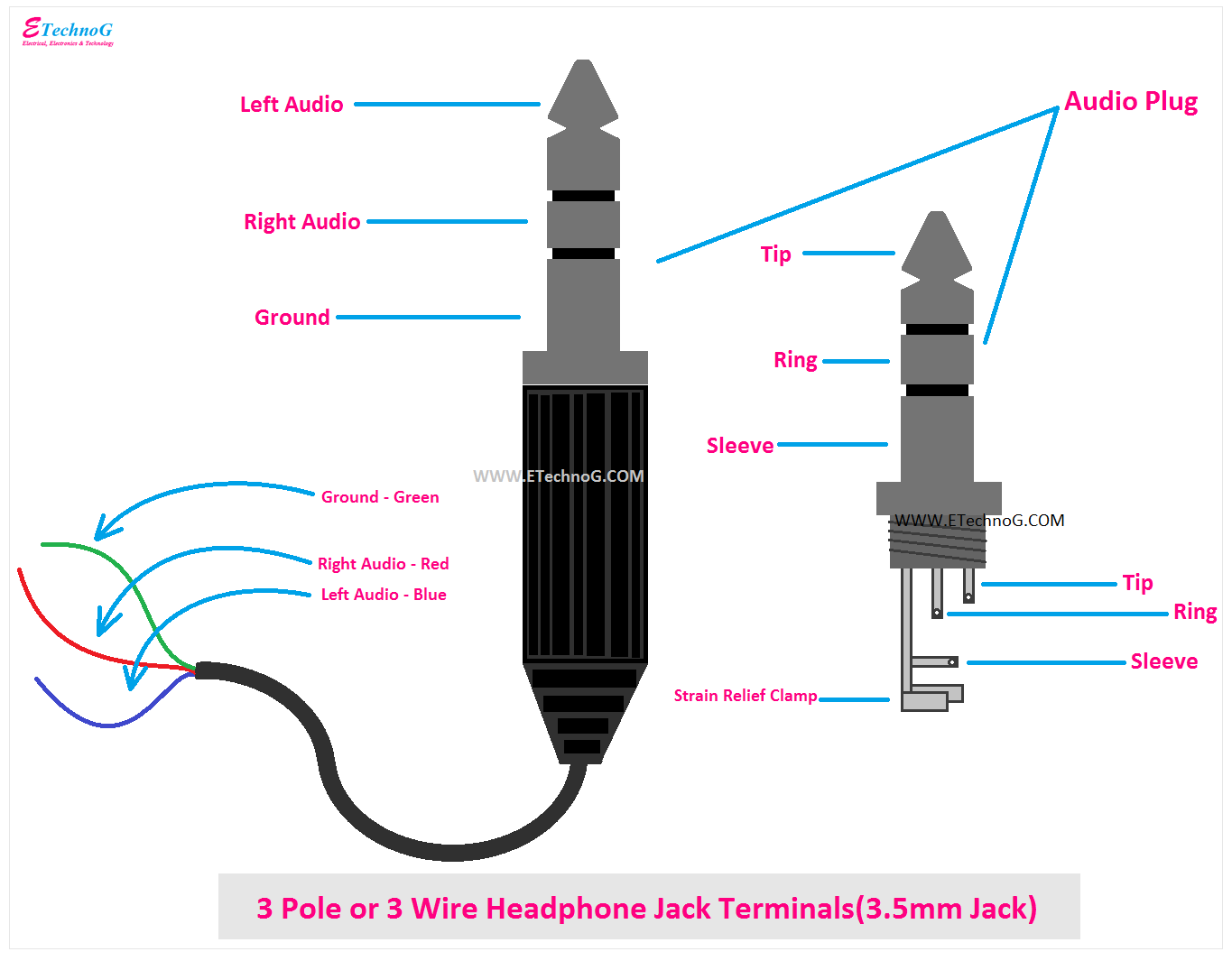
A 3.5 mm headphone jack wiring diagram outlines the specific pin configuration and wire connections within a 3.5 mm audio jack, commonly found on smartphones, laptops, and other devices. It provides a standardized layout for connecting headphones, earphones, or other audio devices to the device’s audio output.
The diagram typically includes the pinouts for the left and right audio channels, as well as ground and microphone connections. Understanding the wiring diagram allows for proper assembly and troubleshooting of audio equipment and ensures compatibility between devices.
The 3.5 mm headphone jack wiring diagram has played a crucial role in the development of mobile audio technology. Its widespread adoption has allowed for the seamless integration of headphones and other audio accessories, enhancing the user experience for music, communication, and gaming applications.
