L1 L2 Wiring refers to the electrical connection of two conductors, designated as L1 and L2, in an electrical circuit. These conductors typically carry alternating current (AC) power from a power source, such as a transformer or generator, to electrical devices.
The primary purpose of L1 L2 Wiring is to provide electrical power to devices in a safe and reliable manner. It involves connecting the line 1 (L1) and line 2 (L2) conductors to the appropriate terminals on the device, ensuring the correct voltage and current flow. This wiring method is commonly used in residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
Moving forward, this article will delve into the important considerations, safety measures, and specific applications of L1 L2 Wiring in various electrical systems.
L1 L2 Wiring plays a critical role in electrical systems, demanding a thorough understanding of its essential aspects. These aspects encompass various dimensions related to its definition, components, applications, and safety considerations.
- Definition: L1 L2 Wiring involves connecting two conductors (L1 and L2) to provide electrical power from a source to devices.
- Components: The primary components are the L1 and L2 conductors, typically used in AC power systems.
- Applications: This wiring method finds applications in residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
- Safety: Proper installation and maintenance are crucial to ensure electrical safety.
- Voltage: L1 and L2 conductors typically carry the same voltage, providing power to devices.
- Current: The current flowing through L1 and L2 conductors depends on the connected load.
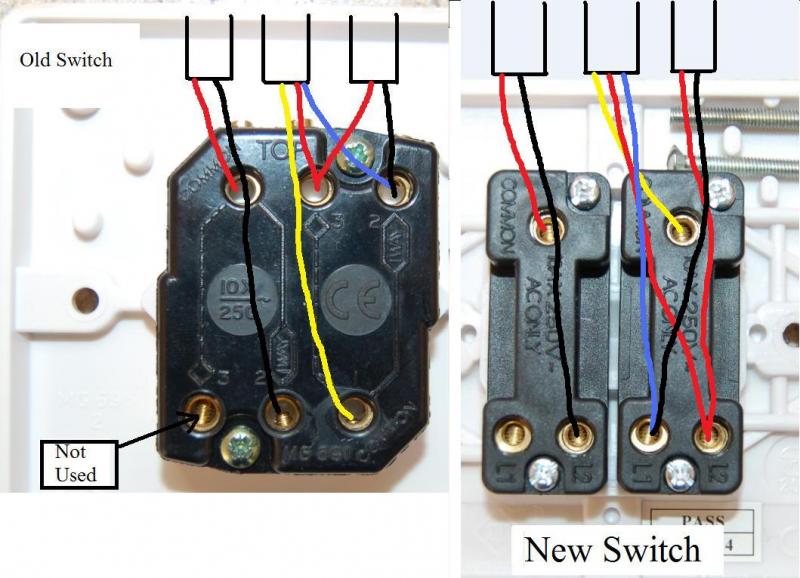
- Wiring Diagram: Electrical diagrams illustrate the L1 L2 Wiring connections for specific devices or systems.
- Codes and Standards: Electrical codes and standards govern the installation and use of L1 L2 Wiring.
- Troubleshooting: Understanding L1 L2 Wiring aids in diagnosing and resolving electrical issues.
These key aspects provide a comprehensive overview of L1 L2 Wiring, highlighting its significance in electrical systems. By delving into each aspect, we gain a deeper understanding of this fundamental wiring technique and its applications.
Definition
Understanding this definition is pivotal in grasping the essence of L1 L2 Wiring. It encapsulates the fundamental concept of establishing electrical connections between two conductors, designated as L1 and L2, to transmit power from a source to various devices. Delving into specific facets of this definition unveils its significance and practical implications.
- Components: L1 and L2 conductors are the primary components, typically made of copper or aluminum, which physically carry the electrical current.
- Power Source: The source of power can be a transformer, generator, or utility grid, providing the voltage and current necessary for the devices.
- Connection: The connection of L1 and L2 conductors to devices is achieved through terminals, ensuring proper electrical contact and power flow.
- Voltage and Current: L1 and L2 conductors typically carry the same voltage, while the current flowing through them depends on the connected load and circuit design.
In essence, L1 L2 Wiring serves as the backbone for distributing electrical power in various settings, from residential homes to industrial facilities. By understanding its definition and components, we gain a solid foundation for exploring its applications, safety considerations, and troubleshooting techniques.
Components
In the context of L1 L2 Wiring, the relationship between its components and the overall wiring system is paramount. L1 and L2 conductors, serving as the foundational elements, play a critical role in the effective and safe distribution of electrical power.
Consider a real-life example: In a residential electrical panel, L1 and L2 conductors are the main power supply lines that connect to the circuit breakers. Each circuit breaker then distributes power to a specific circuit within the home. Without these conductors, the electrical system would be incomplete, and devices would not receive the necessary power.
