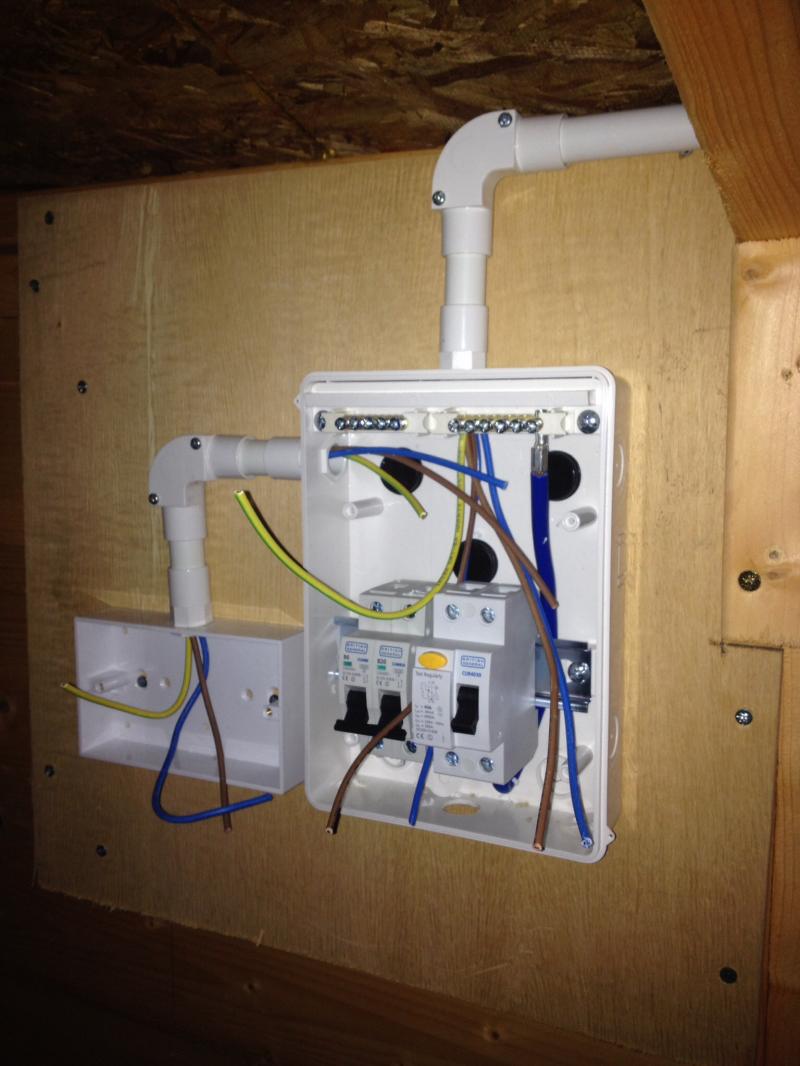
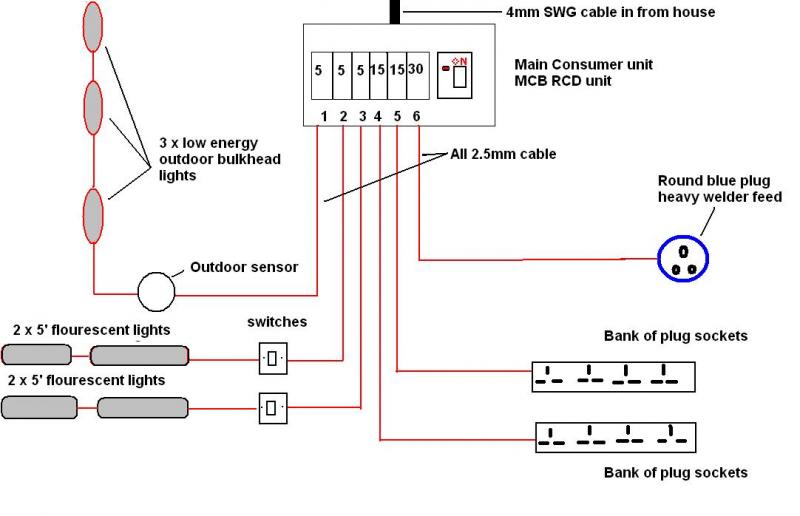
A shed wiring diagram is a visual representation of the electrical system in a shed. It shows the layout of the wiring, including the location of outlets, switches, and lighting fixtures. A shed wiring diagram is essential for ensuring that the electrical system is installed safely and correctly. It can also be helpful for troubleshooting electrical problems.
