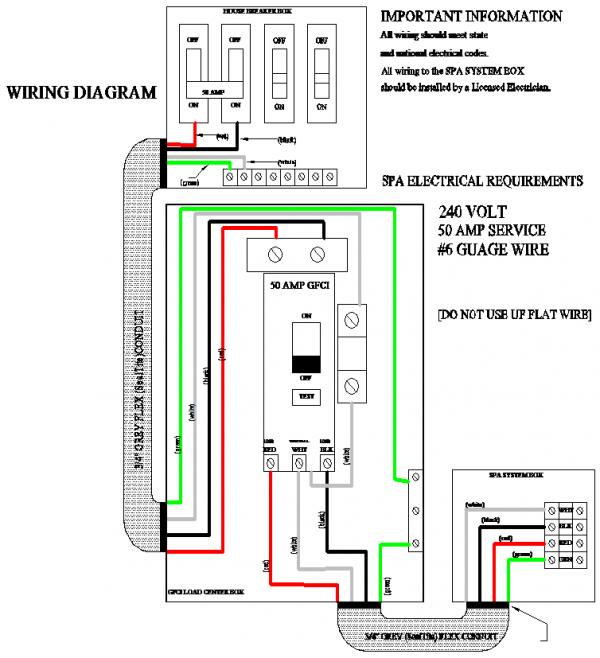
Hot tub wiring requirements are electrical codes and standards that govern the installation and maintenance of electrical systems for hot tubs to ensure safety and prevent electrical hazards. These requirements cover various aspects, including proper grounding, circuit protection, and wiring size to handle the electrical demands of hot tubs. A real-world example is a hot tub rated at 240 volts and 60 amps, which requires a dedicated 60-amp circuit with appropriate gauge wire and overcurrent protection per the National Electrical Code (NEC) standards.
Adhering to these requirements is crucial for the safe operation of hot tubs, as improper wiring can lead to electrical malfunctions, fires, or electrocution. Benefits include reduced risk of electrical accidents and property damage, as well as energy efficiency and extended equipment lifespan by preventing overloading and overheating. A key historical development was the establishment of the National Electrical Code in 1897, which has been instrumental in setting and enforcing electrical safety standards, including those for hot tubs.
This article will delve into the various aspects of hot tub wiring requirements, discussing important considerations, safety measures, and best practices for both residential and commercial installations.
Understanding the essential aspects of hot tub wiring requirements is paramount to ensure the safe and efficient operation of these leisure amenities. These requirements encompass various elements that work together to minimize electrical hazards and promote longevity.
- Grounding: Establishing a safe electrical path to the earth to prevent electrical shocks.
- Bonding: Connecting metal components to the grounding system to equalize electrical potential.
- Circuit Protection: Using circuit breakers or fuses to prevent overheating and electrical fires.
- Conduit: Protecting wires from damage and moisture.
- Wiring Size: Using appropriately sized wires to handle the electrical load.
- Polarity: Ensuring proper alignment of electrical connections.
- GFCI Protection: Utilizing Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters to prevent electrocution.
- Inspection and Maintenance: Regularly checking and servicing electrical systems to ensure ongoing safety.
These aspects are interconnected and play crucial roles in the overall safety and functionality of hot tub electrical systems. For instance, proper grounding prevents electrical shocks by providing a path for stray electrical current to flow safely into the earth, while GFCI protection instantly shuts off power in the event of a ground fault, preventing electrocution. Regular inspections and maintenance help identify and address potential issues before they escalate into more serious problems.
Grounding
Grounding plays a critical role in hot tub wiring requirements by providing a low-resistance path for electrical current to flow safely into the earth. This prevents dangerous electrical shocks that could occur if stray current were to find its way through a person’s body. Without proper grounding, even small amounts of current can be hazardous, especially in wet environments like hot tubs where the risk of electrical shock is heightened.
In hot tub wiring requirements, grounding is achieved through a system of grounding electrodes and bonding conductors. The grounding electrodes, typically metal rods or plates, are driven into the earth and provide a conductive path to the ground. Bonding conductors connect all metal components of the hot tub, including the electrical system, to the grounding electrodes. This ensures that all metal surfaces are at the same electrical potential, eliminating the risk of shock.