The practical significance of understanding this component-wiring relationship lies in its impact on electrical safety and system functionality. Proper installation and maintenance of L1 and L2 conductors are essential to prevent electrical hazards, such as short circuits and fires. Additionally, a thorough understanding of these components empowers individuals to troubleshoot electrical issues effectively.
In summary, the components of L1 L2 Wiring, namely the L1 and L2 conductors, form the backbone of the entire system. Their presence and proper functioning are indispensable for delivering electrical power safely and efficiently to various devices and applications.
Applications
The relationship between “Applications: This wiring method finds applications in residential, commercial, and industrial settings.” and “L1 L2 Wiring” is fundamentally intertwined. L1 L2 Wiring serves as the underlying infrastructure that enables the distribution of electrical power in various settings, making it a critical component of any electrical system.
In residential applications, L1 L2 Wiring is used to power homes, apartments, and other dwellings. It provides electricity to essential household devices such as lighting, appliances, and HVAC systems. In commercial settings, L1 L2 Wiring is utilized in offices, retail stores, and other businesses to power equipment, lighting, and communication systems.
Industrial applications of L1 L2 Wiring include factories, warehouses, and manufacturing plants. In these settings, it provides power to heavy machinery, production lines, and other industrial equipment. Understanding the applications of L1 L2 Wiring is crucial for electrical engineers, technicians, and anyone involved in the design, installation, and maintenance of electrical systems.
In summary, the applications of L1 L2 Wiring extend across residential, commercial, and industrial settings, making it an indispensable component of modern electrical infrastructure. Its importance lies in its ability to safely and efficiently distribute electrical power to various devices and systems, supporting our daily lives and economic activities.
Safety
In the context of L1 L2 Wiring, safety takes precedence, demanding proper installation and diligent maintenance to mitigate electrical hazards and ensure the well-being of individuals and the integrity of electrical systems.
- Electrical Hazards: Improper installation or lack of maintenance can lead to electrical hazards, including short circuits, overloads, and electrical fires. These hazards pose significant risks to property and human life.
- Compliance with Codes: Electrical installations must adhere to established electrical codes and standards, which incorporate safety measures and guidelines to minimize electrical hazards.
- Regular Inspections: Routine inspections and maintenance are essential to identify potential issues, such as loose connections, damaged insulation, or faulty components, preventing their escalation into hazardous situations.
- Qualified Electricians: Entrusting L1 L2 Wiring to qualified electricians ensures adherence to safety protocols, proper installation techniques, and the use of high-quality materials.
In summary, prioritizing safety in L1 L2 Wiring involves adhering to electrical codes, conducting regular inspections, engaging qualified electricians, and fostering a culture of electrical safety awareness. By embracing these measures, we create a safer environment, safeguarding lives and property from electrical hazards.
Voltage
Voltage, a crucial aspect of L1 L2 Wiring, plays a pivotal role in understanding the electrical system’s operation and safety measures. Grasping the concept of voltage in L1 L2 Wiring requires a thorough examination of its components, real-life examples, and implications.
- Equal Voltage: L1 and L2 conductors typically carry the same voltage, ensuring that devices receive the intended voltage for optimal performance.
- Power Distribution: The consistent voltage across L1 and L2 conductors facilitates the efficient distribution of electrical power to various devices and appliances.
- Safety Implications: Maintaining the same voltage on both conductors minimizes the risk of electrical hazards, such as short circuits and equipment damage.
- Voltage Variations: Slight voltage variations can occur due to factors like load fluctuations or distance from the power source, but these variations are typically within acceptable limits.
In summary, understanding the voltage aspect of L1 L2 Wiring is critical for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of electrical systems. By maintaining the same voltage across L1 and L2 conductors, devices can function as intended, and the risk of electrical hazards is reduced.
Current
Understanding the relationship between current and connected load in L1 L2 Wiring is crucial for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of electrical systems. The current flowing through L1 and L2 conductors is not constant but varies depending on the load connected to the circuit.
- Load Characteristics: The connected load refers to the electrical devices or appliances that draw current from the circuit. The type and number of devices connected determine the overall load.
- Current Draw: Different devices have different current draw requirements. For example, a high-power appliance like an air conditioner will draw more current than a low-power device like a lamp.
- Circuit Capacity: The L1 and L2 conductors have a maximum current-carrying capacity, which should not be exceeded to prevent overheating and potential fire hazards.
- Circuit Protection: Circuit breakers or fuses are used to protect L1 L2 Wiring from excessive current by interrupting the circuit if the current exceeds a safe limit.