The term “3.5 mm Headphone Jack Wiring Diagram” encompasses several key aspects that are crucial to understanding its significance and functionality. These aspects range from its physical characteristics to its role in audio connectivity and compatibility.
- Connector Type: Refers to the 3.5 mm TRS (Tip, Ring, Sleeve) or TRRS (Tip, Ring, Ring, Sleeve) connector, which is a standard size and configuration for audio jacks.
- Pin Configuration: Outlines the arrangement of pins within the connector, determining the connection of left and right audio channels, ground, and microphone (if applicable).
- Wiring Standard: Defines the specific wire colors and their corresponding connections to the pins, ensuring compatibility between devices and accessories.
- Audio Signal Transmission: Describes how analog audio signals are transmitted through the wiring, including channel separation and signal quality.
- Headphone Compatibility: Indicates the types of headphones or earphones that can be connected to the jack, considering factors like impedance and sensitivity.
- Device Integration: Explores the integration of the 3.5 mm headphone jack in various devices, such as smartphones, laptops, and audio players.
- Troubleshooting: Provides guidelines for identifying and resolving common issues related to headphone jack connections, such as loose connections or audio distortion.
- Historical Evolution: Traces the development of the 3.5 mm headphone jack from its origins to its widespread adoption in consumer electronics.
- Industry Standards: Discusses the role of industry standards, such as the CTIA and OMTP standards, in ensuring interoperability and compatibility.
- Future Trends: Examines emerging technologies and trends that may impact the future of the 3.5 mm headphone jack, such as wireless audio and USB-C connectivity.
These aspects collectively provide a comprehensive understanding of the 3.5 mm Headphone Jack Wiring Diagram, its technical specifications, compatibility considerations, and broader implications in the realm of audio connectivity.
Connector Type
The connector type plays a crucial role in determining the wiring diagram of a 3.5 mm headphone jack. The TRS (Tip, Ring, Sleeve) connector is the most common type, featuring three contacts for left audio, right audio, and ground. The TRRS connector, on the other hand, has an additional contact for microphone input, making it suitable for headsets and other devices with integrated microphones.
The 3.5 mm Headphone Jack Wiring Diagram specifies the pin configuration and wire connections for each type of connector, ensuring compatibility between devices and accessories. Without a standardized wiring diagram, different manufacturers could use different pin assignments, leading to connection issues and audio problems.
Understanding the connection between the connector type and the wiring diagram is essential for proper assembly and troubleshooting of audio equipment. By adhering to the established standards, manufacturers can ensure that their devices are compatible with a wide range of headphones, headsets, and other audio accessories.
In addition, the 3.5 mm headphone jack wiring diagram serves as a reference for understanding the signal flow and audio transmission within the connector. It provides insights into how analog audio signals are transmitted through the different wires and how the connector’s design affects factors such as channel separation and signal quality.
Pin Configuration
The pin configuration of a 3.5 mm headphone jack wiring diagram defines the arrangement and purpose of each pin within the connector. This configuration determines how the left and right audio channels, ground, and microphone (if applicable) are connected, ensuring proper signal transmission and compatibility between devices and accessories.
- Pin Assignments: Specifies the specific pins designated for each function (left audio, right audio, ground, microphone). Understanding the pin assignments is crucial for correct wiring and troubleshooting.
- Connector Design: Describes the physical layout and orientation of the pins within the connector housing. This aspect affects the compatibility of the jack with different types of headphones and headsets.
- Signal Routing: Outlines the path of audio signals through the pins and the connector’s internal circuitry. This information is essential for optimizing signal quality and minimizing interference.
- Industry Standards: Adherence to industry standards, such as CTIA and OMTP, ensures interoperability between devices from different manufacturers. Understanding these standards is important for ensuring compatibility and avoiding connection issues.
The pin configuration of a 3.5 mm headphone jack wiring diagram is a critical aspect that underpins the functionality and compatibility of audio devices. By following standardized pin assignments and adhering to industry norms, manufacturers can ensure seamless connectivity and high-quality audio transmission across a wide range of devices and accessories.
Wiring Standard
The 3.5 mm Headphone Jack Wiring Diagram establishes a standardized framework for connecting audio devices, ensuring compatibility and interoperability between different manufacturers. A critical component of this framework is the Wiring Standard, which defines the specific wire colors and their corresponding connections to the pins within the connector.