Real-life examples of grounding in hot tub wiring requirements include the use of copper grounding rods driven into the earth and connected to the hot tub’s electrical panel. Bonding conductors are then used to connect the metal frame of the hot tub, the pump, and other electrical components to the grounding system. This creates a complete path for electrical current to flow safely into the ground, preventing shocks.
Understanding the importance of grounding in hot tub wiring requirements is crucial for ensuring the safe operation of these amenities. By providing a safe path for electrical current to flow, grounding minimizes the risk of electrical shocks and protects users from harm. Proper grounding also helps to prevent damage to the hot tub’s electrical components and ensures its longevity.
Bonding
In the context of hot tub wiring requirements, bonding plays a critical role in establishing a safe electrical environment by connecting all metal components to the grounding system. This ensures that all metal surfaces are at the same electrical potential, eliminating the risk of electrical shocks and potential damage to equipment.
-
Equipment Bonding
This involves connecting all metal parts of the hot tub, including the frame, pump, heater, and light fixtures, to the grounding system using bonding conductors. This ensures that all metal surfaces are at the same electrical potential, preventing the buildup of dangerous voltage differences.
-
Pipe Bonding
This involves bonding all metal pipes, including water and gas lines, to the grounding system. This prevents the buildup of static electricity on the pipes, which could lead to sparks or even explosions.
-
Structural Bonding
This involves bonding all metal structural components of the hot tub, such as the supports and decking, to the grounding system. This ensures that all metal surfaces are at the same electrical potential, minimizing the risk of electrical shocks.
-
Grounding Electrode Conductor Bonding
This involves bonding the grounding electrode conductor, which connects the grounding electrodes to the hot tub’s electrical panel, to the grounding system. This ensures that the grounding system is properly connected to the earth, providing a low-resistance path for electrical current to flow safely into the ground.
Proper bonding is essential for ensuring the safe operation of hot tubs by preventing electrical shocks, minimizing the risk of electrical fires, and protecting equipment from damage. It is a crucial aspect of hot tub wiring requirements that should be carefully followed to ensure the safety and longevity of these amenities.
Circuit Protection
Circuit protection is a fundamental component of hot tub wiring requirements, playing a crucial role in preventing overheating and electrical fires. Overheating can occur when excessive current flows through electrical components, leading to a buildup of heat that can damage the components and potentially cause a fire. Circuit protection devices, such as circuit breakers or fuses, are designed to interrupt the flow of current when it exceeds a safe level, preventing overheating and reducing the risk of electrical fires.
In hot tub wiring requirements, circuit protection is typically implemented using circuit breakers or fuses. Circuit breakers are reusable devices that automatically trip when the current exceeds a predetermined level, while fuses are one-time-use devices that blow out when the current exceeds their rated capacity. Both circuit breakers and fuses are essential for protecting the electrical components of a hot tub, including the pump, heater, and lighting, from damage due to overheating.
Real-life examples of circuit protection in hot tub wiring requirements include the use of circuit breakers or fuses in the electrical panel to protect the hot tub’s electrical circuits. The circuit breaker or fuse rating is carefully selected based on the maximum current draw of the hot tub’s electrical components. If the current draw exceeds the circuit breaker or fuse rating, the device will trip or blow out, interrupting the flow of current and preventing overheating.
Understanding the connection between circuit protection and hot tub wiring requirements is essential for ensuring the safe operation of hot tubs. By preventing overheating and electrical fires, circuit protection devices help to protect both the hot tub and its users from harm. Proper circuit protection is a critical component of hot tub wiring requirements and should be carefully considered during installation and maintenance.
Conduit
Within the comprehensive framework of “Hot Tub Wiring Requirements,” the aspect of “Conduit: Protecting wires from damage and moisture” plays a pivotal role in ensuring the safe and reliable operation of hot tubs. Conduit provides a protective encasement for electrical wires, safeguarding them from external elements that could compromise their integrity and functionality.
- Physical Protection: Conduit shields wires from physical damage caused by impact, abrasion, or crushing, which can occur during installation, maintenance, or accidental mishandling. This protection is particularly crucial in areas where wires are exposed or subject to movement.
- Moisture Resistance: Conduit forms a watertight seal around wires, preventing moisture and condensation. This is especially important in outdoor environments where hot tubs are exposed to rain, snow, and humidity. Moisture can degrade wire insulation, leading to electrical faults and safety hazards.