Understanding the relationship between current and connected load helps in selecting appropriate conductors and circuit protection devices. It also enables troubleshooting of electrical issues related to overloading or insufficient current supply.
Wiring Diagram
In the realm of L1 L2 Wiring, wiring diagrams emerge as indispensable tools, providing a visual representation of the electrical connections for specific devices or systems. These diagrams serve as blueprints, guiding electricians and technicians in the safe and efficient installation and maintenance of electrical circuits.
- Components and Connections: Wiring diagrams clearly illustrate the components involved in L1 L2 Wiring, including L1 and L2 conductors, switches, outlets, and devices. They specify the connections between these components, ensuring proper power distribution and functionality.
- Real-Life Examples: Wiring diagrams find practical application in various settings. For instance, in a residential home, they guide the wiring of lighting circuits, ensuring that switches control the appropriate lights and that outlets are correctly connected to power sources.
- Troubleshooting and Repair: Wiring diagrams empower electricians to diagnose and resolve electrical issues. By comparing the actual wiring to the diagram, they can identify discrepancies, loose connections, or faulty components, enabling efficient repairs.
- Safety and Code Compliance: Wiring diagrams contribute to electrical safety by ensuring adherence to electrical codes and standards. They provide a visual representation of the intended wiring configuration, minimizing the risk of electrical hazards and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
In essence, wiring diagrams play a pivotal role in the safe and effective implementation of L1 L2 Wiring. They serve as a valuable resource for electrical professionals, facilitating accurate installations, troubleshooting, and maintenance procedures.
Codes and Standards
Electrical codes and standards serve as the cornerstone of safe and reliable L1 L2 Wiring practices. These regulations, established by governing bodies, provide a comprehensive framework for the installation, operation, and maintenance of electrical systems, including L1 L2 Wiring. Their strict adherence is paramount to ensure the safety of individuals and the integrity of electrical infrastructure.
The impact of electrical codes and standards on L1 L2 Wiring is multifaceted. Firstly, they establish minimum safety requirements for the installation of L1 and L2 conductors, ensuring proper insulation, grounding, and protection against electrical hazards. Secondly, they regulate the use of appropriate materials and equipment, minimizing the risk of electrical fires and accidents. Thirdly, these codes provide guidelines for regular inspections and maintenance, ensuring that L1 L2 Wiring remains in optimal condition over its lifespan.
Real-life examples of the practical applications of electrical codes and standards in L1 L2 Wiring abound. In residential settings, electrical codes mandate the use of properly sized conductors and circuit breakers to prevent overloading and potential fire hazards. In commercial and industrial environments, these codes ensure the safe distribution of power to heavy machinery and equipment, minimizing downtime and maximizing productivity.
Understanding the connection between electrical codes and standards and L1 L2 Wiring is crucial for electrical professionals, homeowners, and anyone involved in the design, installation, or maintenance of electrical systems. By adhering to these regulations, we create a safer and more efficient electrical environment, safeguarding lives and property.
Troubleshooting
Within the realm of “L1 L2 Wiring”, troubleshooting emerges as a crucial aspect, empowering individuals to identify and resolve electrical issues efficiently. Comprehending the intricacies of L1 L2 Wiring lays the foundation for effective troubleshooting, enabling the safe and reliable operation of electrical systems.
- Identifying Faulty Components: Understanding L1 L2 Wiring allows for the pinpointing of faulty components within an electrical circuit. By analyzing voltage and current levels at different points, electricians can isolate the problematic component, such as a loose connection, damaged wire, or malfunctioning device.
- Real-Life Examples: In a residential setting, troubleshooting L1 L2 Wiring can help identify why a particular outlet is not receiving power. By checking the continuity of the circuit and verifying proper connections, electricians can quickly resolve the issue, restoring power to the outlet.
- Implications for Safety: Accurate troubleshooting of L1 L2 Wiring is paramount for safety. Electrical faults can pose significant hazards, including electrical shocks, fires, and equipment damage. By understanding L1 L2 Wiring, individuals can promptly identify and address potential electrical issues, minimizing risks and ensuring a safe environment.
- Circuit Analysis: Troubleshooting L1 L2 Wiring involves analyzing the electrical circuit to determine the root cause of an issue. This includes examining the wiring diagram, measuring voltage and current, and performing continuity tests. By systematically analyzing the circuit, electricians can isolate the fault and implement appropriate corrective actions.
In summary, understanding L1 L2 Wiring plays a vital role in troubleshooting electrical issues. It empowers individuals to identify faulty components, resolve electrical problems efficiently, and ensure the safety and reliability of electrical systems.









Related Posts