Shed wiring diagrams are important because they help to ensure that the electrical system is installed safely and correctly. They can also be helpful for troubleshooting electrical problems. One key historical development in the field of shed wiring diagrams is the development of computer-aided design (CAD) software. CAD software makes it possible to create detailed and accurate wiring diagrams that can be easily shared with others.
In this article, we will discuss the different types of shed wiring diagrams, how to create a shed wiring diagram, and how to use a shed wiring diagram to troubleshoot electrical problems.
Shed wiring diagrams are essential for ensuring that the electrical system in a shed is installed safely and correctly. They can also be helpful for troubleshooting electrical problems. The key aspects of a shed wiring diagram include:
- Layout of the wiring
- Location of outlets
- Location of switches
- Location of lighting fixtures
- Wire gauge
- Circuit breaker sizes
- Grounding
- Codes and standards
- Safety precautions
- Troubleshooting tips
These aspects are all important to consider when creating a shed wiring diagram. By following the codes and standards, using the correct wire gauge and circuit breaker sizes, and taking the necessary safety precautions, you can ensure that your shed’s electrical system is safe and reliable.
Layout of the wiring
The layout of the wiring is an important aspect of a shed wiring diagram. It shows the path that the electrical current will take from the power source to the outlets, switches, and lighting fixtures. A well-planned layout will make it easier to install and troubleshoot the electrical system.
- Conduit: Conduit is a type of pipe that is used to protect electrical wires from damage. It can be made of metal or plastic, and it is typically installed along the walls and ceiling of a shed.
- Electrical boxes: Electrical boxes are used to house outlets, switches, and lighting fixtures. They are typically made of metal or plastic, and they are installed in the walls and ceiling of a shed.
- Wires: Wires are used to carry electrical current from the power source to the outlets, switches, and lighting fixtures. They are typically made of copper or aluminum, and they come in a variety of gauges.
- Grounding: Grounding is a safety feature that helps to protect people from electrical shock. It involves connecting the electrical system to the ground rod, which is a metal rod that is driven into the ground.
The layout of the wiring is an important aspect of a shed wiring diagram because it determines the safety and efficiency of the electrical system. By following the codes and standards, using the correct materials, and taking the necessary safety precautions, you can ensure that your shed’s electrical system is safe and reliable.
Location of outlets
The location of outlets is a critical component of a shed wiring diagram. Outlets are used to power tools, appliances, and other electrical devices. The location of the outlets should be carefully planned to ensure that they are placed in convenient locations where they will be easily accessible. Outlets should also be placed in areas where they will not be exposed to moisture or other hazards.
When planning the location of outlets in a shed, it is important to consider the following factors:
- The intended use of the shed
- The location of the electrical panel
- The length of the electrical cords that will be used
- The location of other objects in the shed
By considering these factors, you can ensure that the outlets in your shed are placed in the most convenient and safest locations.
Here are some real-life examples of how the location of outlets is considered in shed wiring diagrams:
- In a shed that is used for woodworking, the outlets should be placed near the workbench and other work areas.
- In a shed that is used for storage, the outlets should be placed near the shelves and other storage areas.
- In a shed that is used for both work and storage, the outlets should be placed in a variety of locations to accommodate both activities.
By understanding the connection between the location of outlets and shed wiring diagrams, you can ensure that your shed’s electrical system is safe and efficient.
Location of switches
The location of switches is a critical component of a shed wiring diagram. Switches are used to control the flow of electricity to outlets, lights, and other electrical devices. The location of the switches should be carefully planned to ensure that they are placed in convenient locations where they will be easily accessible. Switches should also be placed in areas where they will not be exposed to moisture or other hazards.
