas like bathrooms and kitchens where water is present.
By carefully selecting an outlet compatible with the intended use and location, electricians and homeowners can ensure a safe and reliable electrical system. This understanding helps prevent electrical hazards, meets electrical code requirements, and contributes to the overall functionality and efficiency of the electrical installation.
Switch Type
In “Wiring Outlet To Light Switch”, switch type selection is a critical component directly influencing the safety, functionality, and efficiency of the electrical system. Choosing a switch that matches the circuit requirements ensures the switch can handle the electrical load without overheating or causing damage. For instance, a 15-amp switch is required for a circuit with a 15-amp rating, preventing overloading and potential fire hazards.
Furthermore, selecting a switch with the desired functionality meets specific user needs and preferences. For example, a dimmer switch allows for adjustable light intensity, enhancing ambiance and energy efficiency. Motion sensor switches automatically turn lights on when motion is detected, providing convenience and security. Understanding the circuit requirements and desired functionality is essential for choosing the appropriate switch type.
By carefully considering switch type, electricians and homeowners can ensure a safe and reliable electrical system that meets their specific needs. This understanding helps prevent electrical hazards, optimizes energy consumption, and contributes to a comfortable and efficient living environment.
Electrical Codes
In the context of “Wiring Outlet To Light Switch”, adherence to electrical codes is paramount to ensure the safety, reliability, and code compliance of the electrical installation. Electrical codes provide a set of standardized regulations and guidelines that govern the design, installation, and inspection of electrical systems, ensuring the protection of people and property from electrical hazards.
- Circuit Protection: Electrical codes mandate the use of circuit breakers or fuses to protect circuits from overcurrent, preventing overheating and potential fires.
- Grounding: Proper grounding provides a low-resistance path for fault currents to flow, minimizing the risk of electrical shocks and equipment damage.
- Wire Sizing: Electrical codes specify the minimum wire size for different current-carrying capacities, ensuring that wires can safely handle the electrical load without overheating.
- Outlet and Switch Placement: Codes regulate the placement and spacing of outlets and switches to ensure accessibility, prevent overcrowding, and minimize the risk of electrical hazards.
By adhering to electrical codes in “Wiring Outlet To Light Switch”, electricians and homeowners can ensure that the electrical system meets the highest standards of safety and reliability. These codes provide a framework for proper design, installation, and inspection, helping to prevent electrical fires, shocks, and other hazards, ultimately contributing to a safe and efficient electrical system.
Tools and Materials
In the context of “Wiring Outlet To Light Switch”, having the necessary tools and materials is a critical component that directly affects the safety, efficiency, and overall success of the wiring process. The right tools and materials ensure the proper installation, connection, and testing of electrical components, preventing potential hazards and ensuring reliable operation.
For instance, using a voltage tester to verify that the power is off before starting any wiring work is crucial for electrical safety. The appropriate screwdrivers, wire strippers, and pliers are essential for making secure electrical connections and preventing loose wires. Furthermore, having the correct gauge of wire for the electrical load is vital to avoid overheating and potential fire hazards.
The practical applications of this understanding extend to both residential and commercial electrical installations. Electricians rely on their toolkits and a comprehensive understanding of electrical materials to perform safe and efficient wiring. Homeowners undertaking DIY electrical projects can ensure their safety and the quality of their work by gathering the necessary tools and materials before starting any wiring tasks.
In conclusion, “Tools and Materials: Gathering the necessary tools and materials for the wiring process” is a fundamental aspect of “Wiring Outlet To Light Switch” that should not be overlooked. By having the right tools and materials, individuals can approach electrical wiring with confidence, ensuring the safety, reliability, and code compliance of their electrical systems.
Safety Precautions
When embarking on “Wiring Outlet To Light Switch,” safety precautions play a pivotal role in minimizing electrical hazards and ensuring a safe and functional electrical system. Understanding and implementing these precautions are crucial to prevent potential risks and protect individuals.
-
Power Isolation:
Before initiating any electrical work, isolating the power source is paramount. This involves turning off the circuit breaker or removing the fuse associated with the outlet and light switch. Failure to do so can lead to electrical shocks or electrocution.
-
Proper Grounding:
Grounding provides a safe path for electrical current to flow in case of a fault. Ensuring proper grounding of the outlet, light switch, and electrical box is essential to prevent electrical shocks and protect against electrical fires.
-
Adequate Wiring:
Using appropriately sized wires for the electrical load is crucial. Oversized wires can lead to overheating, insulation damage, and potential fire hazards. Undersized wires, on the other hand, can cause voltage drop, overheating, and reduced efficiency.