Each wire in the 3.5 mm headphone jack cable is assigned a specific color to indicate its function. For instance, the left audio channel is typically represented by a green wire, the right audio channel by a red wire, and the ground connection by a bare or black wire. By adhering to this color-coding scheme, manufacturers can ensure that headphones and other audio accessories are wired consistently, regardless of the brand or model.
The Wiring Standard plays a crucial role in the proper functioning of audio equipment. Incorrect wiring can lead to various issues, such as reversed stereo channels, no audio output, or even damage to the connected devices. By following the established Wiring Standard, manufacturers can guarantee that their products will work seamlessly with a wide range of headphones and other audio accessories.
Audio Signal Transmission
Within the context of the 3.5 mm Headphone Jack Wiring Diagram, understanding audio signal transmission is crucial for achieving optimal sound quality and compatibility. The wiring diagram outlines how analog audio signals are transmitted through the different wires, ensuring proper channel separation and maintaining signal integrity.
- Wire Conductors: The 3.5 mm headphone jack wiring diagram specifies the type and gauge of wire conductors used for each signal path. These conductors play a vital role in transmitting audio signals with minimal loss or interference.
- Signal Routing: The wiring diagram defines the specific path that audio signals take from the source device to the headphones or speakers. This includes the routing of left and right audio channels to maintain stereo separation.
- Shielding: To minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI) and ensure signal purity, the wiring diagram may include shielding mechanisms such as braided shielding or foil wraps around the signal wires.
- Grounding: The wiring diagram establishes a common ground reference for all audio signals, which is essential for reducing noise and ensuring proper signal transmission.
By adhering to standardized wiring practices, manufacturers can ensure that audio signals are transmitted accurately and efficiently through 3.5 mm headphone jacks. This contributes to the overall sound quality, compatibility, and user experience of various audio devices.
Headphone Compatibility
The 3.5 mm Headphone Jack Wiring Diagram plays a critical role in determining headphone compatibility. Impedance and sensitivity are two important factors that influence which types of headphones or earphones can be successfully connected and function optimally with the device’s audio output.
Impedance, measured in ohms, represents the resistance to the flow of electrical current. Headphones with high impedance require more voltage to drive, while those with low impedance are easier to drive. The wiring diagram specifies the output impedance of the device, ensuring that it is compatible with a wide range of headphones.
Sensitivity, measured in decibels per milliwatt (dB/mW), indicates the headphone’s efficiency in converting electrical signals into sound. A higher sensitivity rating means that the headphones produce a louder sound with less power. The wiring diagram takes into account the sensitivity of the headphones to ensure that the device can provide sufficient power to drive them.
By considering these factors in the wiring diagram, manufacturers can ensure that the device’s headphone jack is compatible with a variety of headphones, allowing users to enjoy optimal sound quality and performance.
Device Integration
The 3.5 mm Headphone Jack Wiring Diagram plays a crucial role in the integration of the headphone jack in various devices. The wiring diagram provides the specifications and guidelines for manufacturers to incorporate the headphone jack into their devices, ensuring compatibility with a wide range of headphones and headsets.
The integration of the 3.5 mm headphone jack in devices like smartphones, laptops, and audio players allows users to connect their preferred headphones for personal audio listening, communication, and gaming. The wiring diagram ensures that the audio signals from the device are transmitted properly to the headphones, maintaining sound quality and functionality.
Understanding the connection between “Device Integration: Explores the integration of the 3.5 mm headphone jack in various devices, such as smartphones, laptops, and audio players.” and “3.5 Mm Headphone Jack Wiring Diagram” is essential for device manufacturers, audio engineers, and users who want to achieve optimal audio performance and compatibility. By adhering to the wiring diagram, manufacturers can ensure seamless integration of the headphone jack into their devices, allowing users to enjoy high-quality audio experiences with their headphones.
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting plays a vital role in understanding and resolving common issues related to 3.5 mm headphone jack connections. The 3.5 Mm Headphone Jack Wiring Diagram provides a comprehensive framework for understanding the proper wiring and connections within the headphone jack. When troubleshooting issues, the wiring diagram serves as a valuable reference for identifying potential causes and implementing effective solutions.
Loose connections are a common cause of audio problems. By referring to the wiring diagram, technicians can pinpoint the specific wires and connections that may be affected, allowing them to tighten or repair the connections as needed. Similarly, audio distortion can often be traced back to incorrect wiring or faulty components. The wiring diagram helps identify the signal path and isolate the source of the distortion, enabling targeted troubleshooting and repair.