When planning the location of switches in a shed, it is important to consider the following factors:
- The intended use of the shed
- The location of the electrical panel
- The length of the electrical cords that will be used
- The location of other objects in the shed
By considering these factors, you can ensure that the switches in your shed are placed in the most convenient and safest locations.
Here are some real-life examples of how the location of switches is considered in shed wiring diagrams:
- In a shed that is used for woodworking, the switches should be placed near the workbench and other work areas.
- In a shed that is used for storage, the switches should be placed near the door and other frequently used areas.
- In a shed that is used for both work and storage, the switches should be placed in a variety of locations to accommodate both activities.
By understanding the connection between the location of switches and shed wiring diagrams, you can ensure that your shed’s electrical system is safe and efficient.
Location of lighting fixtures
The location of lighting fixtures is critical component of a shed wiring diagram. Lighting fixtures provide illumination to the shed, making it possible to work and move around safely. The location of the lighting fixtures should be carefully planned to ensure that they provide adequate lighting to all areas of the shed. Lighting fixtures should also be placed in areas where they will not be exposed to moisture or other hazards.
When planning the location of lighting fixtures in a shed, it is important to consider the following factors:
- The intended use of the shed
- The size of the shed
- The location of the electrical panel
- The location of other objects in the shed
By considering these factors, you can ensure that the lighting fixtures in your shed are placed in the most effective and safest locations. Here are some real-life examples of how the location of lighting fixtures is considered in shed wiring diagrams:
- In a shed that is used for woodworking, the lighting fixtures should be placed near the workbench and other work areas.
- In a shed that is used for storage, the lighting fixtures should be placed near the shelves and other storage areas.
- In a shed that is used for both work and storage, the lighting fixtures should be placed in a variety of locations to accommodate both activities.
By understanding the connection between the location of lighting fixtures and shed wiring diagrams, you can ensure that your shed’s electrical system is safe and efficient.
Wire gauge
Wire gauge is an essential aspect of shed wiring diagrams. It refers to the thickness of the electrical wire used in the electrical system. The correct wire gauge is important for ensuring that the electrical system is safe and efficient. If the wire gauge is too small, it can overheat and cause a fire. If the wire gauge is too large, it can be more expensive and difficult to work with.
-
Conductor size
The conductor size is the most important factor to consider when choosing wire gauge. The conductor size is the cross-sectional area of the wire, and it is measured in AWG (American Wire Gauge). The larger the AWG number, the smaller the conductor size.
-
Current carrying capacity
The current carrying capacity of a wire is the amount of electrical current that it can safely carry. The current carrying capacity is determined by the conductor size, the type of insulation, and the ambient temperature.
-
Voltage drop
The voltage drop is the decrease in voltage that occurs when electrical current flows through a wire. The voltage drop is caused by the resistance of the wire. The longer the wire, the smaller the conductor size, and the higher the current, the greater the voltage drop.
-
Cost
The cost of wire is another important factor to consider when choosing wire gauge. The cost of wire is determined by the conductor size, the type of insulation, and the length of the wire.
By understanding the different factors that affect wire gauge, you can choose the correct wire gauge for your shed wiring diagram. This will help to ensure that your electrical system is safe and efficient.
Circuit breaker sizes
Circuit breaker sizes are a critical component of shed wiring diagrams. Circuit breakers are designed to protect electrical circuits from damage caused by overcurrent. If the current flowing through a circuit exceeds the circuit breaker’s amperage rating, the circuit breaker will trip, interrupting the flow of electricity. This helps to prevent electrical fires and other hazards.
The size of a circuit breaker is determined by the maximum amount of current that it is designed to handle. The larger the circuit breaker, the more current it can handle. When choosing a circuit breaker size for a shed wiring diagram, it is important to consider the following factors:
- The intended use of the shed: If the shed will be used for heavy-duty activities, such as welding or woodworking, a larger circuit breaker will be required.
- The size of the shed: A larger shed will require a larger circuit breaker to handle the increased electrical load.