-
Secure Connections:
All electrical connections must be secure to prevent arcing, overheating, and potential electrical fires. Loose connections can cause resistance, leading to heat generation and insulation damage over time. Tightening screws and using wire nuts or terminals ensures secure connections.
Implementing these safety precautions requires careful attention to detail and adherence to established electrical codes. By understanding the potential hazards and taking proactive measures to mitigate risks, individuals can ensure a safe and reliable electrical system in their homes or workplaces.
Wiring Techniques
In the context of “Wiring Outlet To Light Switch,” employing proper wiring techniques is a critical component that directly affects the safety, reliability, and longevity of the electrical system. Proper wiring techniques ensure secure and reliable connections between electrical components, preventing potential hazards and ensuring the efficient flow of electricity.
For instance, when connecting the outlet to the light switch, using the appropriate wire connectors (such as wire nuts or terminal blocks) and securely tightening the screws is essential. Loose connections can lead to arcing, overheating, and increased electrical resistance, potentially causing electrical fires or damage to the wiring. Furthermore, proper wire stripping and insulation techniques prevent short circuits and ensure a safe and code-compliant installation.
The practical applications of proper wiring techniques extend beyond residential electrical work. In commercial and industrial settings, where electrical systems are more complex and carry heavier loads, adhering to standardized wiring practices and regulations is crucial for safety and efficiency. Electricians rely on their knowledge of proper wiring techniques to design, install, and maintain electrical systems that meet the highest standards of safety and reliability.
In summary, “Wiring Techniques: Employing proper wiring techniques for secure and reliable connections” is a fundamental aspect of “Wiring Outlet To Light Switch” that should not be overlooked. By understanding and implementing proper wiring techniques, individuals can ensure the safety, reliability, and code compliance of their electrical systems, preventing potential hazards and ensuring the efficient flow of electricity.
Testing and Inspection
In the context of “Wiring Outlet To Light Switch,” testing and inspection play a pivotal role in ensuring the safety, reliability, and code compliance of the electrical system. Thorough testing and inspection verify the proper functionality of the outlet and light switch, ensuring that they operate as intended without posing any electrical hazards.
-
Circuit Continuity Test:
Using a multimeter, an electrician checks for continuity in the circuit to ensure that electricity can flow properly from the outlet to the light switch and back. This test identifies any breaks or loose connections that could cause electrical problems.
-
Polarity Check:
The polarity of the wiring must be correct for the outlet and light switch to function properly. An electrician uses a non-contact voltage tester to verify that the hot and neutral wires are connected to the correct terminals.
-
Ground Fault Test:
Ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) are safety devices designed to trip the circuit if they detect a ground fault, which can occur when electricity escapes from the intended path. Testing GFCIs ensures they are functioning correctly and will protect against electrical shocks.
-
Code Compliance Inspection:
An electrician visually inspects the wiring to verify that it meets the requirements of the National Electrical Code (NEC) and local codes. This includes checking for proper wire sizing, secure connections, and adequate grounding.
Thorough testing and inspection provide assurance that the “Wiring Outlet To Light Switch” has been completed safely and to code. These procedures help to prevent electrical fires, shocks, and other hazards, ensuring a reliable and efficient electrical system.
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting electrical issues is a critical aspect of “Wiring Outlet to Light Switch.” Identifying and resolving common problems that may arise during or after wiring ensures the safety, reliability, and optimal performance of the electrical system.
-
Faulty Wiring:
Incorrect wiring, loose connections, or damaged wires can lead to flickering lights, tripping circuit breakers, or even electrical fires. Troubleshooting involves inspecting the wiring for any visible defects, checking for loose connections, and ensuring proper wire sizing and insulation.
-
Switch Malfunction:
A faulty switch can prevent the light from turning on or off, or may cause intermittent operation. Troubleshooting involves testing the switch with a multimeter to check for continuity and proper voltage, and replacing the switch if necessary.
-
Outlet Problems:
A faulty outlet can prevent power from reaching the light fixture. Troubleshooting involves checking for loose connections, damaged terminals, or tripped circuit breakers. Replacing the outlet may be necessary if the problem persists.
-
Ground Fault:
A ground fault occurs when electricity escapes from the intended path, potentially causing electrical shocks. Troubleshooting involves using a ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) to detect and interrupt the fault, and identifying and repairing the source of the ground fault.
By understanding and addressing these common issues, electricians and homeowners can ensure a safe and reliable electrical system. Troubleshooting techniques empower individuals to diagnose and resolve electrical problems, preventing potential hazards and maintaining the integrity of the electrical infrastructure.







Related Posts