- Prevention of Corrosion: Conduit acts as a barrier against corrosive elements in the surrounding environment, such as salt, chemicals, or fumes. These elements can cause wires to and deteriorate, compromising their conductivity and increasing the risk of electrical failures.
- Improved Aesthetics: Conduit can enhance the overall aesthetics of a hot tub installation by concealing wires and creating a clean, organized appearance. This is particularly relevant in visible areas where exposed wires could detract from the visual appeal of the hot tub.
In summary, conduit plays a multifaceted role in “Hot Tub Wiring Requirements.” By safeguarding wires from damage, moisture, corrosion, and aesthetic concerns, conduit ensures the safe, reliable, and visually appealing operation of hot tubs.
Wiring Size
Within the comprehensive framework of “Hot Tub Wiring Requirements,” selecting appropriately sized wires is paramount to ensure the safe and efficient operation of hot tubs. Undersized wires can lead to overheating, voltage drop, and potential fire hazards, while oversized wires represent an unnecessary expense and may not provide optimal performance. Understanding the principles and implications of “Wiring Size: Using appropriately sized wires to handle the electrical load” is crucial for proper installation and maintenance of hot tubs.
- Current Carrying Capacity: Wires have a maximum current carrying capacity, which is determined by their size, material, and insulation. Exceeding this capacity can cause overheating and insulation failure.
- Voltage Drop: When current flows through a wire, there is a voltage drop due to resistance. Using undersized wires can result in excessive voltage drop, leading to reduced performance of the hot tub’s components.
- Real-Life Example: A hot tub with a pump drawing 20 amps requires at least 12-gauge wire to safely handle the electrical load. Using 14-gauge wire, which has a lower current carrying capacity, could lead to overheating and potential fire hazards.
- Code Compliance: “Hot Tub Wiring Requirements” typically specify minimum wire sizes based on the electrical load and distance to the electrical panel. Complying with these codes ensures adherence to safety standards and optimal performance.
In summary, “Wiring Size: Using appropriately sized wires to handle the electrical load” is a critical aspect of “Hot Tub Wiring Requirements.” Selecting the correct wire size ensures safe operation, prevents voltage drop, and complies with electrical codes. By understanding the principles and implications discussed above, homeowners and professionals can ensure the reliable and efficient functioning of their hot tubs.
Polarity
In the context of “Hot Tub Wiring Requirements,” “Polarity: Ensuring proper alignment of electrical connections” plays a critical role in maintaining the safe and efficient operation of hot tubs. Polarity refers to the correct alignment of electrical wires to ensure that current flows in the intended direction and that electrical components function as designed.
Improper polarity can lead to various issues, including:
Equipment Damage: Incorrect polarity can cause damage to electrical components due to reversed current flow. Electrical Hazards: Reversed polarity can create shock hazards and increase the risk of electrical fires. Reduced Performance: Improper polarity can affect the performance of hot tub components, such as pumps and heaters, leading to reduced efficiency or even failure.
As a critical component of “Hot Tub Wiring Requirements,” polarity must be carefully considered during installation and maintenance. Real-life examples of polarity in this context include:
AC Power: Hot tubs typically use alternating current (AC), which requires proper polarity to ensure that the current flows in the correct direction. Neutral and Ground Wires: Neutral and ground wires must be properly identified and connected to ensure correct polarity and prevent electrical hazards. Polarized Plugs and Outlets: Polarized plugs and outlets are designed to enforce proper polarity, ensuring that live and neutral wires are connected correctly.
Understanding the practical significance of polarity in “Hot Tub Wiring Requirements” is crucial for ensuring the safe and reliable operation of hot tubs. By adhering to polarity guidelines, homeowners and professionals can minimize electrical hazards, prevent equipment damage, and optimize the performance of their hot tubs.
GFCI Protection
In the context of “Hot Tub Wiring Requirements,” “GFCI Protection: Utilizing Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters to prevent electrocution” is a critical safety measure designed to protect users from electrical shocks. GFCIs are sensitive devices that continuously monitor the electrical current flowing through a circuit. If an imbalance is detected, such as when current escapes through an unintended path (e.g., a person’s body to the ground), the GFCI quickly interrupts the circuit, effectively preventing electrocution.