Troubleshooting headphone jack connections requires a combination of theoretical knowledge and practical skills. The 3.5 Mm Headphone Jack Wiring Diagram provides a solid foundation for understanding the underlying principles and serves as a practical tool for troubleshooting and resolving common issues. Whether it’s loose connections, audio distortion, or other problems, the wiring diagram empowers users to diagnose and fix these issues, ensuring optimal audio performance from their headphones.
Historical Evolution
The historical evolution of the 3.5 mm headphone jack is closely intertwined with the development of the 3.5 Mm Headphone Jack Wiring Diagram. As technology advanced and consumer electronics evolved, the need for a standardized wiring scheme became increasingly apparent. This led to the development of the 3.5 mm headphone jack wiring diagram, which defined the specific pin configuration and wire connections within the connector.
The widespread adoption of the 3.5 mm headphone jack in consumer electronics was driven by several key factors. Firstly, its compact size and versatility made it suitable for use in a wide range of portable devices, including smartphones, laptops, and MP3 players. Secondly, the standardized wiring diagram ensured compatibility between different devices and headphones, allowing users to connect their headphones to any device with a 3.5 mm headphone jack.
Today, the 3.5 mm headphone jack wiring diagram remains an essential component of many consumer electronics devices. It provides a reliable and convenient way to connect headphones and other audio devices, ensuring compatibility and high-quality audio transmission.
Industry Standards
Within the context of the 3.5 Mm Headphone Jack Wiring Diagram, industry standards play a critical role in ensuring interoperability and compatibility between different devices and headphones.
The 3.5 mm headphone jack is a standardized connector that allows for the connection of headphones, headsets, and other audio devices to various electronic devices like smartphones, laptops, and music players. To ensure that these devices can communicate effectively, standardized wiring and pin configurations are necessary.
Prominent industry standards such as CTIA (Cellular Telecommunications Industry Association) and OMTP (Open Mobile Terminal Platform) define the pin arrangement and wire connections for 3.5 mm headphone jacks. By adhering to these standards, manufacturers can guarantee that their devices will work seamlessly with a wide range of headphones and accessories.
For example, the CTIA standard specifies that the left audio channel signal should be carried on the tip contact of the connector, while the OMTP standard defines the same signal to be carried on the ring contact. If devices were not manufactured according to these standards, compatibility issues could arise, resulting in reversed audio channels or no audio output.
Understanding the connection between industry standards and the 3.5 Mm Headphone Jack Wiring Diagram is crucial for manufacturers, engineers, and consumers alike. It ensures that devices are interoperable, headphones function as expected, and users can enjoy a seamless audio experience regardless of the device they are using.
Future Trends
As technology continues to evolve, the future of the 3.5 mm headphone jack remains uncertain. This section of the 3.5 Mm Headphone Jack Wiring Diagram delves into emerging trends and technologies that may shape the future of audio connectivity, examining their potential impact on the traditional headphone jack.
- Wireless Audio: Bluetooth and other wireless technologies have gained immense popularity in recent years, offering convenience and freedom from tangled wires. The proliferation of wireless headphones and earbuds is likely to continue, potentially reducing the demand for wired headphones and, by extension, the 3.5 mm headphone jack.
- USB-C Connectivity: USB-C is a versatile connector that can transmit both power and data, and it is becoming increasingly common in smartphones, laptops, and other devices. USB-C headphones offer the advantage of digital audio transmission, which can provide higher quality sound compared to analog connections. As USB-C becomes more widely adopted, it could lead to a decline in the use of 3.5 mm headphone jacks.
- Integrated Audio Solutions: Some manufacturers are exploring integrated audio solutions that eliminate the need for a separate headphone jack. These solutions may involve built-in speakers or the use of proprietary wireless protocols. While these technologies are still in their early stages, they could potentially disrupt the traditional headphone jack market.
- Specialized Use Cases: Despite the rise of wireless audio, the 3.5 mm headphone jack is likely to remain relevant in certain specialized use cases. For example, professional musicians and audio engineers may prefer wired headphones for their reliability and low latency. Additionally, wired headphones may still be preferred for gaming applications where low latency is crucial.
The future of the 3.5 mm headphone jack is difficult to predict, as it will depend on the adoption rate of emerging technologies and the preferences of consumers. However, understanding these future trends is essential for manufacturers and consumers alike to make informed decisions about their audio connectivity needs.









Related Posts