- The number of electrical devices that will be used in the shed: The more electrical devices that will be used in the shed, the larger the circuit breaker will need to be.
By considering these factors, you can choose the correct circuit breaker size for your shed wiring diagram. This will help to ensure that your electrical system is safe and efficient.
Grounding
Grounding is a critical component of shed wiring diagrams. It helps to protect people and property from electrical shock and fire. Grounding involves connecting the electrical system to a metal rod that is driven into the ground, creating a path for electrical current to flow safely to the ground.
Without proper grounding, electrical current can build up in the electrical system and cause a shock or a fire. Grounding helps to prevent this by providing a safe path for electrical current to flow.
There are several real-life examples of grounding in shed wiring diagrams. For example, the grounding wire is typically green or bare copper. It is connected to the grounding rod and to all of the electrical outlets and switches in the shed.
The practical application of grounding in shed wiring diagrams is to ensure that the electrical system is safe and code-compliant. Grounding helps to protect people and property from electrical shock and fire.
Codes and standards
Codes and standards are a critical component of shed wiring diagrams. They ensure that the electrical system is installed safely and in accordance with local building codes. By following the codes and standards, you can help to prevent electrical fires and other hazards.
There are a number of different codes and standards that apply to shed wiring diagrams. These codes and standards are developed by organizations such as the National Electrical Code (NEC) and the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA). The NEC is a set of minimum requirements for the safe installation of electrical wiring and equipment. The NFPA develops codes and standards for a variety of fire safety issues, including electrical safety.
When creating a shed wiring diagram, it is important to consult the relevant codes and standards to ensure that the electrical system is installed safely. Some of the most important codes and standards to consider include the following:
- NEC Article 408: Switches
- NEC Article 410: Lighting Fixtures
- NEC Article 550: Electric Ranges, Ovens, and Counter-Mounted Cooking Units
- NFPA 70: National Electrical Code
- NFPA 79: Electrical Standard for Industrial Machinery
By following the codes and standards, you can help to ensure that your shed’s electrical system is safe and code-compliant.
Safety precautions
Safety precautions are a crucial component of shed wiring diagrams. They ensure that the electrical system is installed safely and in accordance with local building codes. By following safety precautions, you can help to prevent electrical fires and other hazards.
One of the most important safety precautions is to use the correct wire gauge for the electrical circuit. If the wire gauge is too small, it can overheat and cause a fire. The correct wire gauge will depend on the amperage of the circuit and the length of the wire run.
Another important safety precaution is to properly ground the electrical system. Grounding provides a path for electrical current to flow safely to the ground in the event of a fault. Without proper grounding, electrical current can build up in the electrical system and cause a shock or a fire.
By following safety precautions, you can help to ensure that your shed’s electrical system is safe and code-compliant. This will help to protect people and property from electrical shock and fire.
Troubleshooting tips
Troubleshooting tips are an essential part of shed wiring diagrams. They can help you to identify and fix problems with your electrical system quickly and easily. Here are a few of the most common troubleshooting tips for shed wiring diagrams:
-
Check the circuit breaker or fuse
If your shed’s electrical system is not working, the first thing you should do is check the circuit breaker or fuse. If the circuit breaker has tripped or the fuse has blown, you will need to reset it or replace it.
-
Check the wiring
Once you have checked the circuit breaker or fuse, you should check the wiring. Look for any loose connections or damaged wires. If you find any loose connections, tighten them. If you find any damaged wires, you will need to replace them.
-
Check the outlets and switches
If you are having problems with an outlet or switch, you should check the outlet or switch itself. Make sure that the outlet or switch is turned on and that the plug is securely inserted into the outlet. If the outlet or switch is still not working, you may need to replace it.
-
Call a qualified electrician
If you are unable to troubleshoot the problem yourself, you should call a qualified electrician. An electrician will be able to diagnose the problem and fix it quickly and safely.
By following these troubleshooting tips, you can help to keep your shed’s electrical system running safely and efficiently.









Related Posts