The connection between “GFCI Protection: Utilizing Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters to prevent electrocution” and “Hot Tub Wiring Requirements” is crucial due to the inherent risks associated with hot tub use. Hot tubs involve a combination of water and electricity, creating a potentially hazardous environment for electrical shocks. GFCIs play a vital role in mitigating these risks by providing an additional layer of protection beyond standard circuit breakers. They are particularly effective in preventing electrocution caused by ground faults, which can occur when electrical current takes an unintended path to the ground through a person’s body.
Real-life examples of “GFCI Protection: Utilizing Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters to prevent electrocution” within “Hot Tub Wiring Requirements” include:
NEC Requirements: The National Electrical Code (NEC) mandates the use of GFCIs on all hot tub circuits to ensure compliance with electrical safety standards. Dedicated Circuits: Hot tubs must be connected to dedicated circuits equipped with GFCIs to isolate them from other electrical loads and enhance protection. Testing and Resetting: GFCIs should be tested regularly by pressing the “Test” button to simulate a ground fault and ensure proper functionality. If the GFCI trips, it should be reset to restore power.
Understanding the practical significance of “GFCI Protection: Utilizing Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters to prevent electrocution” in “Hot Tub Wiring Requirements” is paramount for ensuring the safe operation of hot tubs. GFCIs provide a crucial safety net, reducing the risk of electrical shocks and electrocution, especially in wet environments. By adhering to GFCI protection guidelines, homeowners and professionals can enhance the safety of their hot tub installations and provide peace of mind for users.
In summary, “GFCI Protection: Utilizing Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters to prevent electrocution” is an essential component of “Hot Tub Wiring Requirements,” playing a vital role in safeguarding users from electrical hazards. Its importance stems from the need to mitigate the risks associated with hot tub use, where water and electricity coexist. Real-life examples and practical applications reinforce the significance of GFCI protection in ensuring the safe and enjoyable use of hot tubs.
Inspection and Maintenance
In the context of “Hot Tub Wiring Requirements,” “Inspection and Maintenance: Regularly checking and servicing electrical systems to ensure ongoing safety” plays a critical role in preserving the safe and reliable operation of hot tubs. Regular inspections and maintenance procedures are essential to identify potential hazards, address wear and tear, and ensure that all electrical components are functioning optimally. Neglecting inspection and maintenance can lead to a decline in the safety and performance of hot tubs, increasing the risk of electrical accidents, fires, and equipment damage.
As a crucial component of “Hot Tub Wiring Requirements,” “Inspection and Maintenance: Regularly checking and servicing electrical systems to ensure ongoing safety” involves several key aspects:
Visual Inspection: Regularly inspecting hot tub electrical components, such as wires, connections, and panels, for signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections. Electrical Testing: Using voltmeters, ground fault testers, and other tools to verify proper voltage levels, grounding, and circuit continuity. Cleaning and Tightening: Removing dirt, debris, and corrosion from electrical components and ensuring that all connections are properly tightened to prevent arcing and overheating. Record Keeping: Maintaining a log of inspection and maintenance activities, including dates, findings, and any repairs or replacements made.
Real-life examples of “Inspection and Maintenance: Regularly checking and servicing electrical systems to ensure ongoing safety” within “Hot Tub Wiring Requirements” include:
Monthly Visual Inspections: Homeowners should visually inspect their hot tub’s electrical components monthly, looking for any signs of damage or wear. Annual Professional Inspection: It is recommended to have a qualified electrician perform a comprehensive electrical inspection of the hot tub annually to assess the overall safety and identify any potential issues. Regular Cleaning and Tightening: Regularly cleaning and tightening electrical connections, terminals, and ground rods can prevent corrosion and ensure proper electrical flow.
Understanding the connection between “Inspection and Maintenance: Regularly checking and servicing electrical systems to ensure ongoing safety” and “Hot Tub Wiring Requirements” is crucial for ensuring the longevity and safe operation of hot tubs. By adhering to regular inspection and maintenance schedules, homeowners and professionals can proactively identify and address potential electrical hazards, reducing the risk of accidents, fires, and costly repairs. Regular maintenance also helps extend the lifespan of hot tub electrical components, maximizing the investment and enhancing the overall enjoyment of these amenities.









Related Posts








